Cash gifts offer flexibility and immediate use, while in-kind gifts provide specific items tailored to recipient needs. Discover the advantages and limitations of each gift type in this article.
Table of Comparison
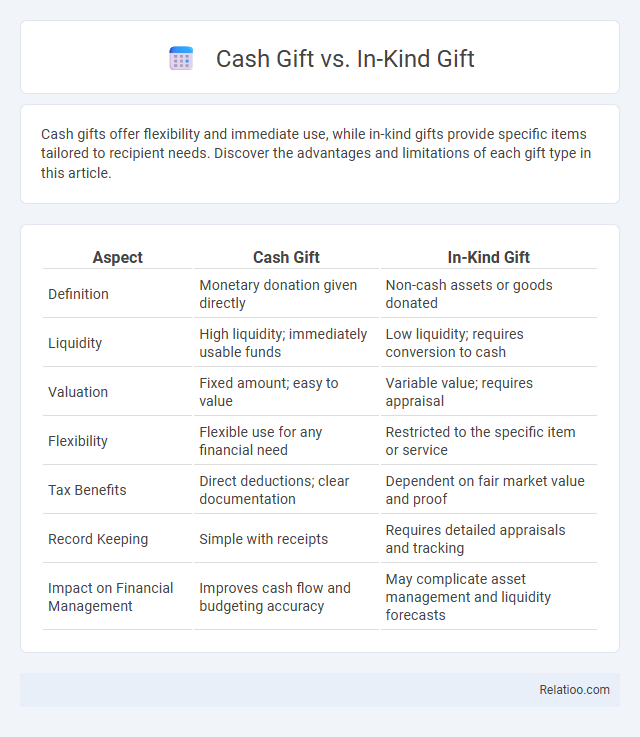
| Aspect | Cash Gift | In-Kind Gift |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary donation given directly | Non-cash assets or goods donated |
| Liquidity | High liquidity; immediately usable funds | Low liquidity; requires conversion to cash |
| Valuation | Fixed amount; easy to value | Variable value; requires appraisal |
| Flexibility | Flexible use for any financial need | Restricted to the specific item or service |
| Tax Benefits | Direct deductions; clear documentation | Dependent on fair market value and proof |
| Record Keeping | Simple with receipts | Requires detailed appraisals and tracking |
| Impact on Financial Management | Improves cash flow and budgeting accuracy | May complicate asset management and liquidity forecasts |
Understanding Cash Gifts: Definition and Examples
Cash gifts refer to monetary transfers given directly to recipients without physical items, often used for birthdays, weddings, or charitable donations. Examples include giving a set amount of money in an envelope, electronic transfers via services like PayPal or Venmo, and cash gifts during holidays or special occasions. Understanding cash gifts helps you decide when it's more appropriate to provide flexible funds rather than specific products or services.
Exploring In-Kind Gifts: What They Entail
In-kind gifts involve donating tangible items or services instead of cash, offering a direct way to support causes with physical resources like clothing, food, or professional expertise. You can benefit organizations by providing specific goods that meet their immediate needs, often ensuring your contribution has a targeted impact. Compared to cash gifts, in-kind donations require careful valuation and coordination to maximize their usefulness and tax advantages.
Key Differences Between Cash and In-Kind Gifts
Cash gifts provide recipients with the flexibility to use funds as needed, while in-kind gifts involve donating specific goods or services, limiting recipient choice. Tax implications also differ, as cash gifts are straightforward to value and report, whereas in-kind gifts require appraisal to determine fair market value. Organizations often prefer cash gifts for ease of use and efficient resource allocation, whereas in-kind gifts may fulfill immediate material needs.
Pros and Cons of Cash Gifts
Cash gifts offer instant liquidity and the freedom to use the funds as needed, making them highly versatile for recipients. However, they lack the personal touch and thoughtfulness often conveyed through in-kind gifts or physical items. Cash gifts may also pose tax implications for both giver and recipient, requiring careful consideration of gift value thresholds and applicable regulations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of In-Kind Gifts
In-kind gifts offer the advantage of providing specific goods or services tailored to the recipient's immediate needs, which can be more impactful than cash gifts in certain situations. However, they may pose disadvantages such as storage challenges, limited flexibility for the recipient, and potential mismatch with actual needs, reducing overall usefulness. Understanding the distinction between cash gifts, which offer freedom to choose, and in-kind gifts, which target specific support, helps you make informed giving decisions based on convenience and impact.
Tax Implications: Cash Gift vs In-Kind Gift
Cash gifts are straightforward for tax purposes and may require filing a gift tax return if the amount exceeds the annual exclusion limit set by the IRS, which is $17,000 per recipient in 2024. In-kind gifts, such as property or stocks, involve calculating the fair market value at the time of transfer, potentially complicating tax reporting and affecting your taxable income or capital gains tax basis. Understanding these differences ensures Your gifting strategy minimizes tax liabilities and complies with federal gift tax regulations.
Recipient Preferences: What Do People Value More?
Recipients often value cash gifts for their flexibility, allowing them to choose purchases that best suit their needs and preferences. In-kind gifts can be appreciated when thoughtfully selected to match the recipient's tastes or requirements, offering a personal touch and immediate utility. However, overall satisfaction tends to be higher with cash gifts due to the freedom and practicality they provide, which aligns with contemporary consumer trends emphasizing convenience and personalized choice.
Situational Suitability: When to Choose Each Gift Type
Cash gifts offer maximum flexibility and suit occasions where the recipient's preferences or needs are unknown, such as weddings or graduations. In-kind gifts are ideal for personalized occasions, like birthdays or holidays, where you can tailor the present to the recipient's specific tastes or hobbies. Your choice between cash, in-kind, or general gifting should consider the event, your relationship with the recipient, and the level of personalization desired.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Gifting
Legal and ethical considerations in gifting vary significantly between cash gifts, in-kind gifts, and general gifting practices. Cash gifts must comply with tax reporting requirements and anti-money laundering laws, while in-kind gifts necessitate accurate valuation and adherence to regulatory standards to prevent fraud or misappropriation. Ethical gifting demands transparency, avoiding conflicts of interest, and ensuring gifts do not influence professional decisions or breach organizational policies.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider
Choosing between cash gifts, in-kind gifts, and general gifting requires assessing the recipient's needs, the occasion, and tax implications. Cash gifts offer flexibility and convenience, allowing recipients to allocate funds as needed, while in-kind gifts provide personalized value through tangible items that hold sentimental or practical significance. Evaluating factors such as liquidity, personal preferences, tax benefits, and the context of the gift ensures the most appropriate and meaningful choice.
Infographic: Cash Gift vs In-Kind Gift
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com