Preoccupation in relationships often leads to distraction and neglect of emotional needs, while awareness fosters genuine connection and understanding between partners. Explore how balancing these states can deepen intimacy and trust in this article.
Table of Comparison
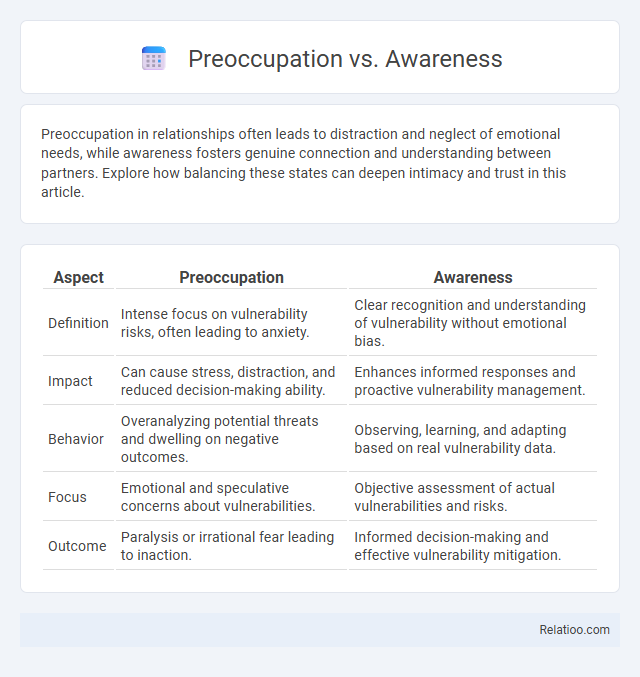
| Aspect | Preoccupation | Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense focus on vulnerability risks, often leading to anxiety. | Clear recognition and understanding of vulnerability without emotional bias. |
| Impact | Can cause stress, distraction, and reduced decision-making ability. | Enhances informed responses and proactive vulnerability management. |
| Behavior | Overanalyzing potential threats and dwelling on negative outcomes. | Observing, learning, and adapting based on real vulnerability data. |
| Focus | Emotional and speculative concerns about vulnerabilities. | Objective assessment of actual vulnerabilities and risks. |
| Outcome | Paralysis or irrational fear leading to inaction. | Informed decision-making and effective vulnerability mitigation. |
Understanding Preoccupation: Definition and Characteristics
Preoccupation refers to a state of intense and persistent focus on a specific thought or concern, often leading to distraction from the immediate environment. It is characterized by repetitive mental engagement that can impact emotional well-being and cognitive performance. Awareness, in contrast, involves conscious recognition and mindfulness of present experiences without being dominated by a singular focus.
Defining Awareness: Key Concepts and Traits
Awareness encompasses the conscious recognition and understanding of your internal state and external environment, enabling focused attention and perception. Key traits include mindfulness, presence, and cognitive clarity, which distinguish it from preoccupation, where your mind is distracted by persistent thoughts. Developing awareness improves emotional regulation and decision-making by enhancing your ability to observe without attachment.
Preoccupation vs Awareness: Core Differences
Preoccupation involves intense, persistent focus on specific thoughts or concerns that can overshadow other mental processes, often leading to distraction or stress. Awareness denotes a conscious recognition and understanding of one's surroundings, thoughts, or emotions without the overwhelming intensity seen in preoccupation. The core difference lies in the depth and impact of focus: preoccupation narrows attention to a point of fixation, whereas awareness maintains balanced and mindful observation of multiple stimuli.
Causes and Triggers of Preoccupation
Preoccupation arises from persistent intrusive thoughts often triggered by stress, anxiety, or unresolved conflicts, differentiating it from mere awareness, which involves conscious recognition without emotional disturbance. Causes of preoccupation include trauma, chronic worry, or obsessive concerns, which continuously capture cognitive resources and inhibit present-moment focus. Triggers such as environmental cues, negative feedback, or internal rumination exacerbate preoccupation by reinforcing anxious or avoidant thought patterns, limiting mental clarity and decision-making capacity.
Benefits of Cultivating Awareness
Cultivating awareness enhances mental clarity by reducing habitual preoccupation with distractions and intrusive thoughts, allowing greater focus on present tasks. Awareness improves emotional regulation, promoting resilience and reducing stress through mindful observation of internal states rather than reactive engagement. Developing this skill supports cognitive flexibility, enabling better decision-making and overall wellbeing by fostering conscious presence over automatic responses.
Psychological Impact: Preoccupation vs Awareness
Preoccupation often leads to mental distress as it involves obsessive thinking that disrupts your emotional balance, whereas awareness enhances psychological resilience by fostering mindful recognition of thoughts without judgment. Preoccupation traps the mind in repetitive negative patterns, increasing anxiety and reducing cognitive flexibility. Awareness cultivates emotional regulation and clarity, promoting healthier psychological outcomes and improved mental well-being.
How Preoccupation Affects Decision-Making
Preoccupation significantly impairs decision-making by narrowing cognitive resources and increasing susceptibility to bias, often leading to impulsive or avoidant choices. In contrast, awareness enhances decision quality through clearer perception and greater emotional regulation, enabling individuals to assess situations more objectively. While focus contributes to sustained attention on relevant information, excessive preoccupation diverts mental energy away from strategic thinking, reducing problem-solving effectiveness.
Techniques to Shift from Preoccupation to Awareness
Shifting from preoccupation to awareness involves mindfulness techniques such as focused breathing and body scans to ground your attention in the present moment. Cognitive reframing allows you to identify and redirect intrusive thoughts, reducing mental clutter and enhancing clarity. You can also practice setting intentional pauses during your daily routine to observe your thoughts without judgment, fostering a state of heightened self-awareness and emotional regulation.
Real-Life Examples: Preoccupation and Awareness in Daily Life
Preoccupation involves persistent focus on specific thoughts or concerns, such as worrying about an upcoming exam, which can detract from present tasks. Awareness means conscious recognition of surroundings or internal states, like noticing traffic signals while driving to ensure safety. In real life, balancing preoccupation with awareness allows individuals to manage stress while staying attentive to their environment, enhancing both mental clarity and situational responsiveness.
Building Sustainable Awareness for Improved Well-being
Preoccupation often limits clarity by fixating attention on specific worries, whereas awareness expands understanding by fostering mindful recognition of present experiences. Building sustainable awareness involves cultivating consistent mindfulness practices that enhance emotional regulation and mental resilience, ultimately improving overall well-being. Sustained focus on awareness shifts the mental landscape from reactive preoccupation to proactive engagement with life's challenges.
Infographic: Preoccupation vs Awareness
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com