Anger often stems from unmet needs and can lead to conflict, while assertiveness communicates boundaries clearly without hostility. Explore how mastering assertiveness over anger improves relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
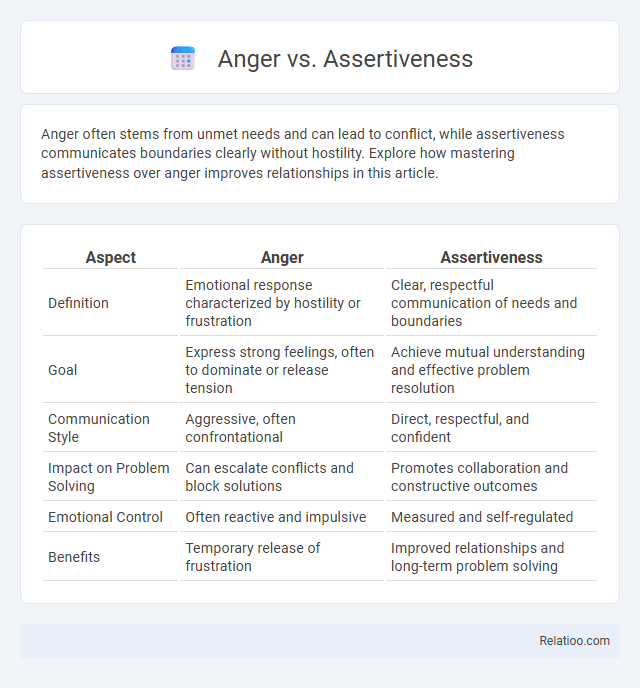
| Aspect | Anger | Assertiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional response characterized by hostility or frustration | Clear, respectful communication of needs and boundaries |
| Goal | Express strong feelings, often to dominate or release tension | Achieve mutual understanding and effective problem resolution |
| Communication Style | Aggressive, often confrontational | Direct, respectful, and confident |
| Impact on Problem Solving | Can escalate conflicts and block solutions | Promotes collaboration and constructive outcomes |
| Emotional Control | Often reactive and impulsive | Measured and self-regulated |
| Benefits | Temporary release of frustration | Improved relationships and long-term problem solving |
Understanding Anger and Assertiveness
Understanding anger involves recognizing it as a natural emotional response to perceived threats or injustices, often signaling underlying needs or boundaries. Assertiveness empowers you to express your thoughts and feelings confidently and respectfully without aggression, facilitating effective communication and conflict resolution. Differentiating between anger and assertiveness helps maintain emotional balance and promotes healthier interpersonal relationships.
The Psychology Behind Anger
Understanding the psychology behind anger reveals it as a natural emotional response to perceived threats or frustration, often triggering a fight-or-flight reaction. Assertiveness, by contrast, involves consciously expressing your feelings and needs calmly and respectfully without aggression. Developing assertiveness helps you manage anger constructively, preventing destructive outbursts and fostering healthier communication.
Defining Assertiveness: Key Traits
Assertiveness is characterized by clear communication, confidence, and respect for both your own rights and the rights of others, distinguishing it from anger, which often involves hostility and loss of control. Key traits of assertiveness include expressing needs and opinions calmly, maintaining eye contact, and using "I" statements to convey feelings without blame. Mastering these traits empowers you to handle conflicts effectively while preserving relationships and self-respect.
Comparing Anger and Assertiveness
Anger is an emotional response characterized by feelings of frustration or hostility, often leading to reactive or aggressive behavior, while assertiveness involves confidently expressing one's needs and boundaries without infringing on others' rights. Unlike anger, assertiveness promotes healthy communication and problem-solving by maintaining respect and clarity in interactions. Understanding the distinction between anger and assertiveness is crucial for emotional regulation and fostering constructive relationships.
Common Triggers for Anger
Common triggers for anger include perceived injustice, frustration over unmet expectations, and feeling disrespected or ignored. Assertiveness allows you to express your feelings calmly and clearly without resorting to aggression or passive behavior. Understanding these triggers helps you manage your responses effectively, maintaining control while standing up for your rights.
Benefits of Assertive Communication
Assertive communication promotes clear and respectful expression of Your needs and feelings, reducing misunderstandings and conflict. Unlike anger, which often escalates tension, assertiveness builds positive relationships by fostering mutual respect and collaboration. Embracing assertive communication enhances emotional intelligence and empowers effective problem-solving in both personal and professional settings.
Emotional Regulation: From Anger to Assertiveness
Emotional regulation involves transforming intense feelings of anger into constructive assertiveness, allowing you to express your needs clearly without aggression. While anger can trigger impulsive reactions that harm relationships, assertiveness promotes healthy communication by respecting both your emotions and others' boundaries. Mastering this skill improves conflict resolution and supports emotional balance in challenging situations.
Practical Strategies to Transform Anger into Assertiveness
Transforming anger into assertiveness involves recognizing emotional triggers and practicing calm communication techniques such as using "I" statements to express feelings without blame. Effective strategies include deep breathing exercises, mindfulness, and setting clear personal boundaries to channel frustration into constructive dialogue. Developing assertiveness fosters healthier relationships and reduces the negative impact of uncontrolled anger by promoting respectful and solution-focused interactions.
The Impact of Anger and Assertiveness in Relationships
Anger often triggers conflict and communication breakdowns, damaging trust and emotional connections in relationships. Assertiveness promotes clear, respectful expression of needs and boundaries, fostering mutual understanding and cooperation. Balancing assertiveness while managing anger can improve relationship dynamics and emotional well-being.
Cultivating Assertiveness for Personal Growth
Cultivating assertiveness fosters personal growth by enabling clear, respectful communication that balances self-expression with empathy, unlike anger which often provokes conflict and hinders relationships. Assertiveness promotes emotional intelligence and self-confidence, critical skills for navigating social interactions and professional environments effectively. Developing assertive behavior enhances conflict resolution and reduces stress, supporting overall mental health and well-being.
Infographic: Anger vs Assertiveness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com