Privacy protects an individual's personal information from unauthorized access, while anonymity ensures actions or identities cannot be traced back to a specific person. Discover how to balance privacy and anonymity effectively in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
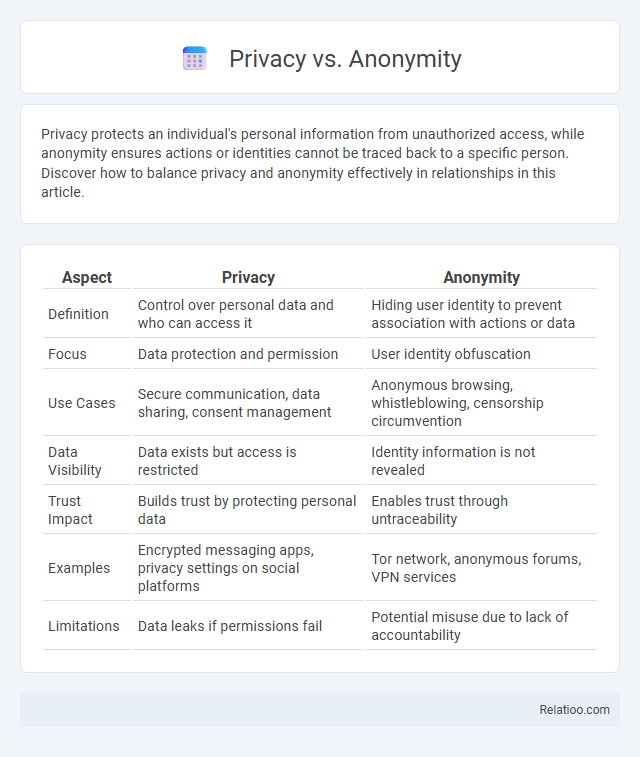
| Aspect | Privacy | Anonymity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Control over personal data and who can access it | Hiding user identity to prevent association with actions or data |
| Focus | Data protection and permission | User identity obfuscation |
| Use Cases | Secure communication, data sharing, consent management | Anonymous browsing, whistleblowing, censorship circumvention |
| Data Visibility | Data exists but access is restricted | Identity information is not revealed |
| Trust Impact | Builds trust by protecting personal data | Enables trust through untraceability |
| Examples | Encrypted messaging apps, privacy settings on social platforms | Tor network, anonymous forums, VPN services |
| Limitations | Data leaks if permissions fail | Potential misuse due to lack of accountability |
Introduction to Privacy and Anonymity
Privacy involves controlling access to personal information to protect individual identity, whereas anonymity emphasizes concealing identity entirely to prevent any association with actions or data. Privacy mechanisms include encryption, access controls, and data minimization, while anonymity relies on techniques like pseudonyms, Tor, and mix networks. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for designing systems that safeguard user data and maintain confidentiality in digital environments.
Defining Privacy: Concepts and Scope
Privacy encompasses the control individuals have over their personal information, including how it is collected, used, and shared, distinct from anonymity, which specifically refers to obscuring one's identity to prevent linkage to personal data. The concept of privacy covers various dimensions such as informational privacy, decisional privacy, and physical privacy, each addressing different aspects of personal autonomy and protection from unauthorized access. Understanding this broader scope allows for more effective policies and technologies that safeguard individuals' rights in digital and physical environments.
Understanding Anonymity: Key Differences
Understanding anonymity involves recognizing its unique role in protecting your identity by obscuring personal details, unlike privacy which controls access to personal information. Anonymity ensures actions or communications cannot be traced back to you, offering a layer of security in digital interactions. In contrast, privacy focuses on safeguarding data and personal boundaries, highlighting key differences between these concepts.
Historical Evolution of Privacy and Anonymity
The historical evolution of privacy reveals a gradual shift from communal norms to individual rights shaped by legal frameworks and technological advances. Anonymity, often intertwined with privacy, originated in ancient practices such as anonymous voting and masked rituals, serving social and political functions. Your understanding of privacy continues to expand as digital innovation challenges boundaries between personal data protection and anonymous interactions.
Privacy in the Digital Age
Privacy in the digital age involves protecting your personal data from unauthorized access, ensuring that your online activities remain confidential and secure. Unlike anonymity, which hides your identity completely, privacy focuses on controlling who can see or use your information while maintaining your digital presence. Understanding privacy settings, encryption, and data policies empowers you to safeguard your information in an increasingly interconnected world.
The Role of Anonymity Online
Anonymity online plays a crucial role in protecting users by concealing their identities, thereby enabling free expression and safeguarding personal information from surveillance or tracking. While privacy involves controlling access to personal data, anonymity ensures that users' actions and communications cannot be linked back to their real-world identity. This distinction is vital in environments where censorship, discrimination, or monitoring pose significant risks to individuals.
Legal Frameworks: Privacy vs Anonymity
Legal frameworks distinguish privacy and anonymity by defining privacy as the right to control personal data and restrict access, typically protected under laws like the GDPR and HIPAA. Anonymity is regulated through guidelines ensuring data cannot be traced back to individuals, as seen in anonymization standards under the ePrivacy Directive and data protection acts. Courts often interpret privacy as enforceable individual rights, whereas anonymity is treated as a technical measure to protect identity within legal boundaries.
Risks and Challenges: Balancing Both
Balancing privacy and anonymity involves navigating complex risks such as data breaches, identity theft, and surveillance, which threaten personal security and freedom. Ensuring privacy requires protecting sensitive information, while maintaining anonymity prevents tracing actions back to individuals, yet both face challenges like technology limitations and legal constraints. Strategies must address these risks by implementing robust encryption, transparent policies, and user education to preserve trust without compromising anonymity or privacy.
Technologies Protecting Privacy and Anonymity
Technologies protecting privacy and anonymity leverage encryption protocols, such as end-to-end encryption in messaging apps, to secure communication from unauthorized access. Tools like virtual private networks (VPNs) and the Tor network mask user IP addresses, enhancing anonymity by routing traffic through multiple servers. Data minimization techniques and differential privacy algorithms further safeguard personal information by limiting data collection and adding statistical noise to prevent re-identification.
Future Trends: Convergence or Divergence?
Future trends in privacy, anonymity, and confidentiality indicate a potential convergence driven by advanced technologies like blockchain and AI enhancing both data protection and user anonymity. You will see increasing integration of privacy-preserving techniques such as differential privacy combined with anonymous communication networks to provide holistic security solutions. However, regulatory frameworks may cause divergence as varying regional standards emphasize different aspects, shaping how these concepts evolve independently or together.
Infographic: Privacy vs Anonymity
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com