Separating personal expenses from business expenses is crucial for accurate financial management and tax reporting. Understanding the distinctions ensures compliance and optimizes your financial strategy; learn more in this article.
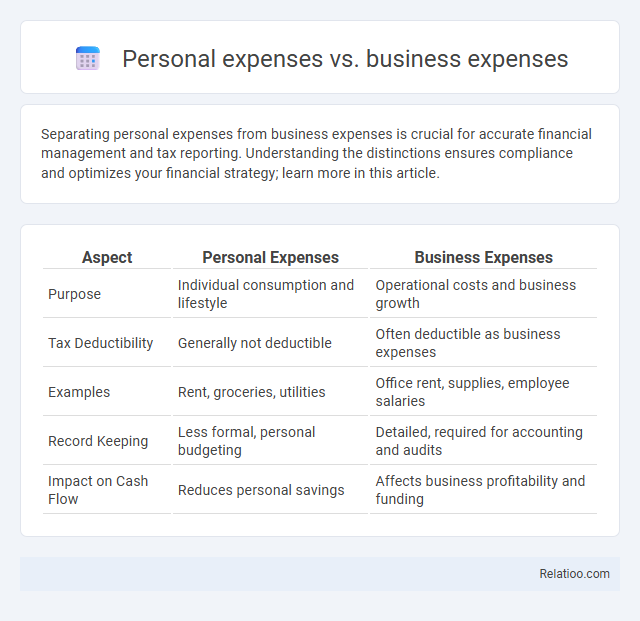
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Personal Expenses | Business Expenses |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Individual consumption and lifestyle | Operational costs and business growth |
| Tax Deductibility | Generally not deductible | Often deductible as business expenses |
| Examples | Rent, groceries, utilities | Office rent, supplies, employee salaries |
| Record Keeping | Less formal, personal budgeting | Detailed, required for accounting and audits |
| Impact on Cash Flow | Reduces personal savings | Affects business profitability and funding |
Understanding Personal Expenses
Understanding personal expenses involves categorizing costs related to daily living, such as housing, groceries, and utilities, which differ significantly from business expenses that include operational costs like supplies, employee wages, and marketing. Accurate expense tracking requires distinguishing between these categories to ensure proper budgeting and financial analysis, aiding in tax preparation and financial planning. Utilizing digital tools and apps enhances the ability to monitor personal spending patterns, identify saving opportunities, and maintain clear records for both personal and business finances.
Defining Business Expenses
Business expenses are costs incurred exclusively for operating a company, such as office supplies, employee salaries, and marketing expenditures. Differentiating between personal expenses and business expenses is crucial for accurate financial management, tax deductions, and compliance with regulations. Your effective expense tracking system ensures all business-related transactions are documented, facilitating better budgeting and financial analysis.
Key Differences Between Personal and Business Expenses
Personal expenses include costs related to individual lifestyle and household needs, such as groceries, utilities, and personal entertainment, which are non-deductible for tax purposes. Business expenses involve costs necessary for operating a business, including office supplies, travel for work, and employee salaries, and are typically tax-deductible. Accurate expense tracking is essential to differentiate these expenses, ensuring proper financial management, tax compliance, and clear separation between personal and business finances.
Common Examples of Personal Expenses
Common examples of personal expenses include groceries, rent or mortgage payments, utilities, transportation costs, and entertainment. These costs are distinct from business expenses, which typically cover office supplies, client meals, travel related to work, and employee salaries. Accurate expense tracking involves categorizing each transaction correctly to ensure clear financial separation between personal and business expenditures.
Common Examples of Business Expenses
Common examples of business expenses include office rent, utilities, employee salaries, marketing costs, and supplies directly related to business operations. Personal expenses such as groceries, personal travel, and household bills must be distinctly separated from business expenses to ensure accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. Effective expense tracking using dedicated accounting software helps categorize transactions properly and provides clear accountability for business-related expenditures.
Why Separating Expenses Matters
Separating personal expenses from business expenses is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance, helping you avoid costly audits and penalties. Clear expense tracking ensures better budgeting and cash flow management, allowing you to identify deductible business costs effectively. Maintaining distinct records simplifies accounting processes and supports informed financial decision-making for your business growth.
Tax Implications: Personal vs Business Expenses
Distinguishing personal expenses from business expenses is critical for accurate tax reporting and maximizing deductions. Business expenses such as office supplies, travel, and marketing costs are typically tax-deductible, lowering taxable income, while personal expenses are not deductible and can trigger IRS scrutiny if misclassified. Effective expense tracking using software like QuickBooks or Expensify ensures proper categorization, compliance with tax regulations, and optimized tax benefits during audits.
Tips for Tracking and Managing Expenses
Distinguishing personal expenses from business expenses is crucial for accurate bookkeeping and tax compliance, ensuring you can maximize deductions and avoid audits. Utilize dedicated apps or software designed for expense tracking, linking business accounts separately to streamline recording and categorize transactions efficiently. Maintain consistent documentation and regularly review your expenses to keep your financial management precise and simplify your tax reporting process.
Mistakes to Avoid When Categorizing Expenses
Misclassifying personal expenses as business expenses can lead to tax complications, audits, and potential penalties that could impact your financial health. Avoid mixing personal and business costs by maintaining separate accounts and meticulously documenting each transaction for accurate expense tracking. Ensuring precise categorization prevents legal issues and optimizes tax deductions for your business.
Best Practices for Expense Documentation
Accurate differentiation between personal expenses and business expenses is essential for effective expense tracking and financial management. Implementing best practices for expense documentation includes maintaining detailed receipts, categorizing each expense properly, and using dedicated accounting software to streamline records. Ensuring Your records are thorough and organized supports compliance with tax regulations and maximizes financial transparency.
Infographic: Personal expenses vs Business expenses
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com