Assumptions in relationships often lead to misunderstandings, while facts provide clear and honest communication essential for trust-building. Discover how distinguishing assumptions from facts can strengthen your connection in this article.
Table of Comparison
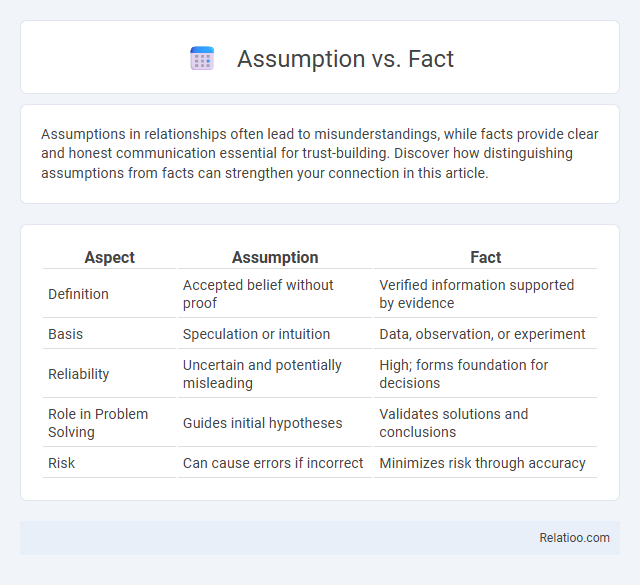
| Aspect | Assumption | Fact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accepted belief without proof | Verified information supported by evidence |
| Basis | Speculation or intuition | Data, observation, or experiment |
| Reliability | Uncertain and potentially misleading | High; forms foundation for decisions |
| Role in Problem Solving | Guides initial hypotheses | Validates solutions and conclusions |
| Risk | Can cause errors if incorrect | Minimizes risk through accuracy |
Understanding Assumptions and Facts
Understanding assumptions requires recognizing that they are beliefs or ideas accepted without proof, whereas facts are objective, verifiable pieces of information. Your ability to distinguish between assumptions and facts relies on critical thinking and evaluating evidence. Clear differentiation prevents misconceptions and strengthens decision-making based on reliable data.
Key Differences Between Assumption and Fact
Assumptions are beliefs accepted without proof, while facts are objective, verifiable truths supported by evidence. Your decisions based on assumptions carry uncertainty, as assumptions rely on interpretation or incomplete information, whereas facts provide a reliable foundation for reasoning. Understanding the distinction between assumption and fact ensures clearer analysis and reduces errors in judgment.
The Role of Assumptions in Decision-Making
Assumptions play a critical role in decision-making by serving as foundational beliefs that guide your reasoning when complete information is unavailable, distinguishing them from verifiable facts which are objective truths. Understanding the difference between assumptions and facts helps you manage uncertainty and evaluate risks more effectively. By scrutinizing your assumptions, you can improve the accuracy of decisions and avoid potential pitfalls caused by incorrect beliefs.
How Facts Shape Our Perceptions
Facts play a crucial role in shaping your perceptions by providing objective, verifiable information that grounds understanding in reality. Unlike assumptions, which are beliefs without proof, facts offer a reliable foundation for decision-making and critical thinking. Distinguishing between assumptions and facts helps prevent misconceptions and biases, enhancing clarity in interpreting situations.
Common Examples of Assumptions vs. Facts
Common examples of assumptions include believing a package will arrive on time without tracking confirmation or assuming a coworker is upset based on their tone without direct communication. Facts are verifiable pieces of information such as delivery dates provided by a shipping company or confirmed project deadlines from management. Understanding the difference between your assumptions and established facts helps improve decision-making and reduces misunderstandings in personal and professional contexts.
Consequences of Mistaking Assumptions for Facts
Mistaking assumptions for facts can lead to flawed decisions and misguided strategies, causing significant negative consequences in both personal and professional contexts. You may face wasted resources, damaged credibility, and missed opportunities when actions are based on incorrect premises rather than verified information. Distinguishing between assumptions and facts is crucial for minimizing errors and achieving successful outcomes.
Strategies to Differentiate Assumptions from Facts
Effective strategies to differentiate assumptions from facts include verifying information through credible sources, cross-referencing data, and employing critical thinking techniques. You can enhance decision-making accuracy by consistently questioning the basis of your beliefs and seeking empirical evidence to support claims. Utilizing tools such as fact-checking websites and expert consultations further minimizes the risk of confusing assumptions with verified facts.
The Impact on Critical Thinking and Reasoning
Distinguishing between assumptions and facts is crucial for enhancing your critical thinking and reasoning skills; assumptions are unverified beliefs often based on incomplete information, while facts are objective truths supported by evidence. Relying on assumptions without verification can lead to flawed conclusions and biased decision-making, hindering effective problem-solving. Incorporating a disciplined approach to identify and challenge assumptions fosters more accurate analysis and strengthens logical reasoning in complex situations.
Assumption Bias: How It Influences Judgement
Assumption bias occurs when individuals rely on unverified beliefs as facts, leading to distorted judgment and decision-making. This cognitive shortcut often causes people to ignore contradictory evidence and reinforces existing stereotypes or misconceptions. Recognizing and challenging assumption bias enhances critical thinking and promotes more accurate, evidence-based conclusions.
Embracing Evidence-Based Thinking
Assumption involves accepting ideas without verification, while facts are verifiable data backed by empirical evidence; distinguishing between these is crucial for embracing evidence-based thinking. Prioritizing data-driven analysis over subjective assumptions enhances decision-making accuracy and fosters critical thinking. Integrating verified facts into reasoning processes reduces biases and supports reliable conclusions in complex problem-solving scenarios.
Infographic: Assumption vs Fact
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com