Preoccupation in relationships involves persistent but manageable focus on a partner, while obsession features intrusive, overwhelming thoughts that disrupt daily life. Discover deeper insights on distinguishing healthy concern from harmful fixation in this article.
Table of Comparison
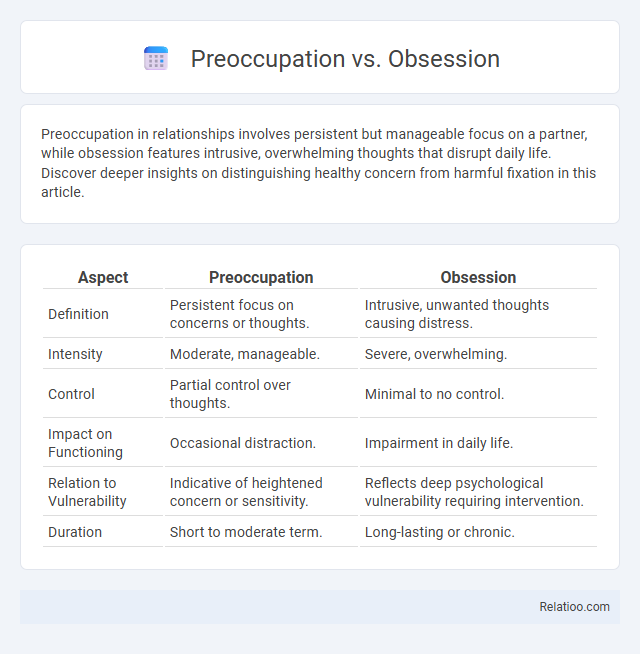
| Aspect | Preoccupation | Obsession |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Persistent focus on concerns or thoughts. | Intrusive, unwanted thoughts causing distress. |
| Intensity | Moderate, manageable. | Severe, overwhelming. |
| Control | Partial control over thoughts. | Minimal to no control. |
| Impact on Functioning | Occasional distraction. | Impairment in daily life. |
| Relation to Vulnerability | Indicative of heightened concern or sensitivity. | Reflects deep psychological vulnerability requiring intervention. |
| Duration | Short to moderate term. | Long-lasting or chronic. |
Understanding Preoccupation: Definition and Characteristics
Preoccupation involves persistent attention on a particular thought or concern that subtly influences your daily activities without dominating your entire mindset. Unlike obsession, which is intrusive and uncontrollable, preoccupation is a milder cognitive engagement characterized by repetitive but manageable focus. Understanding these nuances helps identify when thoughts shift from healthy concern to problematic fixation affecting mental well-being.
What is Obsession? Key Features Explained
Obsession is a persistent and intrusive thought or urge that dominates your mind, often causing significant distress or anxiety. Key features include repetitive nature, uncontrollability, and interference with daily functioning or well-being. Unlike preoccupation, which involves focused attention on a topic, obsession presents as an unwanted, distressing fixation that you cannot easily dismiss.
Psychological Roots: How Preoccupation Differs from Obsession
Preoccupation involves a cognitive focus on particular thoughts or concerns that can be adaptive or related to problem-solving, while obsession manifests as intrusive, persistent, and distressing thoughts often linked to anxiety disorders. You may experience preoccupation as a temporary mental engagement with issues important to you, whereas obsession typically involves compulsive behaviors driven by uncontrollable and repetitive thought patterns. Psychological roots of preoccupation stem from normal attentional processes, but obsessions arise from maladaptive cognitive mechanisms tied to OCD and other mental health conditions.
Common Triggers for Preoccupation and Obsession
Common triggers for preoccupation include stress, anxiety, unresolved problems, and significant life changes that occupy your mind without necessarily causing distress. Obsession, however, is often triggered by intense fears, intrusive thoughts, or compulsive behaviors linked to mental health disorders like OCD. Both preoccupation and obsession affect mental focus but differ in intensity and impact on daily functioning.
Behavioral Manifestations: Identifying the Signs
Preoccupation, obsession, and fixation each present distinct behavioral manifestations that can help you identify their signs. Preoccupation often appears as persistent but manageable thoughts affecting your concentration, while obsession manifests as intrusive, uncontrollable thoughts causing significant distress and repetitive behaviors. Fixation involves an intense focus on a single idea or object, leading to rigid routines or avoidance of distractions.
Emotional Impact: Preoccupation vs Obsession
Preoccupation involves mild emotional engagement where thoughts about a subject arise frequently but do not disrupt daily functioning, causing minimal stress. Obsession generates intense emotional distress, often characterized by intrusive, repetitive thoughts that interfere with concentration and trigger anxiety or fear. The emotional impact of obsession is significantly stronger than preoccupation, leading to potential impairment in mental health and requiring focused intervention.
Cognitive Patterns Behind Preoccupation and Obsession
Preoccupation involves persistent, but manageable focus on thoughts or concerns that engage cognitive resources without overwhelming function, whereas obsession is characterized by intrusive, uncontrollable thoughts that dominate mental processes and lead to distress. Cognitive patterns behind preoccupation rely on attentional biases toward specific stimuli, allowing purposeful engagement, while obsession triggers maladaptive cognitive loops fueled by heightened anxiety and impaired cognitive inhibition. Neural correlates highlight differential activation in the prefrontal cortex and anterior cingulate cortex, underpinning the regulatory challenges distinguishing obsessive from normative preoccupational thinking.
Effects on Daily Functioning and Quality of Life
Preoccupation involves frequent thoughts that can mildly distract, whereas obsession generates intense, intrusive thoughts disrupting daily routines and causing significant distress. Your ability to complete tasks and engage socially diminishes as obsession intensifies, often leading to decreased productivity and strained relationships. Addressing these cognitive patterns promptly enhances quality of life by restoring focus and emotional balance.
Coping Strategies for Managing Preoccupation and Obsession
Coping strategies for managing preoccupation and obsession include mindfulness techniques that promote present-moment awareness and reduce intrusive thoughts. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) effectively restructures negative thought patterns associated with obsessions, fostering healthier mental habits. Establishing regular routines, practicing relaxation exercises, and seeking professional support are crucial for maintaining emotional balance and preventing escalation of obsessive thinking.
When to Seek Help: Recognizing the Need for Professional Support
When repetitive thoughts interfere with Your daily functioning or emotional well-being, it may indicate an obsession rather than a simple preoccupation. Seeking professional support becomes crucial if these persistent thoughts cause distress, anxiety, or disrupt your ability to focus on tasks or relationships. Early intervention from a mental health professional can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent escalation into more severe conditions.
Infographic: Preoccupation vs Obsession
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com