Social anxiety specifically involves intense fear of social situations and being judged by others, while general anxiety encompasses a broader range of worries and physical symptoms unrelated to social interactions. Discover more about the distinctions between social anxiety and general anxiety in this article.
Table of Comparison
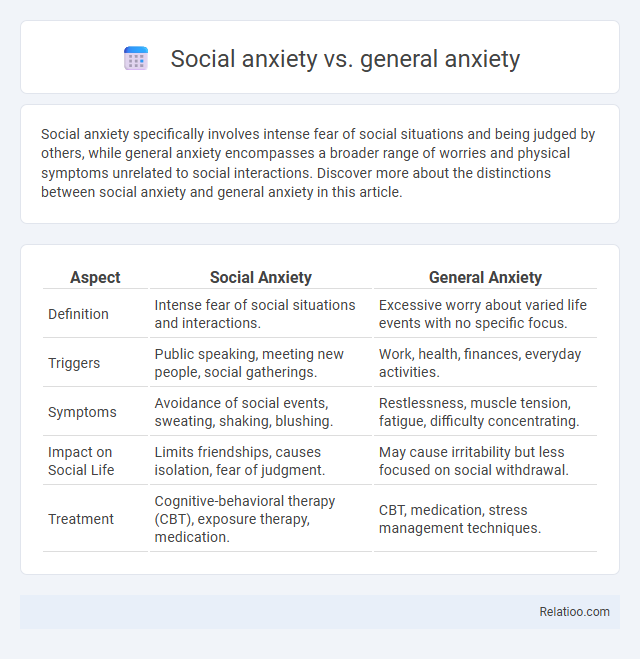
| Aspect | Social Anxiety | General Anxiety |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense fear of social situations and interactions. | Excessive worry about varied life events with no specific focus. |
| Triggers | Public speaking, meeting new people, social gatherings. | Work, health, finances, everyday activities. |
| Symptoms | Avoidance of social events, sweating, shaking, blushing. | Restlessness, muscle tension, fatigue, difficulty concentrating. |
| Impact on Social Life | Limits friendships, causes isolation, fear of judgment. | May cause irritability but less focused on social withdrawal. |
| Treatment | Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, medication. | CBT, medication, stress management techniques. |
Understanding Social Anxiety: Definition and Symptoms
Social anxiety is a specific disorder characterized by intense fear or avoidance of social situations due to the worry of being judged or embarrassed. General anxiety, or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), involves persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life without a specific focus on social interaction. Understanding social anxiety helps you recognize symptoms such as intense self-consciousness, fear of scrutiny, and physical signs like sweating or trembling that distinctly differentiate it from general anxiety.
What is General Anxiety? Key Features and Signs
General anxiety, also known as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), involves persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of daily life, unlike social anxiety which specifically centers on fear of social situations. Key features of GAD include chronic nervousness, restlessness, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. Your ability to manage stress may be compromised as these signs interfere with everyday functioning beyond social interaction concerns.
Core Differences Between Social Anxiety and General Anxiety
Social anxiety primarily revolves around intense fear and avoidance of social situations due to concerns about judgment or embarrassment, whereas general anxiety encompasses a broader and more persistent worry about various aspects of daily life, including health, work, and finances. Core differences include the triggers, with social anxiety focusing on interpersonal scenarios, while general anxiety disorder (GAD) involves excessive and uncontrollable worry about multiple domains without a specific focus. Physiological symptoms like blushing, sweating, and trembling often characterize social anxiety in social interactions, whereas general anxiety may manifest as muscle tension, restlessness, and fatigue across various situations.
Causes and Risk Factors: Social vs General Anxiety
Social anxiety often stems from a fear of social judgment, negative evaluation, or embarrassment in social situations, influenced by genetic predisposition, early childhood experiences, and learned behaviors. General anxiety, conversely, involves excessive worry about a wide range of everyday activities or events, with causes linked to a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors such as chronic stress and trauma. Understanding the distinct risk factors of social versus general anxiety helps you identify specific triggers and tailor effective coping strategies.
How Social Anxiety Impacts Daily Life
Social anxiety specifically affects Your ability to engage confidently in social interactions, causing intense fear of judgment or embarrassment that can lead to avoidance of social situations. Unlike general anxiety, which involves persistent worry across various aspects of life, social anxiety centers on social contexts and public performance. This struggle can disrupt daily activities such as work, school, and relationships, severely impacting Your overall quality of life.
General Anxiety: Effects on Overall Wellbeing
General anxiety significantly impacts your overall wellbeing by causing persistent worry, physical symptoms like fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, which can interfere with daily functioning. Unlike social anxiety, which specifically triggers fear in social interactions, general anxiety affects multiple areas of life, including work, relationships, and sleep quality. Understanding these distinctions helps in addressing anxiety effectively through tailored coping strategies and professional support.
Diagnosis: Identifying Social and General Anxiety Disorders
Diagnosing social anxiety involves evaluating persistent fear of social situations, embarrassment, or judgment, while general anxiety disorder (GAD) diagnosis centers on excessive, uncontrollable worry about various life aspects. Both require a detailed clinical assessment, including symptom duration and severity, but social anxiety emphasizes specific social triggers, unlike GAD's broader anxiety scope. Your healthcare provider will use standardized tools such as the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) or the Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item (GAD-7) scale to distinguish between these conditions accurately.
Treatment Options for Social Anxiety
Treatment options for social anxiety primarily include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors related to social situations, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as sertraline and paroxetine, which help regulate brain chemistry to reduce anxiety symptoms. Exposure therapy, a form of CBT, gradually introduces individuals to feared social scenarios to build confidence and decrease avoidance behaviors. Unlike general anxiety disorder, which may require broader treatment addressing multiple anxiety triggers, social anxiety treatment specifically targets social fears and improves interpersonal functioning.
Managing and Treating General Anxiety
General anxiety encompasses a broad range of worries and persistent feelings of tension, whereas social anxiety specifically involves intense fear of social situations and scrutiny. You can manage general anxiety through cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, and sometimes medication prescribed by a healthcare professional. Effective treatment focuses on identifying triggers, developing coping strategies, and gradually exposing yourself to anxiety-provoking situations to reduce symptoms over time.
Coping Strategies: Overcoming Both Social and General Anxiety
Coping strategies for social anxiety and general anxiety include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, and gradual exposure to anxiety-inducing situations. Social anxiety specifically benefits from social skills training and targeted exposure to social scenarios, while general anxiety management often involves relaxation techniques and lifestyle adjustments like regular exercise and balanced sleep. Combining these approaches enhances overall emotional resilience and reduces symptoms across both anxiety types.
Infographic: Social anxiety vs general anxiety
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com