Vulnerability hangover occurs when feelings of exposure and emotional rawness linger after sharing personal truths, often intensifying anxiety and self-doubt in relationships. Understanding how vulnerability hangover differs from general anxiety can improve emotional resilience and relationship dynamics; discover more insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
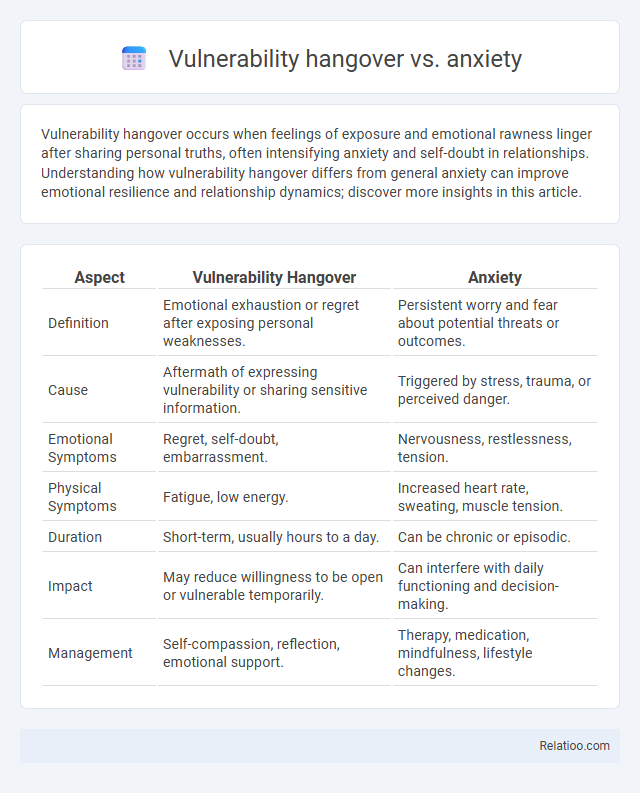
| Aspect | Vulnerability Hangover | Anxiety |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Emotional exhaustion or regret after exposing personal weaknesses. | Persistent worry and fear about potential threats or outcomes. |
| Cause | Aftermath of expressing vulnerability or sharing sensitive information. | Triggered by stress, trauma, or perceived danger. |
| Emotional Symptoms | Regret, self-doubt, embarrassment. | Nervousness, restlessness, tension. |
| Physical Symptoms | Fatigue, low energy. | Increased heart rate, sweating, muscle tension. |
| Duration | Short-term, usually hours to a day. | Can be chronic or episodic. |
| Impact | May reduce willingness to be open or vulnerable temporarily. | Can interfere with daily functioning and decision-making. |
| Management | Self-compassion, reflection, emotional support. | Therapy, medication, mindfulness, lifestyle changes. |
Understanding Vulnerability Hangover: Definition and Signs
Understanding vulnerability hangover involves recognizing the emotional and physical aftereffects following a deeply vulnerable experience. This state differs from anxiety, as vulnerability hangover often presents with feelings of exhaustion, self-doubt, and emotional sensitivity rather than persistent worry or fear. Your ability to identify signs like withdrawal, heightened self-criticism, and fatigue can help manage and overcome the impact of vulnerability hangover effectively.
What Is Anxiety? Key Differences from Vulnerability Hangover
Anxiety is a persistent feeling of worry or fear that can affect your daily functioning, often linked to anticipating future threats or stressors. A vulnerability hangover, by contrast, occurs after openly expressing emotions or personal truths, resulting in feelings of regret, embarrassment, or exposure. Unlike anxiety, which is generally anticipatory and generalized, a vulnerability hangover specifically follows moments of emotional openness and is centered on self-judgment and social evaluation.
