A hypothesis is a testable, evidence-based assumption proposed for scientific validation, while a supposition is a preliminary idea accepted without immediate proof. Explore the distinctions and applications of hypothesis versus supposition in this article.
Table of Comparison
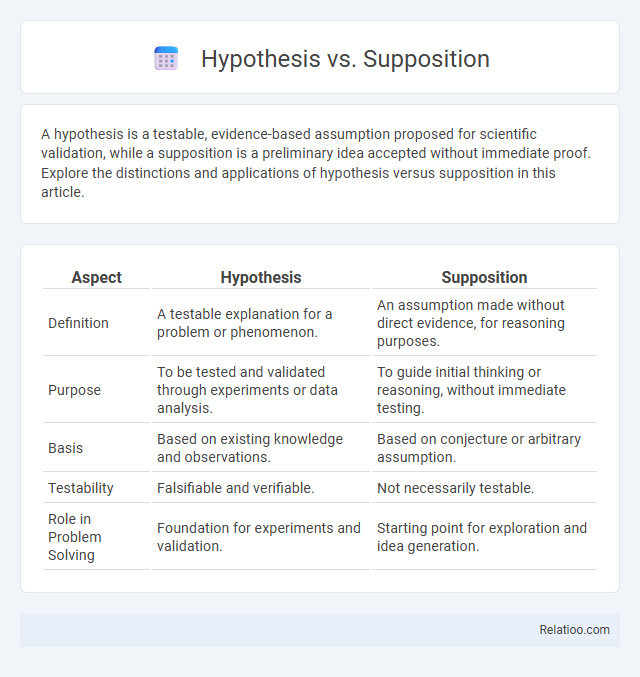
| Aspect | Hypothesis | Supposition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A testable explanation for a problem or phenomenon. | An assumption made without direct evidence, for reasoning purposes. |
| Purpose | To be tested and validated through experiments or data analysis. | To guide initial thinking or reasoning, without immediate testing. |
| Basis | Based on existing knowledge and observations. | Based on conjecture or arbitrary assumption. |
| Testability | Falsifiable and verifiable. | Not necessarily testable. |
| Role in Problem Solving | Foundation for experiments and validation. | Starting point for exploration and idea generation. |
Understanding Hypothesis and Supposition
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction based on limited evidence, used to guide scientific research and experimentation. Supposition involves assuming something to be true without firm evidence, often serving as a starting point for reasoning or argument. Understanding the difference is crucial: hypotheses require empirical testing, whereas suppositions function as preliminary assumptions to explore ideas.
Defining Hypothesis: Key Characteristics
A hypothesis is a testable statement or prediction about the relationship between variables, formulated based on prior knowledge or observations. Key characteristics of a hypothesis include falsifiability, specificity, and the ability to be empirically tested through experiments or data analysis. Unlike a supposition, which is a general assumption without immediate proof, a hypothesis requires clear criteria and measurable outcomes to validate or refute it.
What Is a Supposition?
A supposition is an assumption or belief accepted without proof as a basis for reasoning or argument. It serves as a foundational idea in logic and philosophy, often preceding the formulation of hypotheses or conclusions. Unlike hypotheses, which are testable predictions, suppositions may remain speculative and are used to explore possibilities conceptually.
Core Differences Between Hypothesis and Supposition
A hypothesis is a testable and falsifiable statement based on evidence, aimed at explaining a phenomenon through scientific methods. Supposition involves assuming something to be true without firm evidence, often used as a starting point for reasoning or argument. The core difference lies in hypothesis requiring empirical validation, whereas supposition remains a tentative assumption without the necessity of testing.
Importance in Scientific Research
A hypothesis serves as a testable prediction essential for guiding scientific experiments, while a supposition is an assumption made without immediate proof, often used as a starting point for reasoning. In scientific research, the distinction between hypothesis and supposition lies in the hypothesis's requirement for empirical validation, making it critical for advancing knowledge and ensuring reliability. Understanding these terms enhances your ability to design robust studies and interpret data accurately.
Use Cases: When to Use Hypothesis vs Supposition
A hypothesis is used primarily in scientific research to propose a testable explanation based on empirical evidence and is essential for experimental design and data analysis. Supposition refers to an assumption made without firm evidence, often used in everyday reasoning, theoretical discussions, or when exploring possibilities without immediate validation. Use a hypothesis when formulating predictions for systematic investigation, and opt for supposition when considering hypothetical scenarios or ideas that require further proof.
Real-World Examples
A hypothesis is a testable statement based on observations, such as scientists proposing that increased carbon emissions cause global warming, which is then explored through experiments and data analysis. A supposition is an assumption made without firm evidence, like assuming that a new product will succeed in the market simply because it is innovative. Your understanding improves by recognizing that while hypotheses are grounded in empirical evidence aimed at validation, suppositions serve as starting points or guesses that require further inquiry.
Common Misconceptions
Hypothesis is often confused with supposition, but a hypothesis is a testable statement based on evidence, whereas a supposition is an assumption without direct proof. Common misconceptions arise when people treat suppositions as hypotheses, expecting empirical validation where none is intended. Clarifying these distinctions enhances scientific rigor and prevents misinterpretation in research contexts.
Advantages and Limitations
A hypothesis provides a testable prediction based on empirical evidence, enabling scientific inquiry and experimentation, but its limitation lies in potential bias and the need for falsifiability. A supposition acts as an assumed premise to explore possibilities without requiring immediate proof, offering flexibility in reasoning yet risking inaccuracies if taken as fact. Suppositions facilitate creative thinking and theoretical exploration but lack the rigorous validation inherent in hypotheses, making them less reliable for drawing definitive conclusions.
Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing the right approach between hypothesis, supposition, and assumption depends on the context and purpose of your inquiry. A hypothesis is a testable statement grounded in prior knowledge, making it essential for scientific research and experiments. Suppositions and assumptions serve as preliminary ideas or accepted truths without immediate proof, often used in theoretical discussions or problem-solving to guide reasoning and decision-making.
Infographic: Hypothesis vs Supposition
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com