Deferred Revenue represents payments received before services are delivered, while Accrued Revenue reflects earnings recorded before cash collection. Understand these key accounting concepts and how they impact financial statements in this article.
Table of Comparison
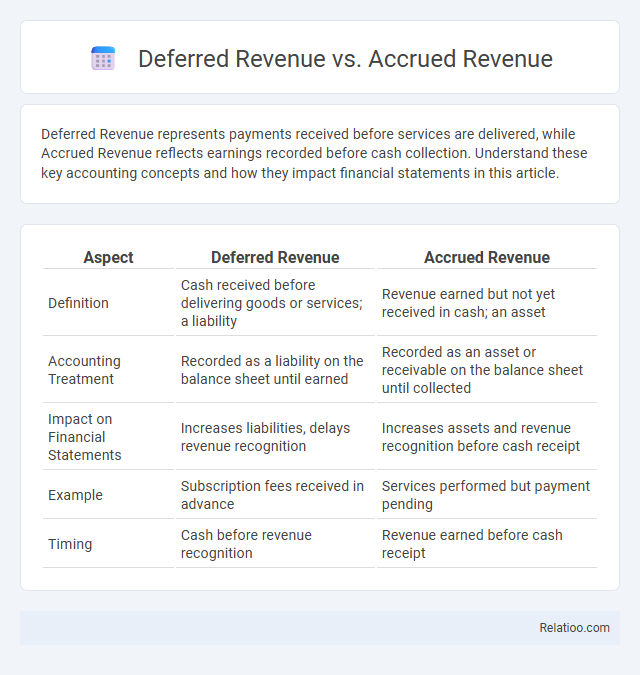
| Aspect | Deferred Revenue | Accrued Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cash received before delivering goods or services; a liability | Revenue earned but not yet received in cash; an asset |
| Accounting Treatment | Recorded as a liability on the balance sheet until earned | Recorded as an asset or receivable on the balance sheet until collected |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Increases liabilities, delays revenue recognition | Increases assets and revenue recognition before cash receipt |
| Example | Subscription fees received in advance | Services performed but payment pending |
| Timing | Cash before revenue recognition | Revenue earned before cash receipt |
Understanding Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue represents payments Your business receives in advance for goods or services not yet delivered, contrasting with accrued revenue which accounts for earnings recognized before payment is received. Subscription-based models often generate deferred revenue by collecting fees upfront for ongoing services, making accurate tracking essential for financial reporting and cash flow management. Understanding deferred revenue helps ensure compliance with revenue recognition standards and improves forecasting accuracy in subscription businesses.
What is Accrued Revenue?
Accrued revenue is income earned by a business for goods or services delivered but not yet invoiced or received payment, reflecting revenue recognized before cash collection. This contrasts with deferred revenue, which involves cash received in advance for services or products not yet delivered, recorded as a liability until fulfillment. Understanding accrued revenue helps you accurately match earned income to the correct accounting period, enhancing financial reporting and cash flow analysis.
Key Differences Between Deferred and Accrued Revenue
Deferred revenue represents payments received in advance for goods or services yet to be delivered, whereas accrued revenue refers to earnings recognized before payment is received, reflecting completed services or delivered goods. Subscription revenue often involves deferred revenue since subscriptions are paid upfront but recognized over the service period. The key difference lies in timing: deferred revenue is a liability from prepayments, while accrued revenue is an asset from earned but unbilled income.
Real-World Examples of Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue represents payments received for services or products yet to be delivered, such as annual software subscriptions paid upfront but recognized monthly. In contrast, accrued revenue occurs when services are provided but not yet billed, like consulting hours rendered at month-end awaiting invoicing. Your business must accurately record deferred revenue to comply with accounting standards, ensuring liabilities reflect unearned income until your service obligation is fulfilled.
Real-World Examples of Accrued Revenue
Accrued revenue occurs when services are delivered or goods are provided before payment is received, such as a marketing agency completing a campaign at month-end but invoicing clients the next month. Deferred revenue, by contrast, involves receiving payment upfront for services or products to be delivered later, like a software company charging annual subscription fees before the service period begins. Understanding these distinctions helps your business accurately match revenue recognition to cash flow timing and comply with accounting standards.
Impact on Financial Statements
Deferred revenue appears as a liability on your balance sheet, reflecting money received for services or products yet to be delivered, which reduces current revenue recognition. Accrued revenue, recorded as a current asset, represents earned income not yet billed or received, increasing your accounts receivable and net income. Subscription revenue impacts both the income statement and balance sheet by allocating revenue over the subscription period, ensuring consistent revenue recognition and accurate matching of expenses.
Recognition Criteria for Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue refers to payments received by a company for goods or services not yet delivered, and its recognition criteria require that revenue is recorded only when the performance obligation is satisfied. Accrued revenue is revenue earned but not yet received or recorded, recognized based on the completion of revenue-generating activities regardless of cash flow. For subscription services, revenue recognition depends on the delivery of services over the subscription period, ensuring your financial statements accurately reflect earned revenue and deferred liabilities.
Recognition Criteria for Accrued Revenue
Accrued revenue is recognized when goods or services have been delivered or performed, but payment has not yet been received, reflecting earned income regardless of cash flow. Deferred revenue represents advance payments received before fulfilling the associated service or product delivery, recognized as a liability until earned. Subscription revenue is typically recognized ratably over the subscription period, aligning revenue recognition with service delivery.
Importance for Businesses and Investors
Deferred revenue represents payments received before delivering goods or services, impacting cash flow and liability management critical for accurate financial statements. Accrued revenue records earned income not yet billed, offering insights into future cash inflows and enhancing revenue recognition accuracy. Subscription models provide predictable recurring revenue streams, improving business valuation and stability that attract investors seeking consistent growth and profitability.
Common Mistakes in Reporting Revenues
Common mistakes in reporting Deferred Revenue, Accrued Revenue, and Subscription revenues often stem from misclassifying these distinct types of income. Deferred Revenue arises from payments received before delivering goods or services but is frequently recognized prematurely, skewing financial statements. You must accurately match revenue recognition with the actual delivery of service or product to avoid misstating your financial performance.
Infographic: Deferred Revenue vs Accrued Revenue
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com