Revenue Recognition records income when earned, regardless of cash receipt, aligning with accrual accounting principles. Discover the key differences and implications for your business in this article.
Table of Comparison
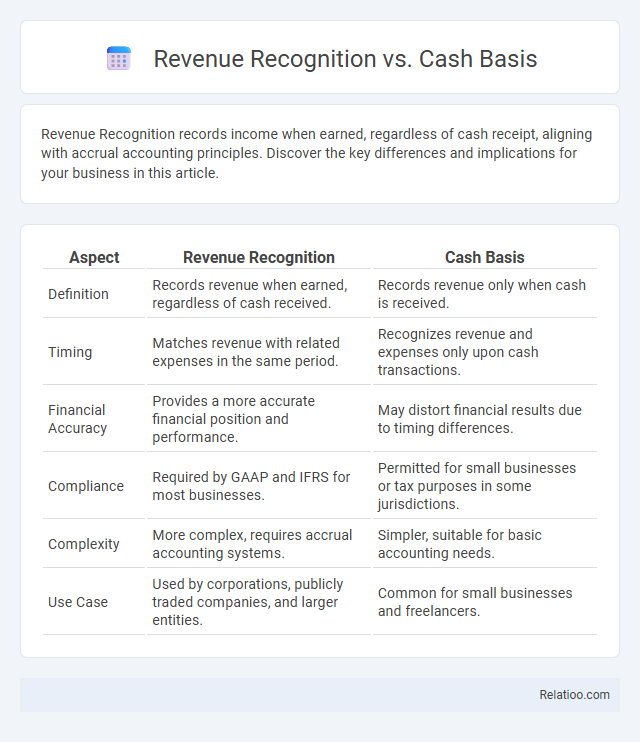
| Aspect | Revenue Recognition | Cash Basis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Records revenue when earned, regardless of cash received. | Records revenue only when cash is received. |
| Timing | Matches revenue with related expenses in the same period. | Recognizes revenue and expenses only upon cash transactions. |
| Financial Accuracy | Provides a more accurate financial position and performance. | May distort financial results due to timing differences. |
| Compliance | Required by GAAP and IFRS for most businesses. | Permitted for small businesses or tax purposes in some jurisdictions. |
| Complexity | More complex, requires accrual accounting systems. | Simpler, suitable for basic accounting needs. |
| Use Case | Used by corporations, publicly traded companies, and larger entities. | Common for small businesses and freelancers. |
Introduction to Revenue Recognition and Cash Basis
Revenue recognition records income when earned, matching revenue to the period services or products are delivered, providing a clear view of financial performance. Cash basis accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands, making it simpler but less accurate for tracking long-term financial health. Your choice between these methods impacts how you report earnings, with revenue recognition offering a more detailed and timely reflection of business activity compared to the immediate but less informative cash basis.
Defining Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition is an accounting principle dictating the specific conditions under which revenue is recognized and recorded in the financial statements, typically when earned and realizable, regardless of cash receipt. This contrasts with cash basis accounting, which records revenue only when cash is received, and subscription models where revenue is recognized over the subscription period as services are delivered. Accurate revenue recognition ensures compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS and reflects the true financial performance of a business.
Understanding Cash Basis Accounting
Cash basis accounting records revenue only when cash is received, making it simpler for small businesses to track actual cash flow without managing accounts receivable. In contrast, revenue recognition under accrual accounting recognizes income when earned, regardless of payment timing, which aligns with subscription models that require revenue to be recognized over the service period. Understanding cash basis accounting helps you manage your finances effectively by focusing on real-time cash movement rather than future payments or deferred revenue.
Key Differences Between Revenue Recognition and Cash Basis
Revenue recognition records income when earned, regardless of when cash is received, aligning with accrual accounting principles. Cash basis accounting records revenue only when cash is actually received, impacting how your financial performance is reported. Subscription models often require revenue recognition methods to accurately match income with the service period, ensuring precise financial statements.
Benefits of Revenue Recognition Method
Revenue recognition method provides a more accurate reflection of a company's financial performance by matching revenue with the period in which it is earned, regardless of when cash is received. This approach enhances financial reporting transparency and compliance with accounting standards like GAAP and IFRS, benefiting stakeholders such as investors and creditors. Compared to cash basis and subscription methods, revenue recognition facilitates better forecasting and decision-making by aligning revenues with related expenses and contractual obligations.
Advantages of Cash Basis Accounting
Cash basis accounting simplifies your financial management by recording transactions only when cash changes hands, providing a clear and immediate overview of your business's cash flow. This method reduces the complexity of tracking receivables and payables, making it ideal for small businesses and subscription-based services with consistent cash inflows. Choosing cash basis accounting helps you maintain accurate cash flow monitoring, which is crucial for timely decision-making and managing subscription revenues effectively.
Common Industries Using Each Method
Revenue recognition is widely adopted in technology and software industries where companies deliver products over time, requiring precise matching of income and expenses under GAAP standards. Cash basis accounting is common among small businesses and sole proprietorships, such as local retailers and freelancers, because it tracks actual cash flow, simplifying tax reporting and financial management. Subscription models dominate industries like SaaS, digital media, and telecommunications, where recurring revenue streams necessitate continuous recognition aligned with customer contract terms.
Impact on Financial Statements
Revenue recognition based on the accrual method records income when earned, affecting accounts receivable and revenue on the income statement, providing a more accurate financial position. Cash basis accounting impacts financial statements by recognizing revenue only when cash is received, leading to potential timing mismatches in income and expenses. Subscription models recognize revenue over the service period, spreading income and impacting deferred revenue liabilities, ensuring consistent revenue reporting and matching expenses in the corresponding periods.
Regulatory Compliance and Accounting Standards
Revenue recognition follows accounting standards such as IFRS 15 and ASC 606, requiring companies to recognize income when performance obligations are satisfied, ensuring regulatory compliance with GAAP or IFRS. Cash basis accounting records revenue only when cash is received, which may not comply with these standards and is generally not accepted for public companies. Subscription-based models must align revenue recognition with contract terms and delivery schedules under ASC 606 or IFRS 15 to maintain compliance and accurate financial reporting.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Business
Selecting the appropriate revenue recognition method is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance, whether you use accrual-based recognition, cash basis accounting, or subscription billing models. Each method offers unique benefits: accrual-based recognition aligns revenue with earned services, cash basis records transactions upon payment, and subscription models require recognizing revenue over the subscription period to match service delivery. Understanding your business type, cash flow patterns, and customer payment habits ensures you choose the most effective approach to optimize Your financial management and regulatory adherence.
Infographic: Revenue Recognition vs Cash Basis
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com