Privacy ensures individuals control over their personal information, while confidentiality involves the obligation to protect that information from unauthorized access. Explore the distinctions and implications of privacy versus confidentiality in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
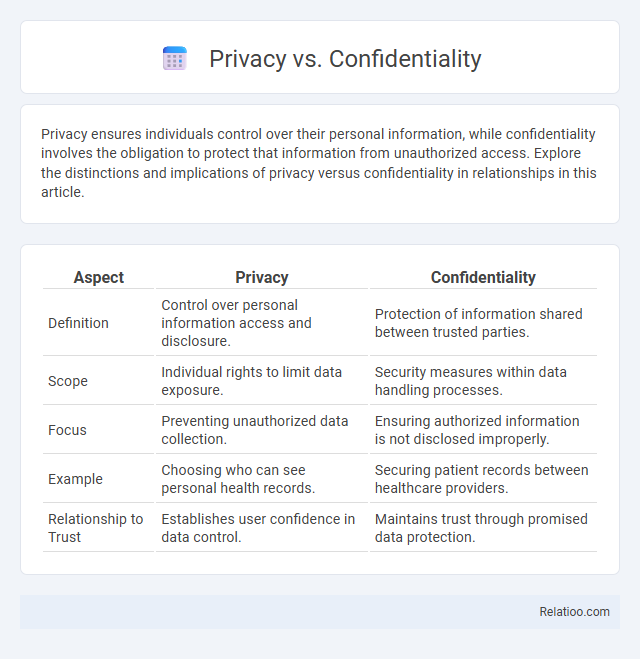
| Aspect | Privacy | Confidentiality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over personal information access and disclosure. | Protection of information shared between trusted parties. |
| Scope | Individual rights to limit data exposure. | Security measures within data handling processes. |
| Focus | Preventing unauthorized data collection. | Ensuring authorized information is not disclosed improperly. |
| Example | Choosing who can see personal health records. | Securing patient records between healthcare providers. |
| Relationship to Trust | Establishes user confidence in data control. | Maintains trust through promised data protection. |
Understanding Privacy and Confidentiality
Privacy refers to an individual's right to control access to their personal information and protect it from unauthorized use or exposure. Confidentiality involves the responsibility of organizations or individuals to safeguard sensitive data entrusted to them, ensuring it is only shared with authorized parties. Understanding the distinction between privacy and confidentiality is essential for implementing effective data protection policies and maintaining trust in personal and professional relationships.
Key Differences Between Privacy and Confidentiality
Privacy refers to Your right to control personal information and decide who accesses it, while confidentiality involves the obligation of others to protect information shared with them. Key differences lie in privacy being an individual's control over personal data, whereas confidentiality is a duty imposed on entities like healthcare providers or legal professionals to safeguard that information. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how sensitive data is managed and protected in various contexts.
Importance of Privacy in the Digital Age
Privacy in the digital age is essential for protecting personal information from unauthorized access and misuse across online platforms, social media, and digital communications. Unlike confidentiality, which pertains to the obligation to protect shared information within specific contexts, privacy empowers individuals to control their data and digital footprints independently. Emphasizing privacy safeguards against identity theft, cybercrime, and infringement of personal freedoms, ensuring trust and security in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Role of Confidentiality in Professional Settings
Confidentiality in professional settings ensures that sensitive information shared by clients or colleagues is protected from unauthorized access, reinforcing trust and ethical standards within the workplace. While privacy refers to an individual's right to control personal information, confidentiality specifically pertains to the obligation of professionals to safeguard this information. Your commitment to maintaining confidentiality safeguards reputations and fosters secure communication essential for effective professional relationships.
Legal Frameworks Governing Privacy and Confidentiality
Legal frameworks governing privacy and confidentiality primarily include regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, which set standards for data protection and patient information privacy. Privacy laws focus on protecting individuals' personal data from unauthorized access, while confidentiality pertains to the ethical and legal duty of entities to safeguard the information entrusted to them. These legal frameworks establish clear obligations for organizations to implement security measures, ensure consent, and provide rights for individuals to control and access their personal information.
Common Misconceptions About Privacy vs Confidentiality
Privacy and confidentiality are often mistakenly used interchangeably, yet they address different concerns; privacy pertains to an individual's right to control personal information, while confidentiality involves the ethical and legal duty to protect information shared within specific relationships. A common misconception is that maintaining confidentiality automatically ensures privacy, but confidentiality only applies to information already shared and does not prevent unauthorized collection or surveillance of personal data. Clarifying these distinctions is crucial in fields like healthcare, legal services, and data protection, where both privacy rights and confidentiality obligations must be rigorously upheld.
Risks of Breaching Privacy or Confidentiality
Breaching privacy exposes Your personal information to unauthorized access, increasing risks such as identity theft, financial loss, and reputational damage. Violating confidentiality compromises sensitive data shared in trusted relationships, leading to legal consequences and loss of professional integrity. Both breaches undermine trust and can result in severe emotional and economic harm to individuals or organizations.
Best Practices for Maintaining Privacy and Confidentiality
Maintaining privacy and confidentiality requires implementing strict access controls, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly updating security protocols to prevent unauthorized disclosures. You should establish clear policies that define data handling procedures and conduct regular training to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards. Monitoring communications and audits further reinforce protection by identifying potential breaches early and safeguarding personal and organizational information effectively.
Real-World Examples: Privacy vs Confidentiality Scenarios
Privacy refers to an individual's right to control personal information, such as a patient deciding who can access their medical records, whereas confidentiality involves the obligation of entities like healthcare providers to protect that information from unauthorized disclosure. In a real-world scenario, a company protects employee data under confidentiality clauses, ensuring that sensitive details are not shared outside the organization, while privacy concerns arise when employees decide what personal information they share with colleagues. Distinguishing between these concepts is crucial for compliance with regulations like GDPR, where privacy rights govern data collection and use, and confidentiality rules mandate secure handling by service providers.
Future Trends in Privacy and Confidentiality
Future trends in privacy and confidentiality emphasize enhanced data encryption, artificial intelligence-driven threat detection, and stricter regulatory frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA expansion. Organizations will adopt zero-trust architectures and decentralized identity management to mitigate risks of data breaches and unauthorized access. Advances in privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), including homomorphic encryption and differential privacy, will further secure sensitive information and balance user privacy with data utility.
Infographic: Privacy vs Confidentiality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com