Social media gratification offers instant connectivity and validation, while face-to-face gratification provides deeper emotional bonds and nonverbal communication cues. Explore the nuances of these relationship dynamics and their impact on social well-being in this article.
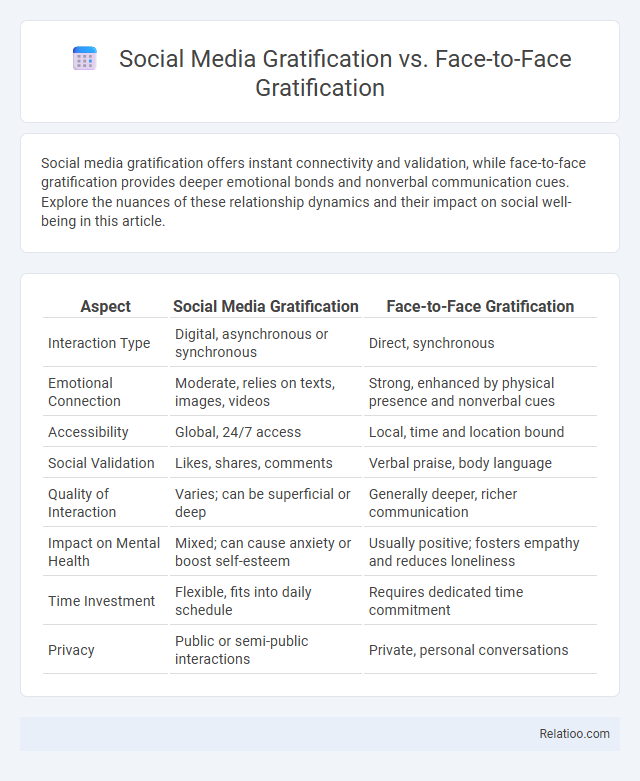
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Media Gratification | Face-to-Face Gratification |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Type | Digital, asynchronous or synchronous | Direct, synchronous |
| Emotional Connection | Moderate, relies on texts, images, videos | Strong, enhanced by physical presence and nonverbal cues |
| Accessibility | Global, 24/7 access | Local, time and location bound |
| Social Validation | Likes, shares, comments | Verbal praise, body language |
| Quality of Interaction | Varies; can be superficial or deep | Generally deeper, richer communication |
| Impact on Mental Health | Mixed; can cause anxiety or boost self-esteem | Usually positive; fosters empathy and reduces loneliness |
| Time Investment | Flexible, fits into daily schedule | Requires dedicated time commitment |
| Privacy | Public or semi-public interactions | Private, personal conversations |
Introduction to Social Media and Face-to-Face Gratification
Social media gratification offers instant access to diverse content, enabling you to fulfill social needs such as belonging, entertainment, and information on-demand. Face-to-face gratification involves direct interpersonal interactions that foster emotional support, empathy, and deeper relational bonds through physical presence and nonverbal cues. Understanding the differences between social media and face-to-face gratification highlights how each satisfies unique psychological and social desires, influencing how individuals balance online and offline communication.
The Psychology Behind Social Media Gratification
Social media gratification activates dopamine pathways by providing instant feedback through likes, comments, and shares, satisfying your need for social validation and connection. Unlike face-to-face gratification, which relies on physical presence and nonverbal cues, online interactions offer controlled, curated experiences that can enhance feelings of self-esteem and belonging. Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind social media gratification helps explain why digital engagement can be both rewarding and addictive.
The Dynamics of Face-to-Face Social Satisfaction
Face-to-face gratification provides immediate, multisensory feedback that strengthens emotional bonds and fosters deeper trust compared to social media interactions. The dynamics of face-to-face social satisfaction rely on nonverbal cues, such as tone, eye contact, and body language, which enhance empathy and understanding. While social media gratification offers convenience and broad connectivity, the richness and authenticity of direct human interaction remain paramount for sustained psychological well-being.
Emotional Impact: Online vs In-Person Interactions
Social media gratification provides instant emotional feedback through likes and comments, fostering a sense of connection, yet often lacks the depth of in-person communication. Face-to-face gratification engages multiple senses and non-verbal cues, creating richer emotional bonds and higher empathy, which You may find more fulfilling. Emotional impact in online interactions can be fleeting or superficial, whereas in-person interactions typically result in stronger, longer-lasting emotional satisfaction.
Instant Feedback: Digital Likes vs Real-Life Reactions
Instant feedback differs significantly between social media gratification and face-to-face gratification, with digital likes providing immediate but often superficial validation. Real-life reactions offer deeper emotional resonance and nonverbal cues, enhancing genuine connection and satisfaction. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate the complex dynamics of gratification in both digital and physical interactions.
Loneliness and Connectivity in Both Realms
Social media gratification often provides immediate but superficial connectivity, which can temporarily alleviate loneliness without fostering deep emotional bonds. Face-to-face gratification offers more meaningful interactions, promoting genuine emotional support and long-lasting social connections that effectively reduce feelings of loneliness. The balance between virtual and real-life engagements shapes individual experiences of social fulfillment and overall psychological well-being.
Depth of Relationships: Virtual vs Physical Connections
Social media gratification offers instant feedback and broad social reach, yet often lacks the emotional depth found in face-to-face interactions, which foster stronger trust and intimacy through nonverbal cues and shared presence. Face-to-face gratification enriches relationship quality by enabling deeper empathy and nuanced communication, critical for sustaining long-term bonds. The contrast highlights that while virtual connections facilitate quantity and convenience, physical interactions remain essential for cultivating profound and enduring relational depth.
The Role of Validation in Both Contexts
Validation plays a crucial role in both social media gratification and face-to-face gratification, influencing your emotional well-being and self-esteem. Social media gratification often relies on quantifiable metrics like likes, comments, and shares, providing instant but sometimes superficial validation. In contrast, face-to-face gratification offers deeper, more personalized validation through nuanced interactions, genuine empathy, and real-time feedback, fostering stronger emotional connections.
Mental Health Implications of Each Interaction Type
Social media gratification offers instant validation through likes and comments but often leads to superficial connections that may exacerbate feelings of loneliness and anxiety. Face-to-face gratification fosters deeper emotional bonds and empathy, significantly benefiting your mental health by reducing stress and promoting well-being. Understanding the distinct psychological impacts of each interaction type helps you manage your social engagement for optimal emotional balance.
Balancing Social Media and Face-to-Face Experiences
Balancing social media gratification and face-to-face gratification is essential to maintain healthy relationships and emotional well-being. Social media offers instant feedback, wider social reach, and continuous connectivity, while face-to-face interactions provide deeper emotional connections, nonverbal cues, and authentic communication. You can optimize your social experiences by allocating time for in-person activities to cultivate meaningful bonds, while using social media for broader social engagement and information sharing.
Infographic: Social Media Gratification vs Face-to-Face Gratification
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com