Assumption involves accepting something as true without proof, while inference is drawing a conclusion based on evidence and reasoning in relationships. Discover how understanding the difference between assumption and inference can improve your communication and trust in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
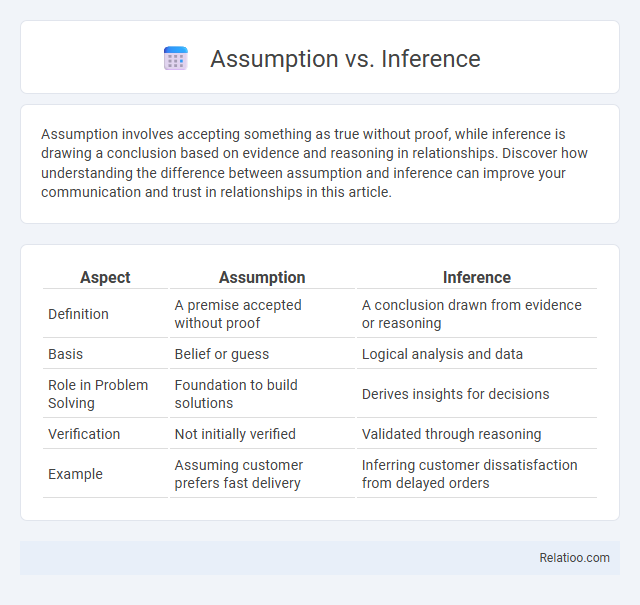
| Aspect | Assumption | Inference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A premise accepted without proof | A conclusion drawn from evidence or reasoning |
| Basis | Belief or guess | Logical analysis and data |
| Role in Problem Solving | Foundation to build solutions | Derives insights for decisions |
| Verification | Not initially verified | Validated through reasoning |
| Example | Assuming customer prefers fast delivery | Inferring customer dissatisfaction from delayed orders |
Introduction to Assumption and Inference
An assumption is a belief or statement accepted as true without proof, often serving as the foundation for reasoning or argumentation. Inference, on the other hand, involves drawing logical conclusions based on evidence and reasoning from available information. Understanding the distinction between assumption and inference is crucial for critical thinking and effective decision-making processes.
Defining Assumption: What It Means
An assumption is a belief or statement accepted as true without proof, forming the basis for reasoning or action. It differs from inference, which is a logical conclusion drawn from evidence, and presumption, which relies on probability or prior knowledge. Understanding the nature of assumptions is essential in critical thinking and decision-making processes.
Understanding Inference: Core Concepts
Inference involves drawing logical conclusions based on available evidence and reasoning, distinguishing it from assumptions, which are beliefs taken for granted without proof. Understanding inference requires analyzing data, identifying patterns, and evaluating information critically to arrive at a reasoned judgment. Your ability to differentiate between assumptions and inferences strengthens decision-making and critical thinking skills.
Key Differences Between Assumption and Inference
Assumptions are beliefs accepted without proof, forming the basis for reasoning, while inferences are conclusions drawn logically from evidence or premises. Assumptions often act as starting points that may or may not be accurate, whereas inferences depend on analyzing available information to reach a reasoned judgment. Key differences include assumptions being subjective guesses and inferences being objective deductions supported by data.
Common Examples in Everyday Life
Assumptions in everyday life often involve accepting facts without proof, such as assuming a friend will arrive on time based on past behavior. Inferences are conclusions drawn from evidence or reasoning, like noticing dark clouds and inferring it might rain soon. Recognizing the difference between assumption and inference helps you make more accurate judgments and avoid misunderstandings in common situations.
The Role of Assumptions in Critical Thinking
Assumptions serve as foundational beliefs that shape the framework of critical thinking by guiding hypothesis formation and reasoning processes. They function as implicit premises that must be identified and evaluated to avoid bias and ensure logical consistency in arguments. Distinguishing assumptions from inferences and conclusions helps critical thinkers question underlying evidence and strengthen decision-making accuracy.
How Inferences Shape Decision Making
Inferences are conclusions derived from analyzing evidence and observations, playing a critical role in shaping decision making by guiding your judgments based on available data. Unlike assumptions, which are accepted without proof, inferences rely on logical reasoning to interpret information, improving accuracy in decisions. Understanding the distinction between assumptions and inferences helps refine your decision-making process by minimizing biases and enhancing critical thinking.
Avoiding Misunderstandings: Assumption vs Inference
Misunderstandings often arise when assumptions, unverified beliefs taken for granted, are confused with inferences, logical conclusions drawn from evidence. Clear differentiation between your assumptions and inferences ensures accurate communication and critical thinking. Recognizing that assumptions lack solid evidence while inferences rely on data helps you avoid misinterpretations and errors in judgment.
Practical Tips to Distinguish Assumption From Inference
Assumption and inference differ in that an assumption is a belief accepted without evidence, while an inference is a conclusion drawn from evidence or reasoning. To distinguish between them, carefully evaluate your thought process: identify whether you're taking information for granted (assumption) or deducing a conclusion based on facts (inference). Your practical approach should involve questioning what evidence supports your thoughts and recognizing when you rely on unverified beliefs versus logical analysis.
Conclusion: Enhancing Analytical Skills
Distinguishing between assumption, inference, and conclusion sharpens your analytical skills by clarifying the foundation and outcome of reasoning processes. An assumption is a premise accepted without proof, an inference is the logical interpretation of assumed or observed information, and a conclusion synthesizes these inferences into a definitive statement. Mastering these concepts improves critical thinking, enabling you to evaluate arguments effectively and draw well-supported conclusions.
Infographic: Assumption vs Inference
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com