The shame spiral traps individuals in self-criticism and feelings of worthlessness, while the anxiety spiral intensifies worry and fear about potential future problems. Discover more about managing these emotional cycles in this article.
Table of Comparison
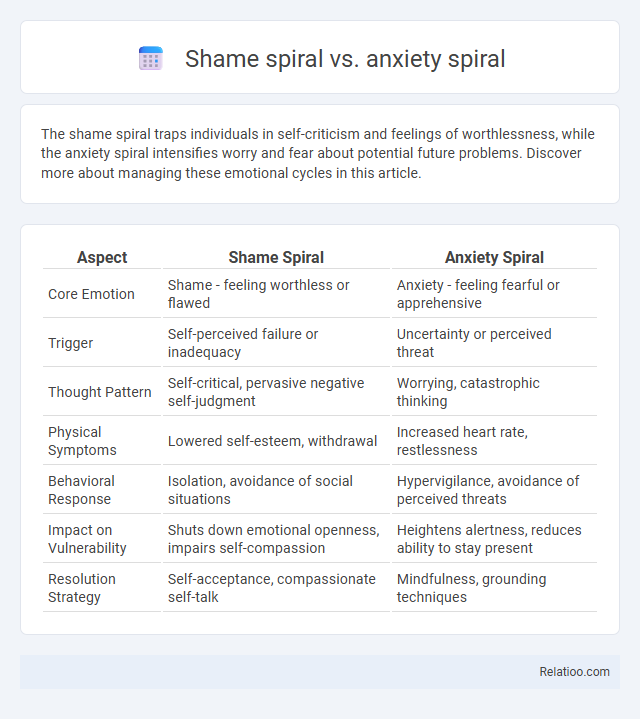
| Aspect | Shame Spiral | Anxiety Spiral |
|---|---|---|
| Core Emotion | Shame - feeling worthless or flawed | Anxiety - feeling fearful or apprehensive |
| Trigger | Self-perceived failure or inadequacy | Uncertainty or perceived threat |
| Thought Pattern | Self-critical, pervasive negative self-judgment | Worrying, catastrophic thinking |
| Physical Symptoms | Lowered self-esteem, withdrawal | Increased heart rate, restlessness |
| Behavioral Response | Isolation, avoidance of social situations | Hypervigilance, avoidance of perceived threats |
| Impact on Vulnerability | Shuts down emotional openness, impairs self-compassion | Heightens alertness, reduces ability to stay present |
| Resolution Strategy | Self-acceptance, compassionate self-talk | Mindfulness, grounding techniques |
Understanding Shame Spirals: Definition and Causes
Shame spirals are intense cycles of self-criticism and emotional pain triggered by feelings of unworthiness or failure, often rooted in past trauma or negative self-beliefs. Anxiety spirals involve escalating worry and fear-driven thoughts that amplify perceived threats, frequently linked to stress or uncertainty about future events. Understanding shame spirals requires recognizing how they uniquely intensify internalized negativity through rumination on personal flaws, distinct from the external threat focus of anxiety spirals.
What Is an Anxiety Spiral? Key Features Explained
An anxiety spiral is a cognitive pattern where your thoughts rapidly escalate from a minor concern to overwhelming fear, often fueled by catastrophic predictions and persistent worry. Key features include excessive rumination, heightened physical symptoms like increased heart rate, and difficulty breaking free from the cycle without intervention. Understanding these traits helps differentiate an anxiety spiral from a shame spiral, which centers on self-criticism and feelings of worthlessness rather than fear.
Emotional Triggers: Shame Versus Anxiety
Shame spirals and anxiety spirals both involve intense emotional triggers, but they stem from different core feelings; shame spirals arise from self-judgment and perceived personal failure, while anxiety spirals center on fear and uncertainty about potential threats. Your emotional experience in a shame spiral often involves feeling exposed and unworthy, intensifying self-critical thoughts, whereas anxiety spirals cause heightened vigilance and worry about future dangers or outcomes. Understanding these distinctions can help you identify and manage the specific triggers underlying your emotional responses effectively.
Cognitive Patterns: Comparing Thought Loops
Shame spirals involve repetitive self-criticism and internalized negative beliefs about one's worth, while anxiety spirals center on excessive worry and anticipation of potential threats or failures. Both cognitive patterns create intrusive thought loops that amplify distress, but shame spirals generate feelings of inadequacy, whereas anxiety spirals produce heightened arousal and fear-based vigilance. Understanding these distinct thought loops is crucial for targeted cognitive behavioral interventions.
Physical Symptoms in Shame and Anxiety Spirals
Shame spirals often trigger physical symptoms such as a sinking feeling in the chest, tense muscles, and a flushed face, reflecting the body's response to self-judgment and social pain. Anxiety spirals commonly manifest through symptoms like accelerated heartbeat, shortness of breath, sweating, and gastrointestinal distress, indicating the body's heightened state of alert to perceived threats. Understanding these distinct physical responses can help you better recognize and manage the emotional patterns underlying shame and anxiety spirals.
Impact on Daily Functioning and Relationships
Shame spirals deeply erode self-esteem and create intense feelings of worthlessness, severely disrupting daily functioning by fostering avoidance behaviors and social withdrawal. Anxiety spirals elevate stress levels and trigger heightened physiological responses, impairing concentration and decision-making, which consequently strain both work performance and interpersonal relationships. Unlike shame spirals that center on self-judgment, anxiety spirals revolve around fear and future uncertainties, yet both significantly compromise emotional resilience and social connectivity.
Coping Mechanisms for Shame Spirals
Shame spirals often trap Your mind in self-critical thoughts, distinct from anxiety spirals, which center on fear and worry, and guilt spirals that focus on regret over actions. Effective coping mechanisms for shame spirals include practicing self-compassion, challenging negative self-talk, and engaging in grounding techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness exercises. Building resilience through supportive social connections and professional therapy can also help You break free from the destructive cycle of shame.
Strategies to Break Free from Anxiety Spirals
Anxiety spirals trap your mind in escalating worry cycles, often linked to shame spirals where negative self-judgment intensifies distress. Strategies to break free from anxiety spirals include mindfulness techniques to anchor your thoughts in the present moment, cognitive-behavioral approaches to challenge and reframe irrational fears, and grounding exercises that redirect focus away from overwhelming emotions. Prioritizing self-compassion reduces the impact of shame, fostering resilience and helping you regain control over spiraling anxiety patterns.
Shame Spiral vs Anxiety Spiral: Key Differences
A Shame Spiral involves intense self-criticism and feelings of worthlessness triggered by perceived personal failures, whereas an Anxiety Spiral centers on excessive worry and fear about future uncertainties or potential threats. Shame Spirals often lead to withdrawal and decreased self-esteem, while Anxiety Spirals typically cause hypervigilance and avoidance behaviors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for targeted therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral techniques for anxiety and self-compassion practices for shame.
Seeking Help: When to Consult a Mental Health Professional
Shame spirals intensify feelings of worthlessness and self-criticism, often leading to social withdrawal, while anxiety spirals amplify worries about future events, causing heightened physical and emotional distress. Recognizing when these spirals disrupt daily functioning or persist beyond a few weeks is crucial for seeking professional help, as mental health specialists can provide tailored coping strategies and therapeutic interventions. Early consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist improves outcomes by addressing underlying emotional patterns and preventing escalation into depression or chronic anxiety disorders.
Infographic: Shame spiral vs Anxiety spiral
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com