Secured liabilities are backed by collateral, reducing lender risk, while unsecured liabilities lack asset backing and carry higher interest rates due to increased risk. Explore the differences in risk, interest, and impact on credit in this article.
Table of Comparison
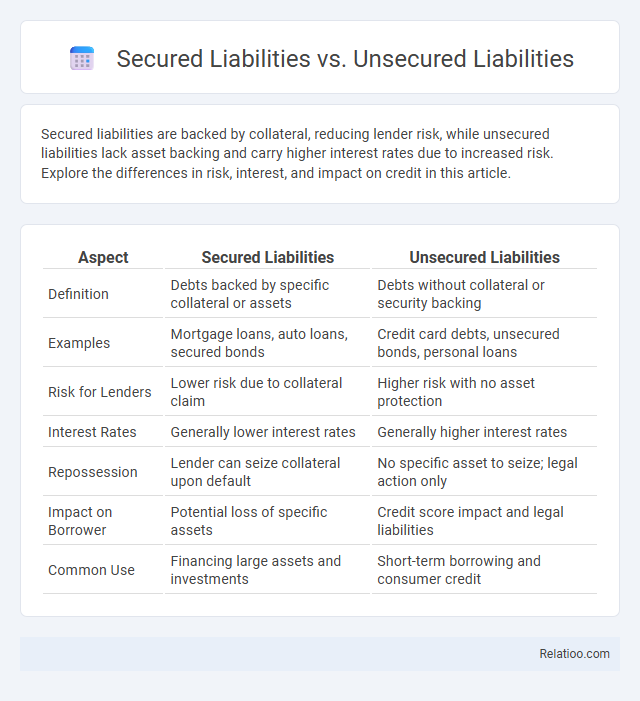
| Aspect | Secured Liabilities | Unsecured Liabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Debts backed by specific collateral or assets | Debts without collateral or security backing |
| Examples | Mortgage loans, auto loans, secured bonds | Credit card debts, unsecured bonds, personal loans |
| Risk for Lenders | Lower risk due to collateral claim | Higher risk with no asset protection |
| Interest Rates | Generally lower interest rates | Generally higher interest rates |
| Repossession | Lender can seize collateral upon default | No specific asset to seize; legal action only |
| Impact on Borrower | Potential loss of specific assets | Credit score impact and legal liabilities |
| Common Use | Financing large assets and investments | Short-term borrowing and consumer credit |
Introduction to Secured and Unsecured Liabilities
Secured liabilities are financial obligations backed by specific assets, providing creditors with collateral rights to recover debts if the borrower defaults. Unsecured liabilities lack such collateral, relying solely on the borrower's creditworthiness and legal obligation to repay. Understanding the distinction between secured and unsecured liabilities is crucial for assessing risk and creditor priority in financial and legal contexts.
Defining Secured Liabilities
Secured liabilities are financial obligations backed by collateral, ensuring creditors have a claim on specific assets if you default on the debt. Unsecured liabilities, by contrast, lack collateral and rely solely on your creditworthiness, making them riskier for lenders. Understanding the distinction between secured liabilities and general liabilities helps you manage risk and protect your assets effectively.
Understanding Unsecured Liabilities
Unsecured liabilities represent debts or financial obligations that are not backed by collateral, making them riskier for lenders compared to secured liabilities, which are tied to specific assets like property or equipment. Your understanding of unsecured liabilities is crucial because they typically carry higher interest rates and can impact your creditworthiness more significantly if not managed properly. Liability, in general, encompasses both secured and unsecured debts, reflecting your overall financial obligations.
Key Differences Between Secured and Unsecured Liabilities
Secured liabilities involve borrowing backed by collateral, such as mortgages or auto loans, providing the lender with asset claims if you default. Unsecured liabilities, like credit card debt or personal loans, lack collateral, resulting in higher interest rates due to increased risk for lenders. Understanding these key differences helps you manage your debt portfolio effectively and make informed financial decisions.
Examples of Secured Liabilities
Secured liabilities are debts backed by collateral, such as mortgages secured by real estate or auto loans tied to vehicles, ensuring the lender can claim the asset if the borrower defaults. In contrast, unsecured liabilities include credit card debts and personal loans that lack collateral, increasing the lender's risk. Understanding the distinction between secured and unsecured liabilities is crucial for effective financial management and risk assessment.
Examples of Unsecured Liabilities
Unsecured liabilities, unlike secured liabilities which are backed by collateral, represent debts that do not have specific assets pledged as security. Examples of unsecured liabilities include credit card debt, medical bills, personal loans, and utility bills, which require you to repay without risking a particular asset. Understanding the nature of your unsecured liabilities is crucial for managing financial risks and planning effective debt repayment strategies.
Risk Factors for Lenders and Borrowers
Secured liabilities involve collateral, reducing risk for lenders as they can claim specific assets if the borrower defaults, while unsecured liabilities carry higher risk due to lack of collateral, resulting in potentially higher interest rates to offset lender risk. Borrowers face greater liability and risk with unsecured debts because defaulting can damage credit without the protection of collateral, whereas secured liabilities might risk valuable assets but often come with lower rates and manageable repayment terms. Understanding these distinctions helps you manage financial risk by choosing appropriate liability forms based on your asset availability and risk tolerance.
Impact on Creditworthiness and Interest Rates
Secured liabilities, backed by collateral such as property or assets, typically lower your credit risk and result in more favorable interest rates due to reduced lender risk. Unsecured liabilities lack collateral, increasing credit risk and often leading to higher interest rates to compensate lenders for potential default. Understanding the distinctions between these liabilities is crucial for managing your financial health and optimizing your creditworthiness.
Legal Implications and Recovery Processes
Secured liabilities involve debt backed by specific collateral, granting creditors legal rights to repossess or liquidate assets if the borrower defaults, ensuring a higher likelihood of recovery. Unsecured liabilities lack collateral, limiting creditors to pursue claims through legal judgments without direct asset claims, often resulting in lower recovery rates and prolonged litigation. Liability, in a broader legal context, encompasses all financial obligations, with recovery processes varying significantly based on the presence or absence of security interests and applicable insolvency laws.
Choosing Between Secured and Unsecured Liabilities
Choosing between secured and unsecured liabilities depends on a company's risk tolerance and asset base. Secured liabilities offer lower interest rates by using collateral, reducing lender risk but increasing the risk of asset forfeiture. Unsecured liabilities typically carry higher interest rates but provide more operational flexibility without pledging specific assets.
Infographic: Secured Liabilities vs Unsecured Liabilities
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com