Fixed annuities provide guaranteed returns with lower risk, while variable annuities offer potential for higher returns linked to market performance but come with increased risk. Explore this article to understand which annuity suits your financial goals best.
Table of Comparison
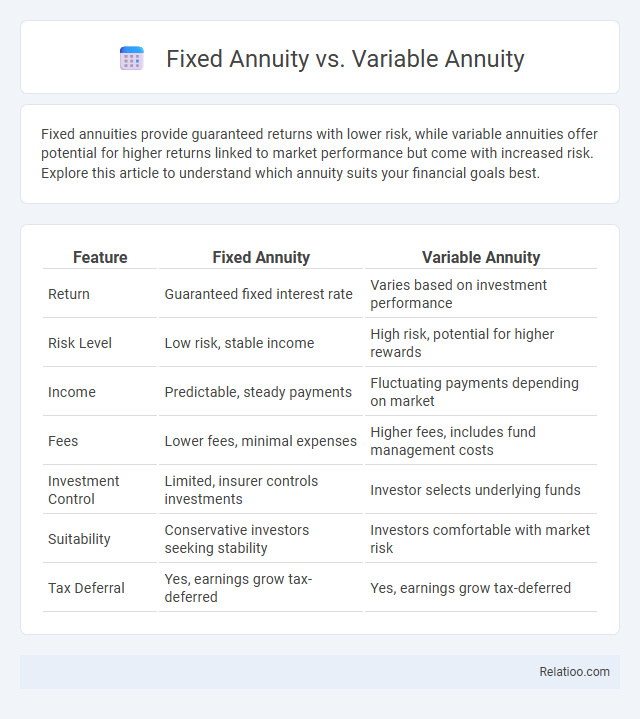
| Feature | Fixed Annuity | Variable Annuity |
|---|---|---|
| Return | Guaranteed fixed interest rate | Varies based on investment performance |
| Risk Level | Low risk, stable income | High risk, potential for higher rewards |
| Income | Predictable, steady payments | Fluctuating payments depending on market |
| Fees | Lower fees, minimal expenses | Higher fees, includes fund management costs |
| Investment Control | Limited, insurer controls investments | Investor selects underlying funds |
| Suitability | Conservative investors seeking stability | Investors comfortable with market risk |
| Tax Deferral | Yes, earnings grow tax-deferred | Yes, earnings grow tax-deferred |
Introduction to Annuities: Fixed vs Variable
Fixed annuities provide guaranteed returns and stable income, making them ideal for conservative investors seeking predictable growth. Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns by investing in underlying securities but come with market risk and fluctuating payouts. Understanding the differences between fixed and variable annuities helps you choose the right option aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
How Fixed Annuities Work
Fixed annuities provide a guaranteed interest rate and consistent, predictable income, making them ideal for those seeking financial stability in retirement. Unlike variable annuities, which fluctuate with market performance, fixed annuities protect your principal and ensure steady growth over time. Understanding how fixed annuities work can help you secure a reliable income stream tailored to your financial goals.
How Variable Annuities Work
Variable annuities allow you to invest your premiums in a range of sub-accounts, similar to mutual funds, offering the potential for higher returns based on market performance. Unlike fixed annuities that provide guaranteed interest rates, variable annuities' payout amounts fluctuate depending on the investment results of your chosen portfolios. This investment flexibility helps tailor your retirement income to your risk tolerance and long-term financial goals.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Variable Annuities
Fixed annuities guarantee a steady, predictable income by offering a fixed interest rate, while variable annuities provide returns based on investment performance, introducing potential for growth but also risk. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize income stability or market-linked growth potential. Fixed annuities protect your principal from market fluctuations, whereas variable annuities allow your investments to be allocated among subaccounts with varying risk levels.
Pros and Cons of Fixed Annuities
Fixed annuities offer guaranteed principal protection and predictable income streams, making them ideal for risk-averse investors seeking stable retirement income. However, fixed annuities typically provide lower returns compared to variable annuities, which offer potential for higher gains linked to market performance but with increased risk. Unlike general annuities that vary widely in structure, fixed annuities prioritize stability over growth, often resulting in reduced liquidity and inflation protection.
Pros and Cons of Variable Annuities
Variable annuities offer the potential for higher returns through investment options tied to market performance, providing growth opportunities that fixed annuities lack. Your investment carries market risk, meaning returns can fluctuate and principal is not guaranteed, unlike fixed annuities that offer stable, predictable income. Variable annuities often include fees and charges that can reduce overall returns, but they provide benefits such as tax-deferred growth and optional death benefits enhancing financial security.
Risk Factors: Fixed vs Variable Annuities
Fixed annuities offer guaranteed returns with minimal risk, providing predictable income streams unaffected by market fluctuations. Variable annuities expose investors to market risk, allowing potential for higher returns but with income and principal value subject to market volatility. Understanding these risk factors helps determine suitability based on individual risk tolerance and retirement income goals.
Suitability: Who Should Choose Which Annuity?
Fixed annuities suit conservative investors seeking guaranteed income and principal protection, emphasizing stability and predictable returns. Variable annuities are ideal for investors with higher risk tolerance who want potential growth through diversified investment options like mutual funds, despite market volatility. General annuities fit individuals aiming for consistent retirement income, but suitability depends on their risk appetite, financial goals, and the specific annuity contract features.
Tax Implications of Each Annuity Type
Fixed annuities offer tax-deferred growth with earnings taxed as ordinary income upon withdrawal, making them predictable for retirement income but without direct market exposure. Variable annuities also provide tax-deferred growth, but gains depend on investment performance, and withdrawals are subject to ordinary income tax plus potential penalties if taken before age 59 1/2. Unlike fixed and variable annuities, indexed annuities grow based on a market index with tax-deferred earnings, but gains are taxed upon distribution similarly to other annuities, making tax treatment consistent across annuity types upon payout.
Which Annuity is Right for You?
Choosing the right annuity depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance; a Fixed Annuity provides guaranteed returns and stability, ideal for conservative investors seeking steady income. Variable Annuities offer growth potential through market-linked investments but come with higher risk and fees, suited for those comfortable with market fluctuations. Your decision should balance the need for security versus growth potential to align with your retirement income strategy.
Infographic: Fixed Annuity vs Variable Annuity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com