A supposition is an assumption made without proof, serving as a basis for reasoning, while a premise is a statement or proposition that forms the foundation of an argument or conclusion. Explore the key differences and how they impact logical reasoning in this article.
Table of Comparison
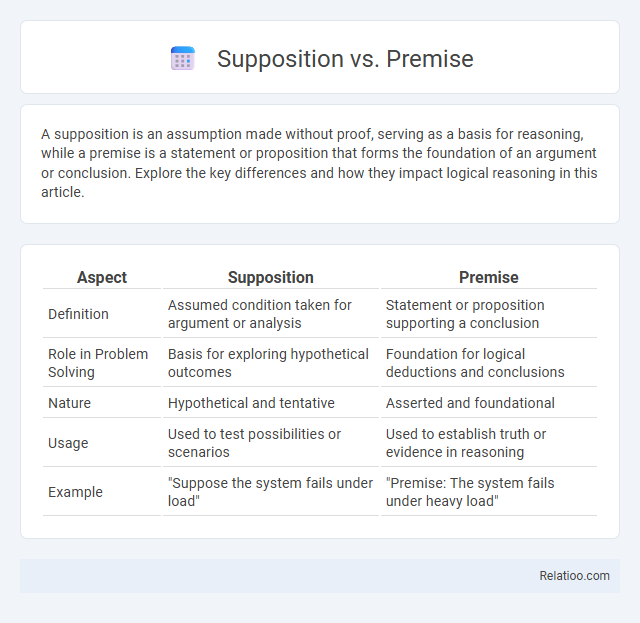
| Aspect | Supposition | Premise |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assumed condition taken for argument or analysis | Statement or proposition supporting a conclusion |
| Role in Problem Solving | Basis for exploring hypothetical outcomes | Foundation for logical deductions and conclusions |
| Nature | Hypothetical and tentative | Asserted and foundational |
| Usage | Used to test possibilities or scenarios | Used to establish truth or evidence in reasoning |
| Example | "Suppose the system fails under load" | "Premise: The system fails under heavy load" |
Understanding Supposition: Definition and Scope
Understanding supposition involves recognizing it as a foundational assumption taken to be true within a specific context, often serving as a hypothetical premise for logical reasoning or argumentation. Unlike a premise, which functions as a statement supporting a conclusion in formal logic, supposition emphasizes the temporary acceptance of an idea to explore its implications or consequences. The scope of supposition extends to various fields such as philosophy, linguistics, and mathematics, where it aids in constructing hypothetical scenarios and testing theoretical propositions.
What is a Premise? Clarifying the Concept
A premise is a foundational statement in logical reasoning that serves as evidence or support for a conclusion. It is a proposition you accept as true and use to build an argument, distinct from a supposition which is more of a hypothetical assumption. Understanding the role of a premise helps you critically evaluate arguments and ensures clarity in discussions or debates.
Core Differences: Supposition vs Premise
A supposition is an assumed idea or hypothesis made without proof, often used as a starting point for reasoning or argumentation, while a premise is a foundational statement or proposition that supports a conclusion within a logical argument. Your understanding of these concepts clarifies that suppositions invite exploration and hypothesis, whereas premises provide concrete grounds that justify conclusions. Differentiating between these terms enhances critical thinking by distinguishing speculative assumptions from established argumentative foundations.
Role of Suppositions in Reasoning
Suppositions serve as foundational assumptions in reasoning, providing initial conditions that guide logical analysis without requiring immediate proof. Unlike premises, which are statements accepted as true within an argument to support a conclusion, suppositions function as hypothetical scenarios to explore outcomes and test validity. Your ability to distinguish these concepts enhances critical thinking and strengthens the construction of sound logical arguments.
The Function of Premises in Logical Arguments
Premises serve as foundational statements in logical arguments, providing the necessary support to reach a valid conclusion. Unlike suppositions, which are assumptions made without proof, premises are intentionally asserted to establish a logical framework and validate the argument's reasoning. Understanding the function of premises helps clarify the structure of deductive reasoning and ensures the argument's soundness and coherence.
Examples Illustrating Supposition and Premise
A supposition is an assumption taken as true for the sake of argument, such as supposing "If it rains tomorrow, the picnic will be canceled," while a premise is a foundational statement in logic, like "All mammals are warm-blooded." For example, in the argument "All humans are mortal (premise), Socrates is a human (premise), therefore Socrates is mortal," the premises establish the basis for the conclusion. Suppositions often initiate hypotheses in discussions, whereas premises serve as accepted truths that support logical reasoning.
Common Misconceptions between Supposition and Premise
Supposition and premise are often confused because both involve assumptions, but a supposition is typically an unproven hypothesis used for exploration or argument, while a premise is a foundational statement accepted as true within logical reasoning to build conclusions. A common misconception is treating a supposition as a proven fact, which undermines critical analysis, whereas a premise serves as a starting point that supports deductive reasoning. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate interpretation in philosophy, logic, and argumentation.
Importance of Distinguishing Suppositions from Premises
Distinguishing suppositions from premises is crucial for clear logical reasoning and sound argument construction. Suppositions serve as assumptions that may or may not be true, while premises provide foundational evidence supporting a conclusion. Your ability to accurately identify and separate these elements ensures stronger analytical thinking and more persuasive arguments.
Supposition vs Premise in Academic Writing
In academic writing, a premise serves as a foundational statement or proposition that supports an argument, while a supposition represents an assumed idea or hypothesis used for exploration or testing. Your clarity in distinguishing a premise as a basis for logical reasoning ensures stronger argumentation, whereas supposition allows flexibility for hypothetical scenarios. Understanding these differences enhances the precision and rigor of scholarly analysis.
Best Practices for Using Suppositions and Premises
Best practices for using suppositions and premises involve clearly distinguishing their roles within an argument or hypothesis to enhance logical clarity. Suppositions serve as assumed conditions or hypotheses for the sake of reasoning, while premises provide foundational statements that support conclusions based on evidence. Ensuring that premises are well-evidenced and suppositions remain explicitly hypothetical prevents logical fallacies and strengthens argumentative rigor.
Infographic: Supposition vs Premise
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com