Anger is an emotional response to perceived provocation, while aggression is a behavior intended to cause harm or assert dominance in relationships. Understanding the difference between anger and aggression is crucial for managing conflicts effectively; explore more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
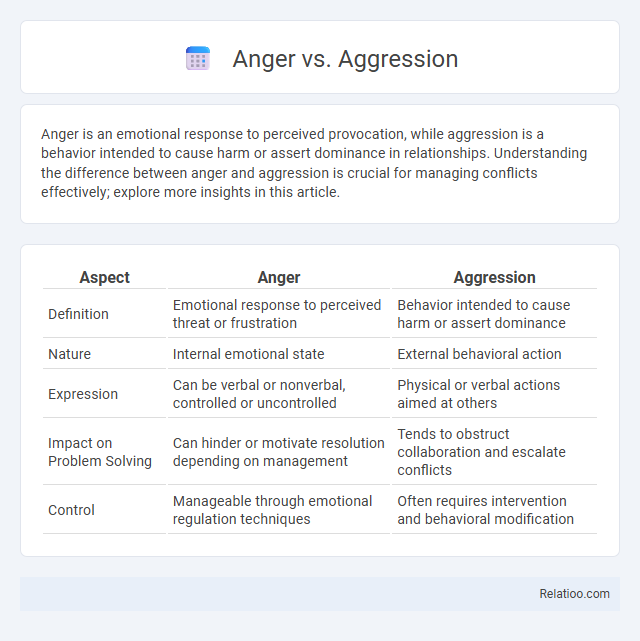
| Aspect | Anger | Aggression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response to perceived threat or frustration | Behavior intended to cause harm or assert dominance |
| Nature | Internal emotional state | External behavioral action |
| Expression | Can be verbal or nonverbal, controlled or uncontrolled | Physical or verbal actions aimed at others |
| Impact on Problem Solving | Can hinder or motivate resolution depending on management | Tends to obstruct collaboration and escalate conflicts |
| Control | Manageable through emotional regulation techniques | Often requires intervention and behavioral modification |
Defining Anger: An Emotional Response
Anger is a natural emotional response characterized by feelings of annoyance, frustration, or hostility triggered by perceived threats or injustices. Unlike aggression, which involves actions intended to cause harm or assert dominance, anger primarily exists as an internal experience that can motivate both positive and negative behaviors. Understanding your anger as an emotional response helps manage its effects without letting it escalate into harmful aggression.
Understanding Aggression: Actions and Behaviors
Aggression encompasses behaviors intended to harm or intimidate others, distinguishing it from anger, which is an emotional state characterized by feelings of displeasure or hostility. While anger can manifest internally or be expressed verbally, aggression involves observable actions such as physical violence, verbal attacks, or destructive conduct. Understanding aggression is essential for identifying harmful behaviors and implementing effective interventions to manage and reduce risks in social and psychological contexts.
Key Differences Between Anger and Aggression
Anger is an emotional response characterized by feelings of displeasure or frustration, while aggression involves behaviors intended to cause harm or assert dominance. Your anger may manifest internally without aggressive actions, but unchecked anger often escalates into aggressive expressions such as verbal outbursts or physical violence. Understanding the distinction helps in managing emotional responses more effectively and preventing harmful behaviors.
Psychological Roots of Anger
Anger originates from psychological triggers such as perceived threats, frustration, or unmet needs, activating your brain's amygdala and stress response system. While anger is an emotional state, aggression is a behavioral response that may or may not result from anger and often involves intent to harm. Understanding the psychological roots of anger helps differentiate it from aggression, enabling better emotional regulation and healthier coping strategies.
What Fuels Aggressive Behavior?
Aggressive behavior is primarily fueled by intense anger combined with environmental triggers such as stress, frustration, and perceived threats. Neurobiological factors like increased amygdala activity and hormonal imbalances, especially elevated testosterone, also play a significant role in escalating aggression. Psychological influences, including learned behavior and cognitive distortions, contribute to how anger transforms into overt aggression.
Healthy Ways to Express Anger
Healthy ways to express anger involve recognizing the difference between anger and aggression, where anger is an emotion and aggression is a behavior that can harm others. You can manage anger through techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and assertive communication to express your feelings without causing damage. Understanding these distinctions helps maintain emotional balance and improves relationships by preventing the escalation of anger into destructive aggression.
The Dangers of Uncontrolled Aggression
Uncontrolled aggression poses serious risks, including physical harm and damaged relationships, as it often escalates beyond anger's emotional expression into violent behavior. Unlike anger, which is a natural and temporary emotional response, aggression involves intentional actions aimed at causing harm or asserting dominance. Persistent uncontrolled aggression increases the likelihood of legal issues, mental health disorders, and social isolation.
Social and Cultural Perspectives on Anger vs Aggression
Social and cultural perspectives shape the expression and interpretation of anger and aggression, with many societies distinguishing anger as a natural emotional response and aggression as a potentially harmful behavior. In collectivist cultures, anger is often suppressed to maintain social harmony, whereas some individualist cultures may view direct expression of anger as a form of assertiveness. Understanding these cultural nuances is essential for managing conflicts and promoting emotional regulation within diverse social contexts.
Recognizing Signals: When Anger Turns to Aggression
Recognizing signals when anger turns to aggression is crucial for maintaining healthy relationships and personal well-being. You may notice physical signs like clenched fists, tense muscles, or increased heart rate along with verbal cues such as raised voice or hostile language, signaling that anger is escalating beyond control. Identifying these patterns early helps prevent harmful behaviors and promotes effective emotional regulation.
Managing Anger and Preventing Aggression
Effective anger management involves recognizing emotional triggers and practicing techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, and cognitive restructuring to reduce physiological arousal. Preventing aggression requires channeling anger into constructive outlets, setting clear personal boundaries, and seeking professional counseling when needed to avoid harmful behaviors. Developing emotional regulation skills promotes healthier responses, decreasing the likelihood of aggressive actions stemming from uncontrolled anger.
Infographic: Anger vs Aggression
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com