Consistency builds trust by ensuring predictable behavior over time, while reliability measures the ability to perform dependably under various conditions. Explore how balancing consistency and reliability strengthens your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
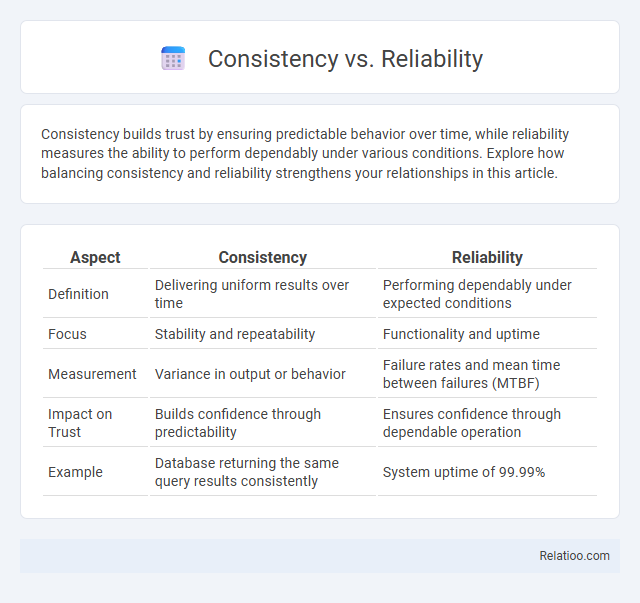
| Aspect | Consistency | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivering uniform results over time | Performing dependably under expected conditions |
| Focus | Stability and repeatability | Functionality and uptime |
| Measurement | Variance in output or behavior | Failure rates and mean time between failures (MTBF) |
| Impact on Trust | Builds confidence through predictability | Ensures confidence through dependable operation |
| Example | Database returning the same query results consistently | System uptime of 99.99% |
Understanding Consistency and Reliability
Consistency refers to the ability of a system or process to produce the same results under identical conditions, ensuring predictable performance. Reliability measures the probability that a system or component operates without failure over a specified period, indicating its operational stability. Understanding consistency and reliability helps you evaluate how well a product or service meets expected standards and performs continuously without unexpected interruptions.
Key Differences Between Consistency and Reliability
Consistency measures the uniformity of results or behavior over time, ensuring that your outcomes remain stable across repeated actions. Reliability refers to the probability that a system or component performs its intended function without failure under specified conditions for a defined period. Dependability encompasses both consistency and reliability, highlighting the overall trustworthiness and availability of a system.
Why Consistency Matters in Performance
Consistency in performance ensures that tasks are completed with uniform quality and precision, reducing errors and improving overall efficiency. Reliability depends on consistent outputs to build trust and predictability in your processes, while dependability is reinforced when your performance remains stable under varying conditions. Your ability to maintain consistency directly impacts the reliability and dependability of outcomes, fostering confidence among stakeholders and driving long-term success.
The Role of Reliability in Trust Building
Reliability plays a crucial role in trust building by consistently delivering expected results under specified conditions, which reinforces confidence over time. Unlike consistency, which merely involves uniformity of actions, reliability emphasizes performance accuracy and dependability in various scenarios. Dependability encompasses both reliability and consistency but adds the dimension of resilience, ensuring ongoing trust even amidst changing circumstances.
Measuring Consistency: Methods and Metrics
Measuring consistency involves evaluating the degree to which results remain stable over multiple trials, often using metrics such as standard deviation, variance, and coefficient of variation. Techniques like test-retest reliability, inter-rater reliability, and internal consistency (e.g., Cronbach's alpha) provide quantifiable data to assess performance uniformity. Your ability to interpret these metrics enables more accurate predictions about system behavior and enhances quality control in various applications.
Evaluating Reliability: Tools and Techniques
Evaluating reliability involves using tools such as reliability block diagrams, fault tree analysis, and statistical methods like mean time between failures (MTBF) to measure system performance over time. Techniques like accelerated life testing and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) help identify potential weaknesses and predict component lifespans. These approaches quantify reliability by assessing failure rates, enabling engineers to design more robust and dependable systems.
Practical Examples of Consistency vs Reliability
Consistency refers to the ability of a process or system to produce the same results repeatedly under unchanged conditions, such as a coffee machine brewing the exact same cup every morning. Reliability measures the probability that a system performs its intended function without failure over time, like a car starting without issues for five years. Your choice between consistency and reliability impacts tasks like selecting machinery where consistency guarantees uniform output while reliability ensures long-term performance.
Consistency vs Reliability in Business Operations
Consistency in business operations ensures repeatable processes and uniform quality, fostering customer trust and brand stability. Reliability measures the ability of systems or services to perform as expected over time, minimizing downtime and operational failures. While consistency focuses on maintaining standards, reliability emphasizes sustained performance under varying conditions, both key to driving efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Strategies to Improve Both Consistency and Reliability
Consistency and reliability are crucial for enhancing your system's dependability, achieved through strategies like regular maintenance, standardized procedures, and continuous monitoring. Implementing robust quality control measures and automated testing tools helps identify and rectify discrepancies early, ensuring predictable performance. Investing in training and clear documentation further supports these efforts by minimizing human error and fostering a culture of accountability.
Choosing Between Consistency and Reliability: Making the Right Decision
Choosing between consistency and reliability involves evaluating the specific demands of your project or system to ensure optimal performance. Consistency guarantees uniform results across multiple attempts, which is critical for processes requiring standardization, whereas reliability emphasizes the system's ability to function correctly over time under varying conditions. Prioritizing dependability integrates both concepts, enhancing decision-making by balancing steady output and operational trustworthiness based on context-specific criteria.
Infographic: Consistency vs Reliability
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com