Assumptions are unstated beliefs taken for granted, while conclusions are definitive statements derived from evidence. Explore how distinguishing assumptions from conclusions enhances critical thinking in this article.
Table of Comparison
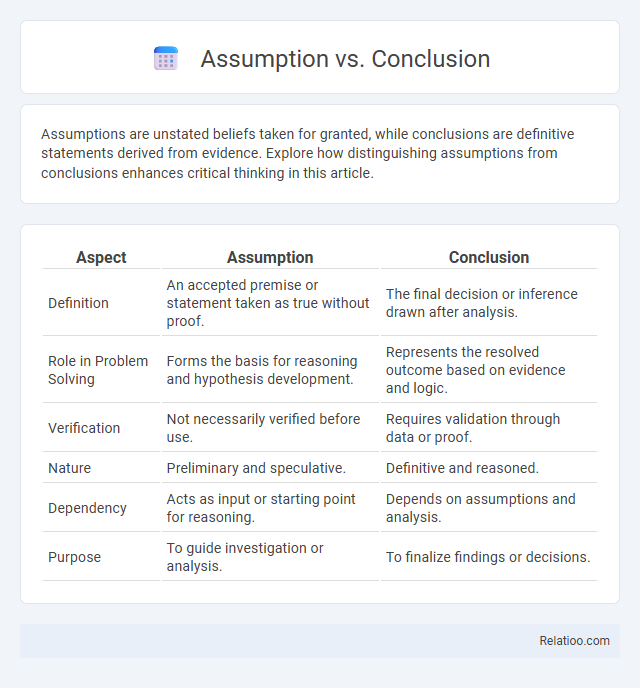
| Aspect | Assumption | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An accepted premise or statement taken as true without proof. | The final decision or inference drawn after analysis. |
| Role in Problem Solving | Forms the basis for reasoning and hypothesis development. | Represents the resolved outcome based on evidence and logic. |
| Verification | Not necessarily verified before use. | Requires validation through data or proof. |
| Nature | Preliminary and speculative. | Definitive and reasoned. |
| Dependency | Acts as input or starting point for reasoning. | Depends on assumptions and analysis. |
| Purpose | To guide investigation or analysis. | To finalize findings or decisions. |
Understanding Assumptions: Definition and Examples
Understanding assumptions involves recognizing them as unstated beliefs or premises that form the foundation of reasoning, essential for validating arguments. Assumptions differ from conclusions, which are explicit statements derived from premises, and from assertions, which are explicit claims made without proof. For example, in the argument "All humans are mortal; Socrates is human; therefore, Socrates is mortal," the assumption is that the premise "All humans are mortal" is true, enabling the conclusion.
What Is a Conclusion? Core Concepts Explained
A conclusion is the final statement in an argument that logically follows from the premises or assumptions presented. It represents the main point or claim that you are trying to prove based on the evidence and reasoning provided. Understanding the distinction between assumptions and conclusions is crucial for evaluating the strength and validity of your arguments.
Differences Between Assumptions and Conclusions
Assumptions are unstated premises or beliefs taken for granted within an argument, while conclusions are explicit statements derived logically from these premises. The key difference lies in their roles: assumptions provide the foundational support necessary for reaching conclusions, whereas conclusions represent the intended outcome or claim based on that support. Understanding these distinctions enhances critical reasoning by clarifying which elements require validation versus those that follow logically.
Role of Assumptions in Critical Thinking
Assumptions serve as foundational premises in critical thinking, enabling individuals to build logical arguments and test hypotheses. Unlike conclusions, which are derived from evidence and reasoning, assumptions are accepted without proof but guide the direction of analysis. Identifying and evaluating assumptions is essential to avoid bias and enhance the validity of critical assessments and conclusions.
How Conclusions Are Formed: Logical Steps
Conclusions are formed through logical steps that involve analyzing premises and assumptions to derive a coherent final statement. Your ability to distinguish assumptions--unstated beliefs taken for granted--and premises--which provide explicit support--is crucial for constructing valid conclusions. This structured reasoning process ensures that conclusions logically follow from the given information, enhancing clarity and argument strength.
Common Pitfalls: Confusing Assumptions with Conclusions
Mistaking assumptions for conclusions often leads to flawed reasoning, as assumptions are unstated premises taken for granted, whereas conclusions are the final judgments drawn from evidence. Your ability to distinguish these concepts is crucial to avoid misinterpreting arguments and to strengthen critical thinking skills. Common pitfalls include treating assumptions as proven facts or accepting conclusions without scrutinizing underlying assumptions.
Importance of Validity: Are Your Assumptions Sound?
Assumptions form the foundation of your reasoning, while conclusions are derived statements based on those premises; distinguishing between them is crucial for logical clarity. The validity of your assumptions directly impacts the strength of your conclusions, making sound, evidence-based assumptions essential for credible analysis. Ensuring your assumptions are well-founded safeguards the overall integrity of your arguments and decision-making process.
Strengthening Arguments: From Assumption to Conclusion
Strengthening arguments requires identifying key assumptions that link evidence to conclusions, ensuring these assumptions are both plausible and necessary for the argument's validity. Assumptions serve as foundational premises that fill logical gaps, while conclusions are the claims derived from supporting evidence and assumptions combined. Effective argument analysis involves testing whether the assumptions genuinely support the conclusion and reinforcing weak links to bolster overall argumentative strength.
Real-Life Examples of Assumptions vs Conclusions
Assumptions are beliefs you accept without proof, such as assuming a colleague is late due to traffic, while conclusions are logical deductions drawn from evidence, like concluding a friend's silence means they are upset after they ignored your messages. Recognizing the difference helps you avoid misinterpretations by challenging your assumptions and seeking concrete evidence to form accurate conclusions. Your ability to distinguish between assumptions and conclusions improves decision-making and communication in everyday situations.
Tips for Clear Reasoning: Avoiding Faulty Inferences
Distinguishing between assumptions and conclusions is crucial for clear reasoning; assumptions are unstated premises, while conclusions are derived statements supported by evidence. Avoid faulty inferences by identifying hidden assumptions and testing their validity before accepting conclusions. Employ critical questioning, such as probing evidence and alternative explanations, to strengthen logical clarity and prevent errors in argumentation.
Infographic: Assumption vs Conclusion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com