Ostracism involves actively excluding someone from social interactions, leading to feelings of rejection and isolation, while ignoring typically means withholding attention without direct exclusion. Explore the psychological impacts and differences between ostracism and ignoring in relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
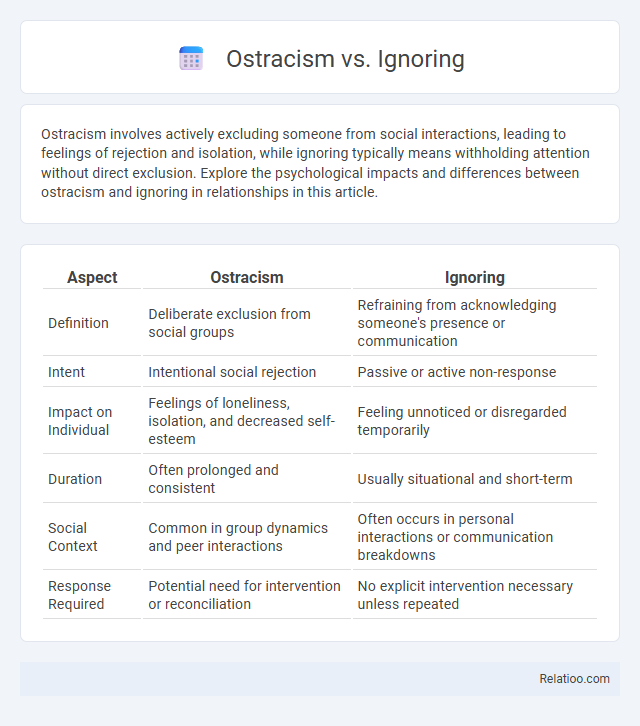
| Aspect | Ostracism | Ignoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate exclusion from social groups | Refraining from acknowledging someone's presence or communication |
| Intent | Intentional social rejection | Passive or active non-response |
| Impact on Individual | Feelings of loneliness, isolation, and decreased self-esteem | Feeling unnoticed or disregarded temporarily |
| Duration | Often prolonged and consistent | Usually situational and short-term |
| Social Context | Common in group dynamics and peer interactions | Often occurs in personal interactions or communication breakdowns |
| Response Required | Potential need for intervention or reconciliation | No explicit intervention necessary unless repeated |
Understanding Ostracism and Ignoring: Key Differences
Ostracism involves the deliberate exclusion of an individual from a social group, often characterized by active acts of rejection or shunning, whereas ignoring refers to the passive act of withholding attention without explicit rejection. Understanding ostracism centers on recognizing its psychological impact, such as feelings of loneliness and lowered self-esteem, as it signals social disapproval. Ignoring, while potentially hurtful, lacks the intentional exclusion factor and can occur unintentionally, making it less overtly damaging compared to ostracism.
Psychological Impact: Ostracism vs Ignoring
Ostracism deeply affects your psychological well-being by inducing feelings of social pain, rejection, and lowered self-esteem, often leading to anxiety and depression. Ignoring, while less intense, can cause feelings of neglect and invisibility, subtly impacting your emotional state and sense of belonging. Both experiences disrupt your need for social connection but ostracism triggers more severe psychological consequences due to its explicit social exclusion.
Social Dynamics: How Ostracism and Ignoring Affect Relationships
Ostracism involves the deliberate exclusion of an individual from social interactions, often leading to feelings of rejection and diminished self-worth, which can severely damage trust and intimacy in relationships. Ignoring, while less overt, creates social distance through neglecting communication or emotional responsiveness, potentially causing confusion and emotional withdrawal over time. Both ostracism and ignoring disrupt social dynamics by impairing emotional connection and exacerbating relational tension, but ostracism typically elicits stronger negative psychological effects and more pronounced social isolation.
Recognizing Signs: Ostracism vs Ignoring Behaviors
Recognizing signs of ostracism versus ignoring behaviors involves understanding the subtle social cues that differentiate exclusion and neglect. Ostracism often manifests through active exclusion from group activities, deliberate silence, or social isolation, signaling a clear intent to marginalize You. Ignoring, however, typically appears as passive neglect, such as lack of eye contact or failure to acknowledge presence, which can feel less intentional but equally painful over time.
Common Scenarios: When Ostracism or Ignoring Occurs
Ostracism often occurs in group settings such as workplaces, social circles, or online communities when an individual is deliberately excluded to enforce social norms or express disapproval. Ignoring typically happens in day-to-day interpersonal interactions, like avoiding eye contact or not responding to messages, signaling disinterest or mild conflict without overt exclusion. Your awareness of these scenarios can help you recognize and address subtle social dynamics affecting your relationships and well-being.
Coping Strategies for Ostracism and Ignoring
Coping strategies for ostracism and ignoring often involve seeking social support to restore a sense of belonging and self-worth. Cognitive reframing techniques help individuals reinterpret exclusion incidents, reducing emotional distress by focusing on alternative social connections or personal growth. Engaging in mindfulness and self-affirmation practices also mitigates the negative psychological impact of social rejection by enhancing emotional regulation and self-esteem.
Ostracism in the Workplace vs Everyday Life
Ostracism in the workplace involves deliberate exclusion of employees from group interactions, leading to decreased productivity, job satisfaction, and mental health issues, whereas ignoring often reflects passive neglect without intent to harm. In everyday life, ostracism similarly causes feelings of isolation and rejection, impacting social relationships and emotional well-being. Research highlights that workplace ostracism triggers unique stressors related to professional identity and economic security, differentiating it from general social exclusion.
Long-Term Consequences: Emotional and Mental Health Effects
Ostracism and ignoring both inflict significant long-term emotional and mental health consequences, including heightened feelings of loneliness, depression, and anxiety. While ignoring may cause temporary hurt and confusion, ostracism leads to more profound psychological damage by undermining your sense of belonging and self-worth over time. Recognizing these effects is crucial for addressing the impact of social exclusion on overall well-being.
Preventing Ostracism and Ignoring in Social Groups
Preventing ostracism and ignoring in social groups requires fostering inclusive communication and actively engaging all members to ensure everyone feels valued. Encouraging empathy, open dialogue, and conflict resolution skills helps reduce feelings of exclusion and promotes stronger group cohesion. Your role in maintaining respectful interactions and addressing signs of social neglect is essential for a supportive community environment.
Moving Forward: Rebuilding Connections After Exclusion
Rebuilding connections after exclusion requires understanding the distinct impacts of ostracism, ignoring, and social rejection on emotional well-being. You can foster meaningful reconnections by addressing feelings of isolation through open communication and empathy, promoting trust and mutual respect. Implementing consistent social engagement strategies helps overcome barriers created by exclusion and supports emotional healing.
Infographic: Ostracism vs Ignoring
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com