Public pensions offer guaranteed lifetime benefits funded by government contributions, while private pensions depend on individual investments and market performance. Discover the key differences and benefits of each pension type in this article.
Table of Comparison
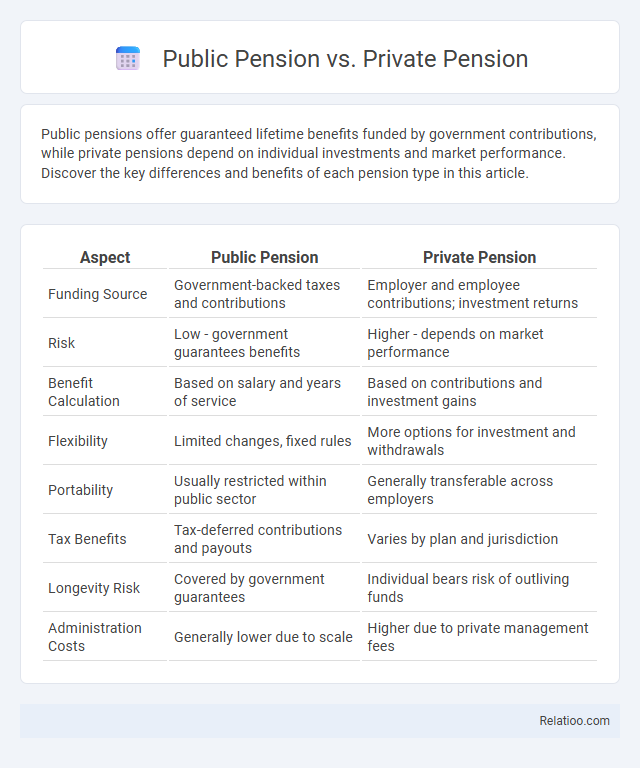
| Aspect | Public Pension | Private Pension |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Government-backed taxes and contributions | Employer and employee contributions; investment returns |
| Risk | Low - government guarantees benefits | Higher - depends on market performance |
| Benefit Calculation | Based on salary and years of service | Based on contributions and investment gains |
| Flexibility | Limited changes, fixed rules | More options for investment and withdrawals |
| Portability | Usually restricted within public sector | Generally transferable across employers |
| Tax Benefits | Tax-deferred contributions and payouts | Varies by plan and jurisdiction |
| Longevity Risk | Covered by government guarantees | Individual bears risk of outliving funds |
| Administration Costs | Generally lower due to scale | Higher due to private management fees |
Overview of Public and Private Pensions
Public pensions are government-funded retirement programs designed to provide a stable income to retirees, often financed through payroll taxes and designed to ensure baseline financial security. Private pensions, typically offered by employers or through individual retirement accounts, depend on investment performance and contributions from both employees and employers, aiming to supplement retirement income. Understanding the differences between public and private pensions involves examining funding sources, benefit guarantees, and the level of risk borne by participants.
Key Differences Between Public and Private Pensions
Public pensions are typically funded and managed by government entities, offering defined benefits based on your salary and years of service, ensuring a stable retirement income. Private pensions, often provided by employers or financial institutions, can be defined benefit or defined contribution plans, with returns influenced by investment performance and employer contributions. The key differences lie in funding sources, risk levels, and benefit guarantees, with public pensions generally providing more predictable benefits while private pensions offer potential for higher growth but with greater risk.
Eligibility Criteria for Each Pension Type
Eligibility criteria for public pensions typically require government employment with a minimum service period and age threshold, often mandating contributions to state-managed funds. Private pensions usually depend on individual or employer contributions, with varied age and vesting requirements dictated by the specific plan provider. Your qualification for any pension type depends on your employment sector, contribution history, and adherence to age or service conditions set by the relevant pension scheme.
Funding Sources and Financial Stability
Public pension plans are primarily funded through mandatory payroll taxes and government contributions, ensuring steady cash flow supported by taxpayer revenues and often backed by sovereign guarantees. Private pension plans rely on employer and employee contributions combined with investment returns, making their funding sources more variable and subject to market fluctuations. The financial stability of public pensions depends on demographic trends and political support, while private pensions face risks tied to investment performance and the solvency of sponsoring employers.
Benefit Calculation Methods
Public pension benefit calculation typically relies on a defined formula based on years of service and final average salary, ensuring predictable retirement income. Private pension plans often use defined contribution methods, where benefits depend on account performance and individual contributions, introducing variability in retirement benefits. Hybrid pension plans combine features of both, incorporating fixed formulas alongside investment-based components to balance predictability and potential growth.
Portability and Flexibility of Pension Plans
Public pensions typically offer less portability and flexibility since they are tied to government employment and rigid benefit structures. Private pensions often provide greater portability through options like 401(k) rollovers, allowing you to transfer funds between employers more easily. Pension plans vary widely, but prioritizing flexibility ensures your retirement savings adapt to career changes and personal financial needs.
Risk Factors: Who Bears the Investment Risk?
Public pensions typically shift investment risk to the government, providing more stable benefits to recipients, while private pensions often pass the investment risk directly to plan participants or employers, depending on the plan type. Defined benefit public pensions guarantee fixed payouts regardless of market performance, whereas private defined contribution plans expose your retirement savings to market volatility. Understanding who bears the investment risk is crucial for managing your retirement income security.
Tax Implications for Public vs Private Pensions
Public pensions often benefit from favorable tax treatment, including tax-deferred growth and exemptions on contributions or withdrawals depending on the jurisdiction, while private pensions frequently allow contributions to be made pre-tax, reducing taxable income in the contribution year but taxing withdrawals as ordinary income. Public pension benefits may be partially or fully exempt from state income taxes, varying by state, whereas private pension distributions are commonly taxed at ordinary income rates federally and at the state level. Understanding the specific tax codes governing public and private pension plans is crucial for optimizing retirement income and minimizing tax liabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages Compared
Public pensions offer stable, government-backed retirement income with inflation protection but often have lower returns and limited flexibility. Private pensions provide potentially higher returns and personalized investment options but carry more risk and depend on your management skills. Comparing your pension choices involves weighing the security and predictability of public plans against the growth potential and variability of private plans.
Choosing the Right Pension: Factors to Consider
When choosing the right pension, consider factors such as contribution flexibility, risk tolerance, and tax benefits. Public pensions typically offer stable, government-backed income but may have limited growth potential, while private pensions often provide higher returns with greater investment risk and more personalized options. Evaluating employer contributions, vesting periods, and payout structures helps tailor the decision to individual retirement goals and financial situations.
Infographic: Public Pension vs Private Pension
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com