The Science Behind Vulnerability Hangover
The science behind vulnerability hangover reveals it as a psychological and physiological response triggered by exposing one's innermost thoughts and emotions, leading to feelings of shame, regret, or self-doubt. Unlike generalized anxiety, which stems from anticipatory fear or worry about future events, vulnerability hangover specifically arises after moments of emotional exposure and social risk-taking. Research in neuroscience highlights that this phenomenon activates the brain's threat response systems, similar to those engaged during social rejection or embarrassment, differentiating it from the broader anxiety spectrum.
Triggers: What Causes Vulnerability Hangover vs Anxiety?
Vulnerability hangover commonly arises from intense emotional exposure, such as sharing deeply personal feelings or experiences, leading to feelings of regret, embarrassment, or self-doubt afterward. Anxiety often stems from perceived threats, uncertainty, or stressors like social pressure, future uncertainties, or past trauma, triggering prolonged worry and physiological symptoms. While vulnerability hangover is primarily triggered by relational or emotional risk-taking situations, anxiety triggers are broader and can include both internal cognitive processes and external environmental stressors.
Emotional Symptoms: Comparing Vulnerability Hangover and Anxiety
Emotional symptoms of vulnerability hangover often include intense feelings of regret, shame, and emotional exhaustion following moments of overexposure, whereas anxiety typically presents with persistent worry, tension, and fear about future uncertainties. Your emotional response during a vulnerability hangover may involve replaying social interactions and self-criticism, contrasting with anxiety's broader, anticipatory distress impacting various aspects of life. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor coping strategies to reduce emotional turmoil and enhance mental well-being.
Coping Strategies for Vulnerability Hangover
Vulnerability hangover occurs when you feel regret, shame, or exhaustion after exposing your true self, differing from anxiety, which is more about anticipatory worry or fear. Effective coping strategies for vulnerability hangover include practicing self-compassion, reflecting on the courage it took to be open, and seeking supportive conversations to reframe your experience positively. Your resilience grows by acknowledging these feelings without judgment and gradually embracing vulnerability as a strength rather than a weakness.
Effective Anxiety Management Techniques
Vulnerability hangover and anxiety both trigger intense emotional responses, yet vulnerability hangover arises from regretting emotional openness, while anxiety stems from generalized worry or fear. Effective anxiety management techniques include mindfulness meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and controlled breathing exercises that help regulate your emotional state. Addressing vulnerability hangover involves self-compassion practices and reframing negative self-talk to reduce lingering emotional discomfort.
Self-Compassion: Healing from Vulnerability and Anxiety
Vulnerability hangover and anxiety both involve intense emotional discomfort, but vulnerability hangover specifically stems from the aftermath of exposing one's true self, often leading to self-criticism and shame. Practicing self-compassion helps heal both by fostering acceptance and kindness towards oneself, reducing the negative impact of vulnerability hangover and alleviating anxiety symptoms. Cultivating self-compassion encourages emotional resilience, enabling individuals to recover more quickly from vulnerability hangover and manage anxiety with greater ease.
When to Seek Professional Help: Vulnerability Hangover vs Anxiety
Recognizing when to seek professional help is vital for managing both vulnerability hangover and anxiety, as persistent emotional distress or physical symptoms beyond a few days may signal the need for intervention. Your inability to recover from feelings of regret, shame, or exhaustion after vulnerability exposure, especially if coupled with anxiety symptoms like excessive worry or panic attacks, warrants consultation with a mental health specialist. Early support can prevent escalation and improve coping strategies tailored to your specific experience of vulnerability hangover or underlying anxiety disorders.
Building Resilience: Moving Beyond Vulnerability Hangover and Anxiety
Building resilience involves recognizing the emotional aftermath of vulnerability hangover, which often triggers anxiety by amplifying feelings of regret and self-doubt. Developing coping strategies such as mindfulness, cognitive reframing, and emotional regulation helps individuals transform vulnerability hangover into a growth opportunity rather than a source of persistent anxiety. Strengthening resilience nurtures the capacity to embrace vulnerability with confidence, reducing the impact of negative emotions and fostering psychological well-being.
Infographic: Vulnerability hangover vs anxiety
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com