Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep fear of abandonment and a constant need for reassurance, while avoidant attachment involves emotional distance and reluctance to depend on others. Explore this article to understand how these attachment styles impact relationship dynamics and strategies for healthy connection.
Table of Comparison
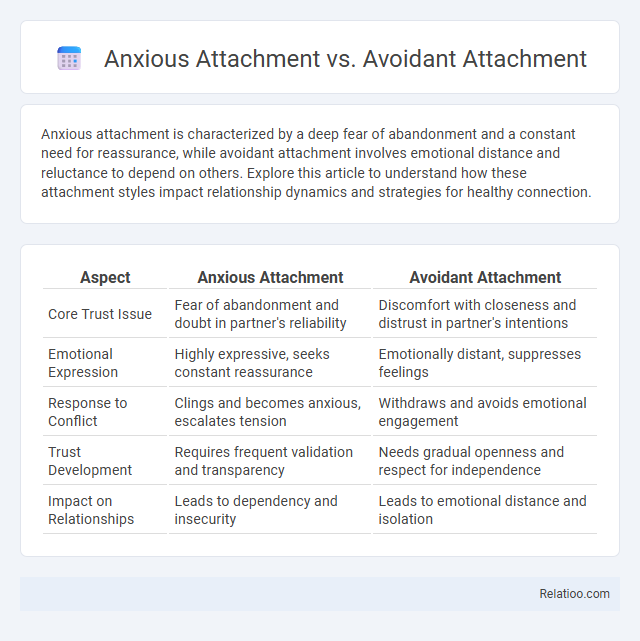
| Aspect | Anxious Attachment | Avoidant Attachment |
|---|---|---|
| Core Trust Issue | Fear of abandonment and doubt in partner's reliability | Discomfort with closeness and distrust in partner's intentions |
| Emotional Expression | Highly expressive, seeks constant reassurance | Emotionally distant, suppresses feelings |
| Response to Conflict | Clings and becomes anxious, escalates tension | Withdraws and avoids emotional engagement |
| Trust Development | Requires frequent validation and transparency | Needs gradual openness and respect for independence |
| Impact on Relationships | Leads to dependency and insecurity | Leads to emotional distance and isolation |
Introduction to Attachment Styles
Attachment styles categorize how individuals form emotional bonds, influencing relationship dynamics and personal well-being. Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep fear of abandonment and a strong desire for closeness, leading to heightened emotional sensitivity and dependency. Avoidant attachment involves discomfort with intimacy and a preference for emotional distance, resulting in self-reliance and reluctance to share feelings.
Defining Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a deep fear of abandonment and excessive need for reassurance, leading to clingy and dependent behaviors in relationships. Unlike avoidant attachment, where individuals maintain emotional distance and suppress feelings, anxious attachment involves heightened sensitivity to partner's responsiveness and emotional availability. Understanding these attachment styles is essential for addressing relational insecurities and fostering healthy emotional bonds.
Defining Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by emotional detachment and discomfort with closeness, often resulting from caregivers' unresponsiveness during early development. Individuals with avoidant attachment tend to prioritize independence and self-sufficiency, minimizing the importance of intimate relationships. This contrasts with anxious attachment, where individuals seek excessive closeness and reassurance, and secure attachment, which balances intimacy and autonomy effectively.
Key Differences Between Anxious and Avoidant Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by a fear of abandonment and a strong desire for closeness, often leading to clinginess and emotional dependence. Avoidant attachment, in contrast, involves discomfort with intimacy and a tendency to maintain emotional distance to protect oneself from vulnerability. Understanding these key differences helps you navigate your relationships by recognizing whether your attachment style leans towards anxiety or avoidance, guiding healthier emotional connections.
Origins and Development of Attachment Styles
Anxious attachment originates from inconsistent caregiving, causing You to seek excessive closeness and worry about rejection. Avoidant attachment develops when caregivers are emotionally unavailable or rejecting, leading to discomfort with intimacy and a preference for emotional distance. Attachment styles form early in childhood through interactions with primary caregivers, shaping Your patterns of relating in adult relationships.
Behaviors and Signs of Anxious Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by clinginess, fear of abandonment, and heightened sensitivity to relationship cues, often leading to constant reassurance-seeking and emotional dependency. Avoidant attachment manifests through emotional distance, reluctance to trust others, and suppression of feelings, resulting in difficulty forming close bonds. Understanding these distinct behaviors and signs aids in identifying attachment styles and improving interpersonal dynamics.
Behaviors and Signs of Avoidant Attachment
Avoidant attachment is characterized by a strong desire for independence and emotional distance, often leading individuals to suppress their feelings and avoid closeness in relationships. Behaviors include reluctance to trust others, difficulty expressing emotions, and a tendency to minimize the importance of relationships. Signs of avoidant attachment also involve discomfort with intimacy and a preference for self-reliance over seeking support from partners.
Impact on Adult Relationships
Anxious attachment leads to heightened sensitivity to rejection and a constant need for reassurance, often causing emotional volatility in adult relationships. Avoidant attachment results in discomfort with closeness and emotional intimacy, driving individuals to maintain distance and independence at the expense of deeper connection. Understanding your attachment style helps improve communication, trust, and emotional responsiveness, fostering healthier and more stable adult relationships.
Coping Strategies for Each Attachment Style
Anxious attachment often leads to heightened emotional sensitivity and fear of abandonment, so coping strategies include practicing mindfulness to manage anxiety and setting clear communication boundaries with partners. Avoidant attachment typically results in discomfort with closeness, making self-reflection and gradually building trust essential for overcoming emotional distance. Understanding your attachment style empowers you to adopt tailored coping mechanisms that enhance relationship security and emotional well-being.
Moving Toward Secure Attachment
Anxious attachment is characterized by fear of abandonment and heightened emotional sensitivity, while avoidant attachment involves emotional distance and discomfort with intimacy. Moving toward secure attachment requires consistent emotional availability, effective communication, and building trust to foster a balanced, healthy relational style. Therapeutic interventions and mindfulness practices support the development of secure attachment by reducing anxiety and avoidance patterns.
Infographic: Anxious Attachment vs Avoidant Attachment
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com