Tax planning involves strategically arranging your financial activities to minimize tax liabilities before they occur, while tax management focuses on monitoring and handling taxes efficiently throughout the financial year. Discover the key differences and best practices for both approaches in this article.
Table of Comparison
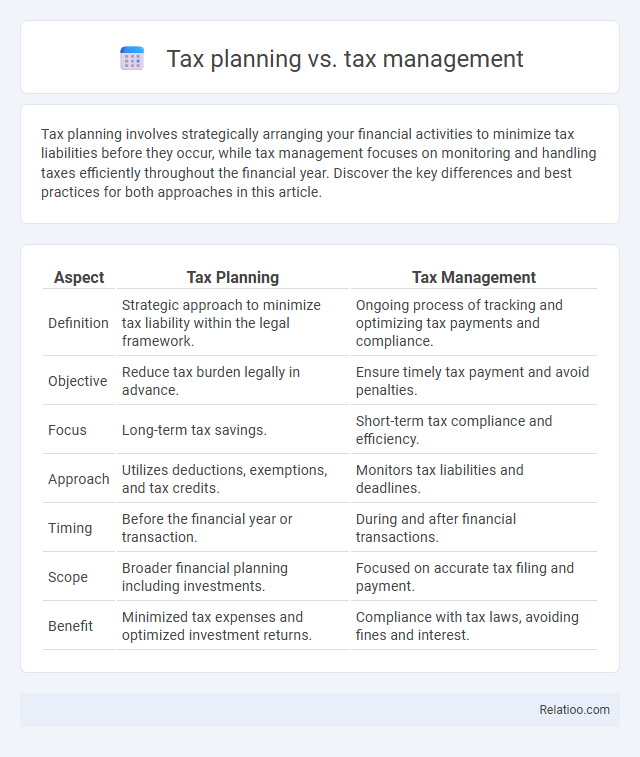
| Aspect | Tax Planning | Tax Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic approach to minimize tax liability within the legal framework. | Ongoing process of tracking and optimizing tax payments and compliance. |
| Objective | Reduce tax burden legally in advance. | Ensure timely tax payment and avoid penalties. |
| Focus | Long-term tax savings. | Short-term tax compliance and efficiency. |
| Approach | Utilizes deductions, exemptions, and tax credits. | Monitors tax liabilities and deadlines. |
| Timing | Before the financial year or transaction. | During and after financial transactions. |
| Scope | Broader financial planning including investments. | Focused on accurate tax filing and payment. |
| Benefit | Minimized tax expenses and optimized investment returns. | Compliance with tax laws, avoiding fines and interest. |
Introduction to Tax Planning and Tax Management
Tax planning involves strategic analysis and organization of financial affairs to minimize tax liability within the legal framework, ensuring efficient use of exemptions, deductions, and credits. Tax management, on the other hand, focuses on the implementation and monitoring of tax-related activities to ensure compliance, timely filing, and optimal cash flow throughout the fiscal year. Both practices are essential for individuals and businesses aiming to reduce tax burden while adhering to government regulations.
Defining Tax Planning
Tax planning involves strategically organizing financial activities to minimize tax liabilities within legal frameworks, enhancing overall financial efficiency. Tax management refers to the ongoing process of implementing tax planning strategies, ensuring compliance with tax laws, and timely filing of returns. Tax itself is a mandatory financial charge imposed by governments on individuals and businesses to fund public services and infrastructure.
Defining Tax Management
Tax management involves strategic planning and efficient handling of tax obligations to minimize liabilities and ensure compliance with tax laws. It encompasses activities such as tax planning, filing returns, and managing audits to optimize your financial outcomes. Effective tax management reduces risks and maximizes tax benefits within legal frameworks.
Objectives of Tax Planning
Tax planning aims to minimize tax liability by strategically aligning financial activities with tax laws and regulations. The primary objective of tax planning is to achieve tax efficiency, ensuring compliance while maximizing after-tax income through legal deductions, exemptions, and credits. Tax management focuses on the proper administration and filing of taxes, whereas tax involves the compulsory contributions imposed by governments on income, property, or transactions.
Objectives of Tax Management
Tax management aims to ensure compliance with tax laws while minimizing tax liabilities through strategic planning and effective record-keeping. It focuses on objectives such as timely tax payment, accurate filing, and optimal utilization of available deductions and exemptions to safeguard your financial health. Unlike general tax planning, tax management encompasses the entire process of monitoring and controlling tax-related activities to achieve long-term fiscal efficiency.
Key Differences Between Tax Planning and Tax Management
Tax planning involves strategizing financial decisions to minimize tax liability within legal frameworks, whereas tax management focuses on the accurate calculation, timely payment, and compliance with tax laws. Tax planning proactively identifies deductions, credits, and exemptions to optimize tax benefits before filing, while tax management ensures proper bookkeeping, record-keeping, and reporting for efficient tax administration. Understanding these key differences aids businesses and individuals in achieving tax efficiency and regulatory adherence.
Importance of Effective Tax Strategies
Effective tax strategies are essential for optimizing your financial outcomes by minimizing liabilities and maximizing savings through lawful deductions and credits. Tax planning involves proactively forecasting your tax obligations to align with your financial goals, while tax management focuses on the ongoing implementation and compliance of these strategies throughout the fiscal year. A comprehensive understanding of tax concepts enables you to avoid penalties, improve cash flow, and ensure long-term financial stability.
Common Tax Planning Techniques
Common tax planning techniques include income deferral, tax credit utilization, and strategic investment in tax-exempt securities, which aim to minimize taxable income and maximize after-tax wealth. Tax management involves continuous monitoring and adjustment of financial activities to comply with tax laws while optimizing tax liability. Effective tax planning integrates these techniques to achieve long-term tax efficiency and financial goals.
Essential Tax Management Practices
Essential tax management practices involve strategically organizing your financial activities to minimize tax liabilities while ensuring compliance with tax laws. Effective tax management includes accurate record-keeping, timely filing of returns, and proactive planning to take advantage of credits and deductions. Understanding the differences between tax planning, which focuses on future tax liability reduction, and tax management, which involves executing those plans and handling tax payments, is crucial for optimizing Your overall tax position.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Optimal Tax Efficiency
Tax planning, tax management, and tax each play distinct roles in optimizing your financial outcomes by minimizing liabilities and ensuring compliance with legal requirements. Tax planning involves strategizing your financial activities to benefit from available deductions and credits, while tax management focuses on the day-to-day handling of tax obligations to avoid penalties and interest. Choosing the right approach depends on your specific financial situation and goals, with a balanced integration of both planning and management essential for achieving optimal tax efficiency.
Infographic: Tax planning vs tax management
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com