Zero Trust security eliminates reliance on perimeter defenses by continuously verifying every user and device, enhancing protection against evolving cyber threats. Discover how Zero Trust transforms cybersecurity compared to traditional perimeter security in this article.
Table of Comparison
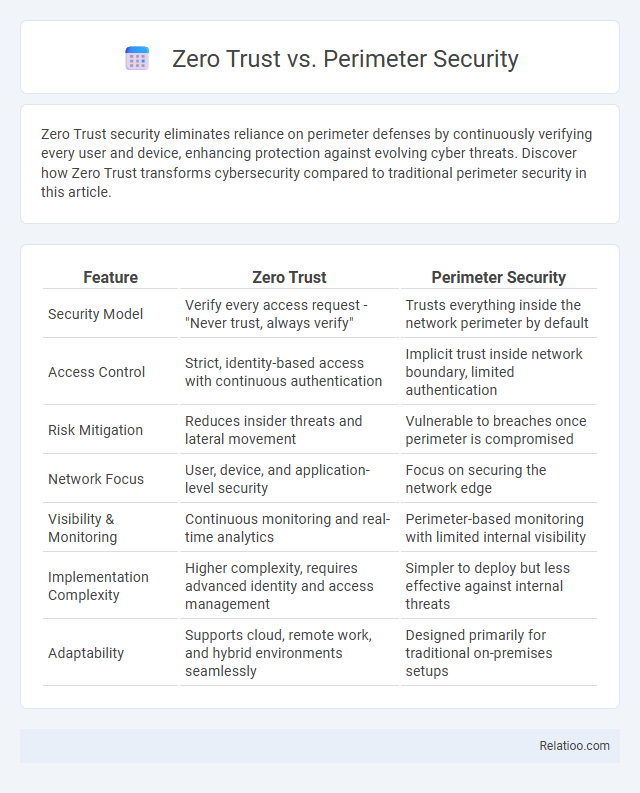
| Feature | Zero Trust | Perimeter Security |
|---|---|---|
| Security Model | Verify every access request - "Never trust, always verify" | Trusts everything inside the network perimeter by default |
| Access Control | Strict, identity-based access with continuous authentication | Implicit trust inside network boundary, limited authentication |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces insider threats and lateral movement | Vulnerable to breaches once perimeter is compromised |
| Network Focus | User, device, and application-level security | Focus on securing the network edge |
| Visibility & Monitoring | Continuous monitoring and real-time analytics | Perimeter-based monitoring with limited internal visibility |
| Implementation Complexity | Higher complexity, requires advanced identity and access management | Simpler to deploy but less effective against internal threats |
| Adaptability | Supports cloud, remote work, and hybrid environments seamlessly | Designed primarily for traditional on-premises setups |
Introduction to Zero Trust and Perimeter Security
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity model that assumes no entity, inside or outside the network, is trustworthy by default, requiring continuous verification of every user and device accessing resources. Perimeter Security traditionally focuses on defending the network's boundary through firewalls and intrusion detection systems to keep threats out. Your organization's security strategy benefits from understanding that Zero Trust enhances perimeter defenses by continuously validating access, reducing risks posed by insiders and sophisticated external attackers.
Core Principles of Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture centers on verifying every user and device continuously, regardless of network location, to minimize attack surfaces unlike traditional perimeter security which relies on strong defenses at network boundaries. Core principles include strict identity verification, least-privilege access, and micro-segmentation to restrict lateral movement within IT environments. These measures ensure adaptive protection against evolving cyber threats by treating all network traffic as untrusted until proven otherwise.
Fundamentals of Perimeter Security Models
Perimeter security models establish a boundary defense system protecting networks by controlling access at gateways using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists. These models assume threats originate outside the network, focusing on keeping unauthorized users out while trusting internal traffic. Your cybersecurity strategy should evaluate perimeter security fundamentals against Zero Trust principles, where continuous verification supersedes fixed boundaries to enhance protection.
Key Differences: Zero Trust vs Perimeter Security
Zero Trust security eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device, regardless of location, while Perimeter Security relies on defending a defined boundary to keep threats out. Zero Trust focuses on granular access controls, strict identity verification, and micro-segmentation, whereas Perimeter Security prioritizes firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems at the network edge. Your cybersecurity strategy benefits from understanding these key differences to choose the approach that best addresses evolving threat landscapes and internal risk factors.
Advantages of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security eliminates implicit trust by continuously verifying every user and device, significantly reducing the risk of internal and external breaches compared to traditional perimeter security that relies on a single barrier. Your network gains enhanced protection through micro-segmentation and strict access controls, minimizing lateral movement within the system. Unlike perimeter security models, Zero Trust adapts seamlessly to modern cloud environments and remote workforces, offering scalable and proactive defense against sophisticated cyber threats.
Limitations of Perimeter-Based Defenses
Perimeter-based defenses rely heavily on defined network boundaries, which leaves gaps when users access resources remotely or from mobile devices, making it easier for attackers to bypass traditional firewalls. Zero Trust security overcomes these limitations by continuously verifying every user and device, regardless of location, minimizing implicit trust within the network. Your security strategy should integrate Zero Trust principles to effectively address the evolving threat landscape that perimeter security alone cannot contain.
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Zero Trust demands continuous verification of every user and device, creating implementation challenges such as complex identity management, increased latency, and extensive micro-segmentation within networks. Perimeter Security relies on clearly defined boundaries, but struggles with protecting remote users and cloud environments, resulting in potential blind spots and weaker defense against insider threats. Security strategies must consider integration complexity, scalability, employee training, and evolving threat landscapes to effectively balance protection with usability across diverse IT infrastructures.
Real-World Case Studies and Examples
Zero Trust security frameworks dramatically improve protection by assuming breach and verifying each access request, reducing risks demonstrated in real-world cases such as Google's BeyondCorp implementation, which eliminated traditional VPN vulnerabilities. In contrast, perimeter security relies on defending a network boundary, often failing against sophisticated insider threats or lateral movement in breaches like the Target data breach, where attackers bypassed perimeter defenses. Security approaches combining Zero Trust principles with perimeter controls provide layered defense, as seen in enterprises adapting to hybrid work environments, enhancing resilience against evolving cyber threats.
Industry Adoption Trends and Statistics
Zero Trust architecture has seen a 30% annual increase in adoption across industries, outperforming traditional perimeter security models that still dominate 45% of corporate networks. Recent studies reveal that 70% of cybersecurity budgets are now directed towards Zero Trust frameworks, reflecting a shift from perimeter-based defenses that often fail against evolving threats. Your organization can benefit from these trends by prioritizing Zero Trust, as it offers granular access control and reduces breach risks more effectively than conventional perimeter security.
Future of Network Security: Moving Beyond the Perimeter
Zero Trust architecture eliminates reliance on traditional perimeter security by enforcing strict identity verification and continuous monitoring for every user and device, regardless of location. Perimeter security focuses on defending network boundaries but struggles against modern threats like insider attacks and cloud migration. The future of network security lies in adopting Zero Trust principles combined with advanced analytics and micro-segmentation to create adaptive, resilient defenses beyond fixed network perimeters.
Infographic: Zero Trust vs Perimeter Security
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com