Budgeting allocates your income to cover expenses and plan financial priorities, while saving sets aside a portion of income for future needs or emergencies. Discover effective strategies to balance budgeting and saving in this article.
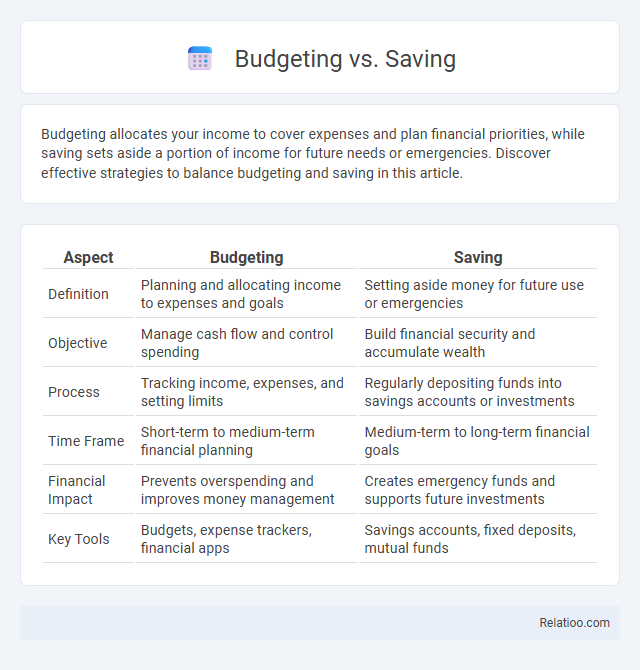
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Budgeting | Saving |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planning and allocating income to expenses and goals | Setting aside money for future use or emergencies |
| Objective | Manage cash flow and control spending | Build financial security and accumulate wealth |
| Process | Tracking income, expenses, and setting limits | Regularly depositing funds into savings accounts or investments |
| Time Frame | Short-term to medium-term financial planning | Medium-term to long-term financial goals |
| Financial Impact | Prevents overspending and improves money management | Creates emergency funds and supports future investments |
| Key Tools | Budgets, expense trackers, financial apps | Savings accounts, fixed deposits, mutual funds |
Understanding the Difference: Budgeting vs Saving
Budgeting involves creating a detailed plan to allocate income towards expenses, savings, and debt repayment, ensuring financial discipline and control. Saving refers to setting aside a portion of income for future needs or emergencies, emphasizing accumulation rather than allocation. Understanding the difference between budgeting and saving is crucial for effective money management, as budgeting guides the distribution of funds while saving focuses on preserving a specific amount of money over time.
Why Budgeting Matters for Financial Health
Budgeting matters for financial health because it creates a clear plan for income and expenses, preventing overspending and reducing debt. Effective budgeting enables better allocation of resources, ensuring that savings goals are met and emergencies are covered. Consistent budgeting improves financial discipline, leading to long-term wealth accumulation and financial stability.
The Core Principles of Effective Saving
Effective saving hinges on controlling expenses, setting clear financial goals, and prioritizing regular contributions to savings. Budgeting establishes a framework to allocate income wisely, while money management integrates saving as a disciplined habit to build financial security. Emphasizing the core principles of saving enhances long-term wealth accumulation and ensures preparedness for unexpected expenses.
How Budgeting Supports Your Saving Goals
Budgeting creates a clear financial roadmap by allocating specific amounts for expenses, helping you control spending and prioritize saving goals effectively. By tracking your income and expenses, budgeting identifies areas to reduce costs and redirect funds toward savings, accelerating wealth accumulation. Sound budgeting transforms abstract saving goals into actionable plans, ensuring your money management aligns with long-term financial stability.
Common Budgeting Methods and Their Pros & Cons
Common budgeting methods include the zero-based budget, envelope system, and 50/30/20 rule, each offering unique advantages and drawbacks. The zero-based budget allocates every dollar to specific expenses, promoting thorough control but requiring detailed tracking that may be time-consuming. The envelope system uses cash envelopes for categories, enhancing spending discipline but limiting flexibility, while the 50/30/20 rule simplifies budgeting by dividing income into needs, wants, and savings, though it may not address individual financial complexities.
Practical Saving Strategies for Every Income
Effective money management involves balancing budgeting, saving, and strategic spending to build financial security. Practical saving strategies for every income include automating transfers to a separate savings account, prioritizing emergency funds, and cutting discretionary expenses without sacrificing essentials. By tailoring these approaches to Your financial situation, You can steadily grow Your savings regardless of income level.
Budgeting Mistakes That Hinder Saving
Common budgeting mistakes that hinder saving include underestimating expenses, failing to track spending accurately, and neglecting to set realistic savings goals. Without a clear budget, your money management becomes inefficient, leading to missed opportunities to build a financial cushion. Prioritizing accurate budgeting habits ensures you can save consistently and meet your financial objectives.
Integrating Budgeting and Saving for Maximum Impact
Integrating budgeting and saving creates a powerful strategy for optimizing your financial health by allocating specific portions of income towards essential expenses and targeted savings goals. Effective money management involves tracking spending patterns within your budget to identify opportunities for increasing your savings without sacrificing necessary expenditures. By aligning budgeting with proactive saving habits, you ensure consistent growth of your financial reserves and enhanced control over your economic stability.
Tools and Apps for Tracking Budgets and Savings
Effective money management relies heavily on the use of budgeting and saving tools designed to track your spending habits and progress towards financial goals. Apps like Mint, YNAB (You Need A Budget), and PocketGuard provide real-time insights, customizable budget categories, and automated savings plans to help you control expenses and grow your savings efficiently. By leveraging these digital tools, you gain clear visibility over your finances, making it easier to stick to budgets while optimizing your savings strategies.
Setting Financial Goals: Budget or Save First?
Setting financial goals requires a clear understanding of whether to budget or save first, as budgeting helps you allocate income efficiently while saving builds a financial safety net. Your priorities should align with immediate needs and long-term aspirations, using budgeting to control expenses and saving to accumulate funds for specific goals. Effective money management integrates both by creating a balanced plan that ensures you spend wisely and consistently grow your savings.
Infographic: Budgeting vs Saving
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com