Outsourcing involves delegating business processes to an external provider to gain cost efficiency and expertise, while transference shifts risk to a third party, typically through contracts or insurance. Explore the detailed differences and strategic impacts of outsourcing versus transference in this article.
Table of Comparison
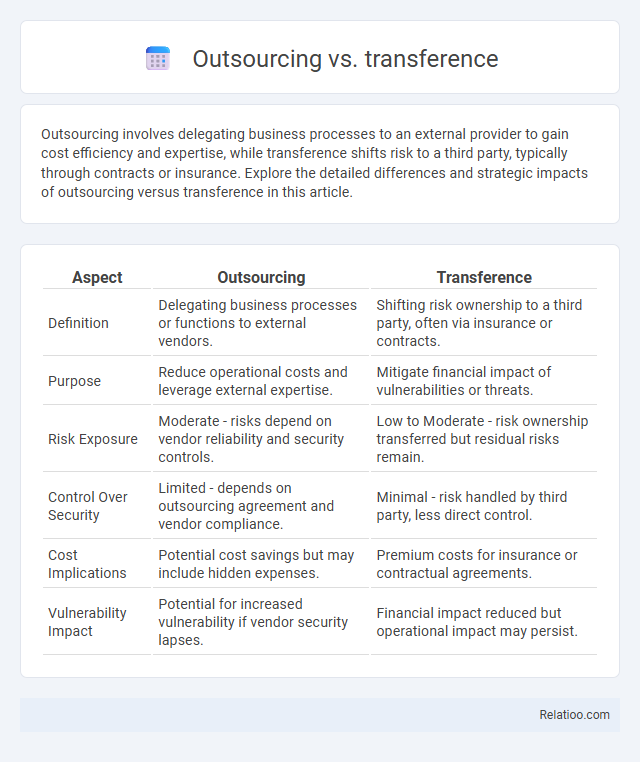
| Aspect | Outsourcing | Transference |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delegating business processes or functions to external vendors. | Shifting risk ownership to a third party, often via insurance or contracts. |
| Purpose | Reduce operational costs and leverage external expertise. | Mitigate financial impact of vulnerabilities or threats. |
| Risk Exposure | Moderate - risks depend on vendor reliability and security controls. | Low to Moderate - risk ownership transferred but residual risks remain. |
| Control Over Security | Limited - depends on outsourcing agreement and vendor compliance. | Minimal - risk handled by third party, less direct control. |
| Cost Implications | Potential cost savings but may include hidden expenses. | Premium costs for insurance or contractual agreements. |
| Vulnerability Impact | Potential for increased vulnerability if vendor security lapses. | Financial impact reduced but operational impact may persist. |
Introduction to Outsourcing and Transference
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to external vendors to reduce costs and improve efficiency, while transference is the shifting of risk or responsibility from one party to another, often used in risk management and insurance contexts. You can leverage outsourcing to optimize operational performance by accessing specialized expertise outside your organization. Understanding the differences between outsourcing and transference is crucial for strategic decision-making in managing resources and risk exposure.
Defining Outsourcing: Key Features
Outsourcing involves delegating specific business processes or services to external providers, enabling companies to focus on core activities while leveraging specialized expertise and cost efficiencies. Key features of outsourcing include contractual agreements, performance metrics, and the transfer of operational tasks rather than ownership or risk. Your business can benefit from outsourcing by improving scalability, reducing overhead, and accessing advanced technologies without the burden of direct management.
Understanding Transference: Core Concepts
Transference involves projecting feelings and attitudes from past relationships onto new interactions, often seen in therapeutic contexts where clients transfer emotions onto therapists. This psychological concept differs from outsourcing, which delegates tasks externally, and from legal transference, involving the formal transfer of rights or property. Understanding transference helps you navigate emotional dynamics and improve interpersonal awareness.
Major Differences Between Outsourcing and Transference
Outsourcing involves contracting external organizations to handle specific business functions, transferring both the responsibility and operational control, while transference refers to shifting risk or liability to another party without delegating day-to-day management. The major difference lies in outsourcing encompassing operational execution by third parties, whereas transference typically involves risk-sharing mechanisms like insurance or contractual agreements without handing over operational duties. Your decision should consider how much control and responsibility you want to retain versus delegate when choosing between outsourcing and transference.
Advantages of Outsourcing
Outsourcing offers significant advantages such as cost reduction, access to specialized expertise, and enhanced operational efficiency. By delegating non-core tasks to external providers, your business can focus on strategic initiatives and improve overall productivity. This approach also provides scalability and flexibility, adapting quickly to market changes without the burden of additional internal resources.
Benefits of Transference
Transference in risk management allows Your organization to shift potential financial losses to a third party, enhancing stability and cash flow predictability. Unlike outsourcing, which delegates operational tasks, transference specifically handles the assumption of risk, often through insurance or contractual agreements. This strategic approach reduces exposure to uncertainties, enabling better resource allocation and focused business growth.
Common Use Cases for Outsourcing
Outsourcing often involves delegating specific business functions like IT support, customer service, or payroll management to specialized third-party providers to reduce costs and improve efficiency. Transference, in contrast, typically refers to risk management practices where potential liabilities or risks are transferred to insurers or other entities. Common use cases for outsourcing include leveraging external expertise for software development, enhancing scalability in call centers, and optimizing supply chain logistics while maintaining core business focus.
Typical Applications of Transference
Typical applications of transference in psychology involve exploring the emotional responses a patient projects onto their therapist, which mirrors past relationships and unresolved conflicts. You experience transference most prominently in psychoanalysis and psychodynamic therapy, where it helps uncover unconscious patterns affecting your current behavior. Outsourcing and transference differ as outsourcing pertains to delegating business processes, while transference specifically refers to psychological phenomena within therapeutic settings.
Decision Factors: When to Choose Outsourcing or Transference
Choosing between outsourcing and transference depends on risk tolerance, cost implications, and control requirements. Outsourcing is ideal for non-core activities requiring specialized expertise and cost efficiency, while transference suits risks better handled through insurance or contractual risk shifts. Decision factors include evaluating organizational capabilities, the nature of risk, budget constraints, and regulatory compliance to determine the optimal strategy.
Future Trends in Outsourcing and Transference
Future trends in outsourcing indicate a significant shift towards automation and artificial intelligence integration, driving cost efficiency and innovation across industries. Transference strategies are evolving with increased emphasis on risk management and compliance, especially in global supply chains impacted by geopolitical uncertainties. Organizations are increasingly blending outsourcing and transference methods to optimize operational flexibility and enhance strategic resilience in rapidly changing markets.
Infographic: Outsourcing vs transference
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com