Anger arises from perceived injustice or threat, triggering intense emotional reactions, while frustration results from obstacles blocking goals, causing mild irritation. Explore this article to understand the subtle differences between anger and frustration in relationships.
Table of Comparison
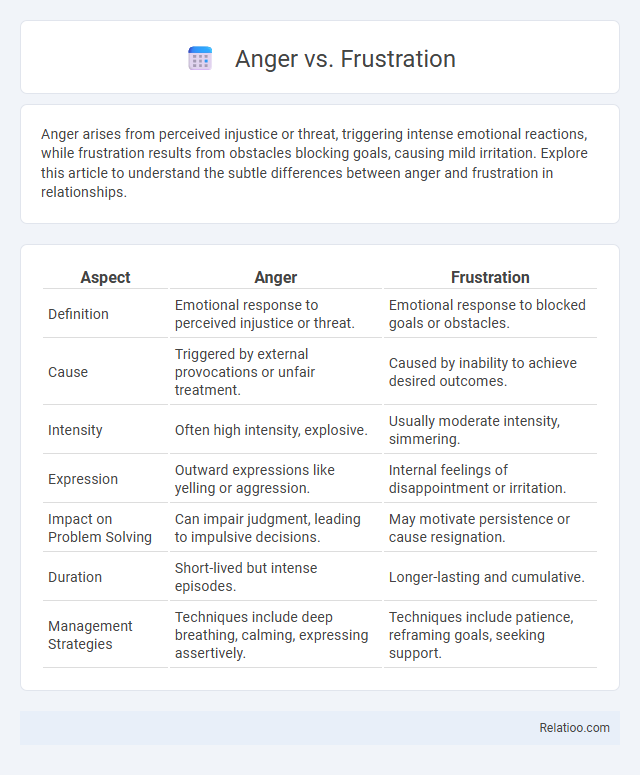
| Aspect | Anger | Frustration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response to perceived injustice or threat. | Emotional response to blocked goals or obstacles. |
| Cause | Triggered by external provocations or unfair treatment. | Caused by inability to achieve desired outcomes. |
| Intensity | Often high intensity, explosive. | Usually moderate intensity, simmering. |
| Expression | Outward expressions like yelling or aggression. | Internal feelings of disappointment or irritation. |
| Impact on Problem Solving | Can impair judgment, leading to impulsive decisions. | May motivate persistence or cause resignation. |
| Duration | Short-lived but intense episodes. | Longer-lasting and cumulative. |
| Management Strategies | Techniques include deep breathing, calming, expressing assertively. | Techniques include patience, reframing goals, seeking support. |
Understanding Anger: Definition and Causes
Anger is an intense emotional response to perceived threats, injustices, or frustrations, often triggered by situations that challenge personal boundaries or values. Unlike frustration, which arises from obstacles obstructing goals or desires, anger involves a stronger physiological arousal and a readiness to address the source of distress. Understanding the neurobiological basis of anger, including the role of the amygdala and hormonal responses like adrenaline release, provides insight into its causes and potential management strategies.
What is Frustration? Key Differences
Frustration occurs when your goals or desires are blocked, leading to feelings of disappointment and helplessness, whereas anger is an emotional response to perceived threats or injustices, often resulting in hostility or aggression. Unlike anger, frustration tends to build up gradually and stems from unmet expectations rather than direct provocations. Understanding these key differences can help you manage emotional responses more effectively.
Psychological Roots of Anger
Anger's psychological roots stem from perceived threats, unmet expectations, or feelings of injustice, triggering the brain's fight-or-flight response primarily in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Frustration arises when obstacles block goals, leading to emotional stress that can escalate into anger if unresolved. Understanding these distinct emotional processes helps in developing effective coping strategies and emotional regulation techniques.
Triggers That Lead to Frustration
Frustration arises when obstacles block your goals, such as repeated failures or unmet expectations, leading to emotional tension. Triggers often include lack of control, ambiguous situations, and continuous setbacks in personal or professional life. Understanding these specific triggers helps you manage frustration before it escalates into anger.
Emotional Symptoms: Anger vs Frustration
Emotional symptoms of anger often include intense feelings of rage, irritability, and a strong urge to confront the source of the emotion, while frustration typically manifests as feelings of disappointment, helplessness, and restlessness when goals are blocked. Your ability to recognize these distinctions can help manage emotional responses more effectively, reducing the risk of escalating conflicts. Understanding that anger is a more aggressive and outward expression and frustration is a milder, internal irritation improves emotional awareness and coping strategies.
Behavioral Responses Compared
Behavioral responses to anger often involve aggressive actions or verbal outbursts aimed at addressing perceived threats or injustices, while frustration typically triggers irritability or withdrawal when goals are blocked. Unlike anger, which can escalate quickly and lead to confrontational behaviors, frustration may result in passive resistance or internalized stress until the obstacle is removed. Understanding the nuances between your reactions to anger and frustration helps in managing emotions effectively and preventing negative interpersonal consequences.
Impact on Relationships: Anger or Frustration?
Anger often triggers intense emotional reactions that can strain or damage Your relationships by causing conflicts and misunderstandings, while frustration typically stems from unmet expectations and may lead to withdrawal or passive aggression rather than outright confrontation. Frustration can accumulate over time, subtly eroding trust and communication if not addressed, whereas anger's immediate intensity can prompt urgent discussions or impulsive decisions. Understanding these differences helps manage emotions effectively to maintain healthier, more resilient relationships.
Managing Anger Effectively
Managing anger effectively involves recognizing the distinct triggers that separate anger from frustration, as frustration often arises from unmet expectations while anger may stem from perceived threats or injustice. Your ability to identify these emotional nuances allows for targeted coping strategies such as deep breathing, cognitive restructuring, and mindfulness practices which reduce impulsive reactions. Implementing consistent anger management techniques improves emotional regulation, leading to healthier interpersonal relationships and overall mental well-being.
Coping Strategies for Frustration
Coping strategies for frustration include mindfulness techniques such as deep breathing and meditation to reduce physiological arousal and promote emotional regulation. Cognitive reframing helps reinterpret frustrating situations by shifting negative thought patterns toward problem-solving and acceptance. Engaging in physical activity or creative outlets also serves as an effective method to channel frustration constructively and prevent escalation into anger.
When to Seek Help: Recognizing Unhealthy Patterns
Persistent anger that leads to aggressive behavior or physical harm signals a need for professional help. Frustration becomes unhealthy when it results in chronic stress, withdrawal, or impacts daily functioning. Seeking therapy or counseling is crucial when these emotions interfere with relationships, work performance, or overall mental health stability.
Infographic: Anger vs Frustration
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com