Supposition involves a reasoned assumption based on evidence, while a guess is a spontaneous conclusion without supporting facts. Discover the key differences and their impact on relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
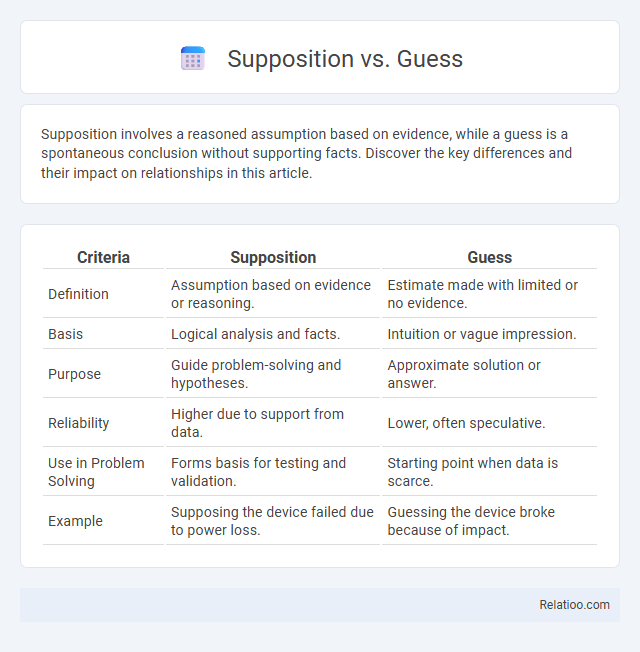
| Criteria | Supposition | Guess |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assumption based on evidence or reasoning. | Estimate made with limited or no evidence. |
| Basis | Logical analysis and facts. | Intuition or vague impression. |
| Purpose | Guide problem-solving and hypotheses. | Approximate solution or answer. |
| Reliability | Higher due to support from data. | Lower, often speculative. |
| Use in Problem Solving | Forms basis for testing and validation. | Starting point when data is scarce. |
| Example | Supposing the device failed due to power loss. | Guessing the device broke because of impact. |
Introduction to Supposition and Guess
Supposition involves forming a hypothesis based on available evidence or logical reasoning, while guess relies more on intuition or a lack of sufficient information. Your understanding improves when you distinguish supposition as a deliberate proposition and guess as an informal attempt to answer an unknown. These concepts are foundational for refining critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Defining Supposition: Meaning and Usage
Supposition refers to an assumption or hypothesis made without firm evidence, used primarily in philosophical, scientific, or logical contexts to explore possibilities. Unlike a guess, which is often casual and based on intuition, a supposition requires a thoughtful consideration of potential truths to develop arguments or conduct analyses. Understanding supposition involves recognizing its role in reasoning processes where tentative claims guide inquiry and debate.
What is a Guess? Key Characteristics
A guess is an estimate or conclusion made without sufficient information, relying primarily on intuition or incomplete evidence. It lacks certainty and is often used when quick decisions are necessary, distinguishing it from a supposition, which is a more reasoned assumption based on existing knowledge. Your guess can serve as a starting point for further investigation but should be verified for accuracy.
Semantic Differences between Supposition and Guess
Supposition involves a reasoned assumption based on evidence or logical inference, whereas a guess reflects a more spontaneous or uncertain estimate without solid proof. Your understanding of a situation improves with supposition, which relies on critical thinking, while a guess depends largely on intuition or lack of complete information. Recognizing these semantic differences sharpens your communication and decision-making in conveying certainty levels.
Supposition in Formal vs Informal Contexts
Supposition in formal contexts involves careful reasoning and is often used in academic, legal, or scientific discussions to present hypotheses or assumptions based on evidence. In informal contexts, supposition tends to be more casual and speculative, akin to making an educated guess without definitive proof. Your understanding of supposition should adapt to the setting, recognizing its role in structured arguments versus everyday conversation where precision is less critical.
How Guess Differs in Everyday Language
Guess in everyday language implies making an uncertain or intuitive judgment without complete information, often based on instinct or limited evidence. Supposition, in contrast, refers to a more deliberate assumption or hypothesis used as a starting point for further reasoning or discussion. While both involve uncertainty, guesses are spontaneous and informal, whereas suppositions are typically more structured and reasoned.
Examples of Supposition and Guess in Sentences
Supposition involves assuming something is true based on limited evidence, as in "Her supposition that the meeting was canceled proved accurate." Guess implies making an estimate or conclusion without full information, exemplified by "I guess the train arrives around 6 PM." Your understanding improves by distinguishing supposition as a reasoned assumption and guess as a spontaneous conjecture in various contexts.
When to Use Supposition vs Guess
Supposition involves forming a hypothesis based on limited evidence, often used in academic or logical contexts, while guess implies making an estimate without sufficient information or proof, typically in casual or uncertain situations. You should use supposition when proposing a theory that requires validation or further inquiry and choose guess when expressing an informal or spontaneous estimate. Understanding these distinctions helps improve clarity and precision in communication.
Common Misconceptions and Mistakes
Supposition, guess, and assumption are often confused, but each carries distinct meanings and levels of certainty; supposition implies a reasoned belief based on evidence, guess is a conjecture without sufficient information, and assumption involves accepting something as true without proof. Common misconceptions arise when people use guess and supposition interchangeably, leading to inaccuracies in communication and decision-making. To improve clarity, you should carefully evaluate the basis of your statements and select the term that accurately reflects your level of confidence and evidence.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Term
Choosing the right term hinges on the context and certainty behind the statement: "guess" implies a spontaneous or uninformed estimate, "assumption" refers to something accepted without proof for the sake of argument, and "supposition" suggests a hypothesis based on some evidence or reasoning. In scientific or analytical conclusions, "supposition" best conveys a reasoned hypothesis, while "guess" suits informal or uncertain predictions. Understanding these nuances ensures precise communication in academic, professional, and everyday contexts.
Infographic: Supposition vs Guess
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com