The inner critic incessantly undermines self-worth through harsh self-judgment, while imposter syndrome fosters persistent feelings of fraudulence despite evident success. Explore this article to understand how these psychological barriers impact relationships and strategies to overcome them.
Table of Comparison
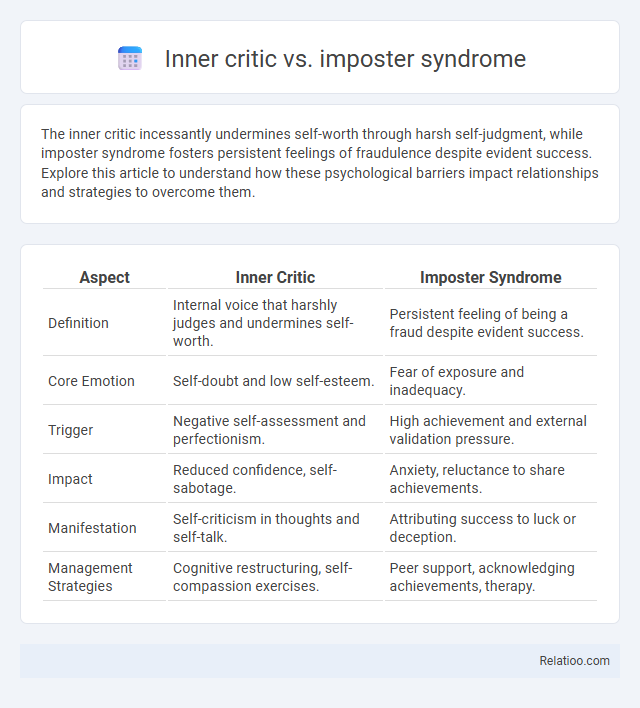
| Aspect | Inner Critic | Imposter Syndrome |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal voice that harshly judges and undermines self-worth. | Persistent feeling of being a fraud despite evident success. |
| Core Emotion | Self-doubt and low self-esteem. | Fear of exposure and inadequacy. |
| Trigger | Negative self-assessment and perfectionism. | High achievement and external validation pressure. |
| Impact | Reduced confidence, self-sabotage. | Anxiety, reluctance to share achievements. |
| Manifestation | Self-criticism in thoughts and self-talk. | Attributing success to luck or deception. |
| Management Strategies | Cognitive restructuring, self-compassion exercises. | Peer support, acknowledging achievements, therapy. |
Understanding the Inner Critic
Understanding the Inner Critic involves recognizing its role as an internal voice that judges and criticizes your thoughts and actions, often rooted in past experiences and self-doubt. Unlike Imposter Syndrome, which focuses on feelings of fraudulence despite evidence of competence, the Inner Critic persistently undermines your self-worth by amplifying perceived flaws and mistakes. By identifying these patterns, you can begin to challenge the Inner Critic's negative narratives and build a more compassionate and empowering self-dialogue.
What Is Imposter Syndrome?
Imposter syndrome is a psychological phenomenon where individuals doubt their accomplishments and fear being exposed as a fraud despite evident success and competence. Unlike the inner critic, which is an internal voice that harshly judges and criticizes, imposter syndrome involves persistent feelings of inadequacy and self-doubt that undermine confidence. Understanding imposter syndrome helps distinguish it from general self-criticism by highlighting its basis in perceived external deception rather than internal negative self-talk.
Key Differences Between Inner Critic and Imposter Syndrome
Inner critic manifests as a persistent internal voice that harshly judges personal flaws and mistakes, while imposter syndrome involves a deep-seated fear of being exposed as a fraud despite evident success. The key difference lies in the scope: the inner critic critiques one's character and abilities broadly, whereas imposter syndrome specifically targets accomplishments and the belief of undeserved achievement. Understanding these distinctions aids in applying targeted strategies for overcoming self-doubt and enhancing self-confidence.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Inner critic, imposter syndrome, and self-doubt all involve negative self-talk but differ in focus and intensity; common signs include persistent feelings of inadequacy, fear of failure, and harsh self-judgment. Your inner critic harshly evaluates personal actions, imposter syndrome leads to chronic self-doubt despite evidence of success, and both can trigger anxiety, perfectionism, and avoidance behaviors. Recognizing these symptoms helps you address underlying fears and build healthier self-perception strategies.
Psychological Roots and Triggers
The psychological roots of the inner critic stem from early experiences of criticism and perfectionism, often triggered by feelings of inadequacy or failure. Imposter syndrome arises from deep-seated beliefs of fraudulence and fear of exposure despite evident success, frequently triggered by new challenges or high expectations. Understanding these distinctions helps you identify the unique cognitive patterns fueling self-doubt and address the specific triggers to foster healthier self-perception.
Impact on Personal and Professional Life
The inner critic undermines self-esteem by fostering persistent self-doubt and negative self-talk, leading to decreased confidence in both personal and professional settings. Imposter syndrome generates feelings of fraudulence despite evident accomplishments, causing high stress levels and reduced risk-taking that can stifle career advancement and personal growth. While both create internal barriers, the inner critic emphasizes harsh self-judgment, whereas imposter syndrome centers on fear of being exposed as inadequate, significantly impacting decision-making, relationships, and overall well-being.
Overcoming the Inner Critic
Overcoming the inner critic requires recognizing its persistent negative self-talk that undermines your confidence and self-worth, often confusing it with imposter syndrome, which involves feelings of fraudulence despite evident success. While the inner critic attacks your abilities, imposter syndrome generates pervasive doubt about your achievements, making both mental challenges important to address for personal growth. Techniques like mindfulness, self-compassion, and cognitive restructuring help silence your inner critic, reinforcing your authentic value and resilience.
Strategies to Combat Imposter Syndrome
Imposter syndrome manifests as persistent self-doubt and fear of being exposed as a fraud, often linked with an overly harsh inner critic that amplifies negative self-talk. Strategies to combat imposter syndrome include recognizing and challenging irrational beliefs, practicing self-compassion, and seeking external validation through feedback from trusted peers or mentors. Your ability to reframe achievements and focus on growth rather than perfection helps weaken the inner critic's grip and fosters genuine confidence.
Building Self-Compassion and Confidence
Inner critic and imposter syndrome both undermine self-worth, but building self-compassion involves recognizing these negative voices as distorted rather than factual. Developing confidence requires reframing inner dialogue to emphasize strengths and achievements, which diminishes the power of self-doubt. Techniques such as mindfulness, affirmations, and cognitive-behavioral strategies help transform the inner critic into a supportive inner coach, fostering resilience and authentic self-esteem.
When to Seek Professional Help
When your inner critic or imposter syndrome significantly impairs your daily functioning, causes persistent anxiety, or leads to severe self-doubt, it may be time to seek professional help. Therapists specializing in cognitive-behavioral therapy or mindfulness-based approaches can provide tools to manage negative self-talk and build authentic self-esteem. Your mental health is crucial, and professional support can help transform limiting beliefs into empowering growth opportunities.
Infographic: Inner critic vs Imposter syndrome
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com