Loyalty involves a deep, personal commitment based on trust and emotional bonds, while allegiance is often a formal obligation to a group or cause. Explore the differences and impacts of loyalty versus allegiance in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
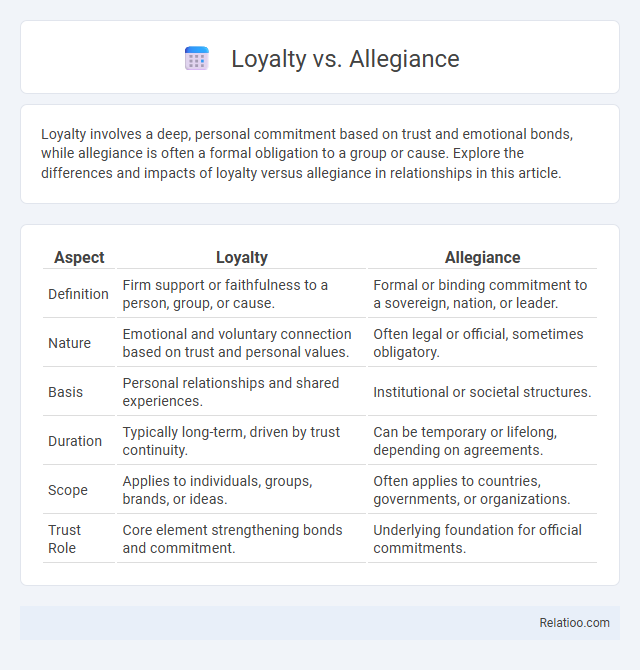
| Aspect | Loyalty | Allegiance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Firm support or faithfulness to a person, group, or cause. | Formal or binding commitment to a sovereign, nation, or leader. |
| Nature | Emotional and voluntary connection based on trust and personal values. | Often legal or official, sometimes obligatory. |
| Basis | Personal relationships and shared experiences. | Institutional or societal structures. |
| Duration | Typically long-term, driven by trust continuity. | Can be temporary or lifelong, depending on agreements. |
| Scope | Applies to individuals, groups, brands, or ideas. | Often applies to countries, governments, or organizations. |
| Trust Role | Core element strengthening bonds and commitment. | Underlying foundation for official commitments. |
Defining Loyalty and Allegiance
Loyalty refers to a strong feeling of support or allegiance towards a person, group, or cause, often characterized by faithfulness and devotion. Allegiance specifically denotes the formal or binding commitment of loyalty, usually to a sovereign, nation, or organization, emphasizing legal or official obligations. Understanding the distinction between loyalty as an emotional bond and allegiance as a formal duty is essential for analyzing social, political, and organizational relationships.
Historical Roots of Loyalty and Allegiance
Loyalty originates from ancient kinship bonds emphasizing trust and support among family and community members, while allegiance has strong ties to feudal societies where vassals pledged service and protection to their lords. Your understanding of loyalty involves emotional commitment rooted in personal relationships, whereas allegiance historically denotes a formal, often legal, obligation to a sovereign or cause. Both concepts evolved through time but retain distinct foundations: loyalty is intimate and relational, whereas allegiance is institutional and duty-bound.
Psychological Foundations: Why We Commit
Loyalty, allegiance, and devotion differ in psychological foundations behind why we commit, reflecting varying depths of emotional investment and social bonds. Loyalty often stems from trust and consistent positive experiences, reinforcing your personal connections and identity within groups. Allegiance involves a deeper, often ideological commitment to principles or institutions, driven by a need for belonging and purpose, while devotion encapsulates an intense, unwavering dedication rooted in intrinsic motivation and emotional attachment.
Loyalty in Personal Relationships
Loyalty in personal relationships emphasizes unwavering support and trust between individuals, fostering deep emotional bonds and stability. It involves consistent commitment, reliability, and prioritizing the well-being of loved ones over external influences. Unlike allegiance, which often pertains to duty toward institutions or groups, loyalty in personal contexts centers on genuine connection and mutual respect.
Allegiance in Social and Political Contexts
Allegiance in social and political contexts refers to a formal or implicit commitment to a nation, government, or cause, often involving a sense of duty and loyalty that shapes civic identity and participation. Your allegiance influences how you engage with social institutions, support policies, and uphold collective values that maintain political stability. While loyalty is personal and emotional, allegiance encompasses both loyalty and active adherence to societal structures and obligations.
Key Differences Between Loyalty and Allegiance
Loyalty refers to a strong feeling of support or devotion toward a person, group, or cause, often driven by personal attachment and trust, while allegiance signifies a formal and binding commitment to a sovereign, nation, or authority, highlighting legal or political duty. Key differences include loyalty's emotional and voluntary nature compared to allegiance's obligatory and often legal framework. Loyalty can be flexible and context-driven, whereas allegiance usually involves explicit pledges or oaths, emphasizing duty over personal sentiment.
Examples of Loyalty and Allegiance in Daily Life
Loyalty often manifests in daily life when you stand by friends during difficult times, showing unwavering support despite challenges. Allegiance is exemplified by citizens adhering to laws and participating in national duties like voting, reflecting commitment to their country or cause. Both loyalty and allegiance reinforce trust and reliability in personal relationships and societal structures.
The Benefits and Risks of Loyalty
Loyalty fosters trust and long-term relationships by showing consistent support, which can enhance collaboration and personal growth. Your unwavering loyalty can build strong emotional bonds, but it also risks blind obedience, potentially leading to exploitation or ignoring critical issues. Understanding these benefits and risks helps you balance commitment with discernment, ensuring loyalty serves your best interests.
The Power of Allegiance in Shaping Identity
Allegiance wields formidable power in shaping identity by fostering a deep sense of belonging and commitment to a group, cause, or nation, which transcends mere loyalty. Unlike loyalty, which often implies a personal or emotional faithfulness, allegiance embodies a profound, principled dedication that binds individuals to shared values and collective purpose. This allegiance reinforces social cohesion and personal identity through the alignment of individual beliefs with collective goals and ethical frameworks.
Loyalty vs Allegiance: Which Matters More Today?
Loyalty and allegiance both reflect commitment, but loyalty emphasizes personal trust and emotional bonds, while allegiance involves formal or ideological devotion to a group or cause. In today's dynamic social and professional environments, loyalty matters more because it fosters genuine relationships and long-term reliability, directly impacting your personal and organizational success. Understanding the subtle difference ensures you build meaningful connections rather than mere obligatory support.
Infographic: Loyalty vs Allegiance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com