Passive-aggressiveness in relationships involves indirect resistance and covert hostility, while aggressiveness entails direct confrontation and verbal or physical expressions of anger. Explore this article to understand the impact of these behaviors and strategies for healthy communication.
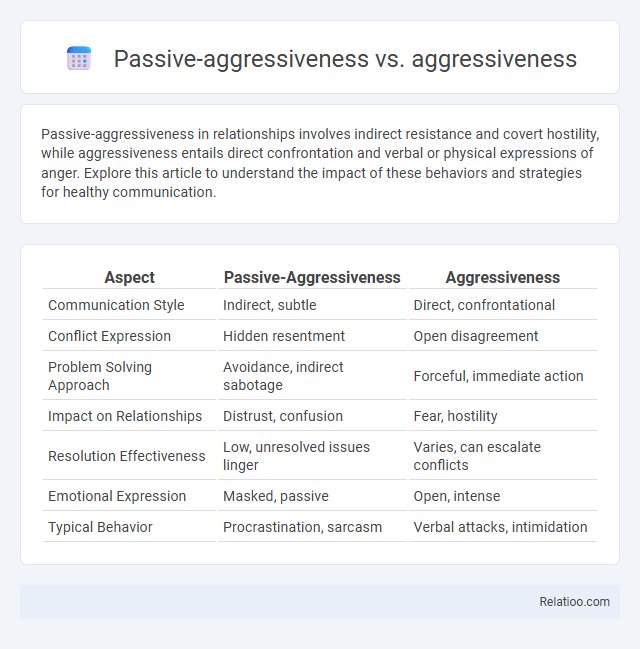
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Passive-Aggressiveness | Aggressiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Style | Indirect, subtle | Direct, confrontational |
| Conflict Expression | Hidden resentment | Open disagreement |
| Problem Solving Approach | Avoidance, indirect sabotage | Forceful, immediate action |
| Impact on Relationships | Distrust, confusion | Fear, hostility |
| Resolution Effectiveness | Low, unresolved issues linger | Varies, can escalate conflicts |
| Emotional Expression | Masked, passive | Open, intense |
| Typical Behavior | Procrastination, sarcasm | Verbal attacks, intimidation |
Understanding Passive-Aggressiveness
Passive-aggressiveness involves indirect expressions of hostility, such as sarcasm or procrastination, contrasting with overt aggressiveness characterized by direct confrontation and open hostility. Understanding passive-aggressiveness helps you recognize subtle behaviors like silent treatment or backhanded compliments that undermine relationships without explicit conflict. Identifying these patterns enables healthier communication and prevents emotional distress caused by unresolved tension.
What Defines Aggressiveness?
Aggressiveness is characterized by direct, confrontational behavior aimed at asserting dominance or achieving goals, often through verbal or physical force. It involves clear expressions of anger or hostility, contrasting with passive-aggressiveness, where resentment is masked by indirect actions like sarcasm or procrastination. Understanding your own responses helps differentiate assertive communication from aggressive tendencies.
Key Differences Between Passive-Aggressiveness and Aggressiveness
Passive-aggressiveness manifests through indirect resistance, such as procrastination, sarcasm, or subtle undermining, whereas aggressiveness is characterized by overt hostility, including verbal attacks, physical intimidation, or blatant confrontation. The key difference lies in expression: passive-aggressive behavior conceals true feelings, often leading to confusion and unresolved conflict, while aggressive behavior expresses feelings openly and directly, often escalating disputes. Understanding these distinctions aids in effectively identifying and addressing communication issues within personal and professional relationships.
Common Behaviors and Examples
Passive-aggressiveness often manifests through indirect resistance, such as procrastination, sarcasm, or silent treatment, while aggressiveness is characterized by overt hostility like yelling, blaming, or confrontation. Common behaviors of passive-aggressiveness include backhanded compliments, intentional inefficiency, and subtle sabotage, whereas aggressiveness involves direct verbal attacks, physical intimidation, or forceful demands. Examples of passive-aggressive actions include ignoring emails on purpose or making snide remarks, whereas aggressive behaviors include yelling during conflicts or issuing threats to intimidate others.
Psychological Roots of Each Behavior
Passive-aggressiveness often stems from underlying feelings of helplessness, fear of confrontation, and suppressed resentment, reflecting an indirect expression of anger tied to low self-esteem and avoidance coping mechanisms. Aggressiveness typically arises from a desire for control, dominance, or protection, frequently linked to heightened stress, unmet needs, or perceived threats triggering the brain's fight response. Passive behavior is generally rooted in anxiety, lack of confidence, or fear of rejection, causing individuals to suppress their own needs and desires to maintain harmony or avoid conflict.
Effects on Relationships and Communication
Passive-aggressiveness often leads to miscommunication and frustration, as underlying hostility is expressed indirectly, causing confusion and eroding trust within relationships. Aggressiveness typically results in open conflict and emotional distress, creating a hostile environment that hinders effective dialogue and damages interpersonal bonds. In contrast, passive behavior may cause resentment and disengagement, limiting honest communication and weakening connection, thereby impeding the resolution of underlying issues.
Recognizing the Signs: Passive-Aggressive vs Aggressive
Recognizing the signs of passive-aggressiveness versus aggressiveness requires understanding their distinct behaviors: passive-aggressive individuals often express hostility through indirect actions like sarcasm, procrastination, or silent treatment, while aggressive individuals display overt hostility through direct confrontation, yelling, or insults. Your ability to identify these patterns helps in managing conflicts effectively and choosing appropriate communication strategies. Awareness of these signs enhances emotional intelligence and promotes healthier interpersonal interactions.
Impact in the Workplace and Social Settings
Passive-aggressiveness in the workplace often undermines team cohesion by fostering mistrust and disguised hostility, which reduces productivity and escalates conflicts over time. Aggressiveness, while sometimes driving results, can create a hostile environment that intimidates colleagues, stifles open communication, and increases employee turnover. In social settings, passive-aggressiveness hinders genuine connections through indirect expressions of anger or resentment, whereas aggressiveness tends to provoke confrontation and alienate others, both ultimately damaging relationships and social harmony.
Strategies for Addressing Both Behaviors
Strategies for addressing passive-aggressiveness and aggressiveness involve clear communication and boundary-setting tailored to each behavior. You should confront aggressiveness directly with assertive yet calm dialogue while managing passive-aggressiveness by encouraging open expression of feelings and clarifying underlying issues. Conflict resolution techniques, including active listening and empathy, support healthier interactions and reduce misunderstandings in both types of behavior.
Promoting Healthy Communication Styles
Promoting healthy communication styles requires understanding the differences between passive-aggressiveness, aggressiveness, and assertiveness, as each impacts relationships uniquely. Passive-aggressiveness involves indirect resistance and hidden hostility, leading to misunderstandings and unresolved conflicts, whereas aggressiveness is characterized by overt hostility and can damage trust and respect. Encouraging assertive communication, which balances expressing one's needs clearly and respectfully while considering others, fosters openness, empathy, and effective problem-solving.
Infographic: Passive-aggressiveness vs Aggressiveness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com