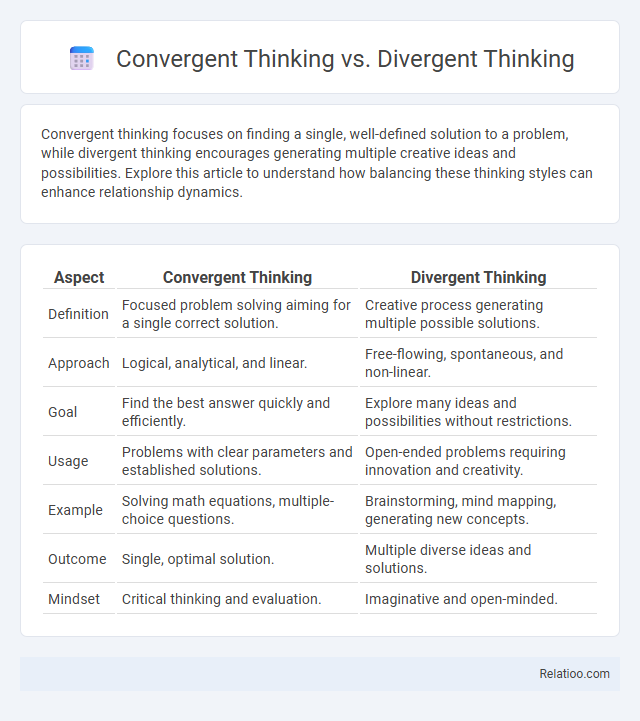
Convergent thinking focuses on finding a single, well-defined solution to a problem, while divergent thinking encourages generating multiple creative ideas and possibilities. Explore this article to understand how balancing these thinking styles can enhance relationship dynamics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Convergent Thinking | Divergent Thinking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused problem solving aiming for a single correct solution. | Creative process generating multiple possible solutions. |
| Approach | Logical, analytical, and linear. | Free-flowing, spontaneous, and non-linear. |
| Goal | Find the best answer quickly and efficiently. | Explore many ideas and possibilities without restrictions. |
| Usage | Problems with clear parameters and established solutions. | Open-ended problems requiring innovation and creativity. |
| Example | Solving math equations, multiple-choice questions. | Brainstorming, mind mapping, generating new concepts. |
| Outcome | Single, optimal solution. | Multiple diverse ideas and solutions. |
| Mindset | Critical thinking and evaluation. | Imaginative and open-minded. |
Introduction to Convergent and Divergent Thinking
Convergent thinking involves narrowing down multiple ideas to find a single, optimal solution, often used in problem-solving and decision-making scenarios. Divergent thinking encourages generating many creative ideas without immediate judgment, fostering innovation and brainstorming processes. Understanding how your mind shifts between these modes enhances creativity and efficiency, while boundlessness represents an unrestricted flow of ideas transcending conventional thinking patterns.
Defining Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking involves analyzing information logically to arrive at a single, correct solution to a problem, emphasizing structure and clarity. It contrasts with divergent thinking, which generates multiple creative ideas, and boundlessness, which transcends traditional cognitive limits. You can enhance decision-making by mastering convergent thinking to efficiently focus on practical, actionable outcomes.
Understanding Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking involves generating multiple creative solutions or ideas by exploring various possibilities without immediate judgment, essential for problem-solving and innovation. It contrasts with convergent thinking, which focuses on narrowing down options to find a single correct answer, and boundlessness, which embraces limitless, non-linear thought without constraints. Understanding divergent thinking enhances cognitive flexibility and fosters originality in decision-making processes across diverse fields such as design, education, and entrepreneurship.
Key Differences Between Convergent and Divergent Thinking
Convergent thinking involves narrowing down multiple ideas into a single, optimal solution, emphasizing logic and accuracy, while divergent thinking generates numerous creative possibilities without immediate judgment or constraints. The key differences between convergent and divergent thinking lie in their approaches to problem-solving: convergent thinking seeks clarity and correctness, utilizing structured methods, whereas divergent thinking encourages open-ended exploration and innovation. Boundlessness refers to an unrestricted thinking process that transcends both, fostering expansive creativity without limits or predefined frameworks.
Benefits of Convergent Thinking
Convergent thinking enhances decision-making by focusing on narrowing down multiple ideas into a single, effective solution, increasing efficiency in problem-solving scenarios. It promotes accuracy and speed by applying logical steps and established criteria to evaluate options, which is critical in fields like engineering and data analysis. This method also supports consistency and reliability, ensuring that conclusions are well-founded and replicable across similar challenges.
Advantages of Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking promotes creativity by encouraging the generation of numerous unique ideas, fostering innovation and flexibility in problem-solving. It allows for exploring multiple possible solutions beyond conventional constraints, which enhances adaptability and breakthrough discoveries. This cognitive approach supports open-ended exploration, leading to original insights that converge thinking might overlook.
Situations That Require Convergent Thinking
Situations that require convergent thinking often involve problem-solving where a single correct solution is necessary, such as standardized testing, math problems, or troubleshooting technical issues. Your ability to analyze information, eliminate errors, and choose the best option from available data is crucial in these contexts. Convergent thinking contrasts with divergent thinking and boundlessness, which emphasize creativity and exploring multiple possibilities rather than focusing on a definitive answer.
When to Apply Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking excels when exploring multiple solutions or generating creative ideas in brainstorming sessions, innovation processes, and problem solving with no clear path. It encourages open-ended exploration, allowing ideas to flow freely without immediate judgment or constraints. This approach proves vital in early stages of projects that benefit from originality and diverse perspectives before converging on a single solution.
Cultivating Both Thinking Styles
Cultivating both convergent thinking and divergent thinking enhances your problem-solving abilities by balancing focused analysis with creative exploration. Convergent thinking narrows down multiple possibilities to find the single best solution, while divergent thinking generates numerous ideas and alternative approaches. Embracing boundlessness encourages transcending traditional limits, allowing your mind to fluidly switch between structured logic and expansive creativity for innovative results.
Conclusion: Balancing Convergent and Divergent Approaches
Balancing convergent and divergent thinking enhances problem-solving by integrating structured analysis with creative idea generation, fostering innovative yet practical solutions. Embracing boundlessness extends this balance by encouraging open exploration beyond traditional cognitive limits, promoting breakthrough insights. Optimal decision-making requires fluidly shifting between focused convergence, expansive divergence, and unbounded creativity to address complex challenges effectively.
Infographic: Convergent Thinking vs Divergent Thinking
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com