Ostracism silently excludes individuals from social groups, while bullying involves overt aggression and intimidation to harm others. Discover the key differences and effects of ostracism and bullying in this article.
Table of Comparison
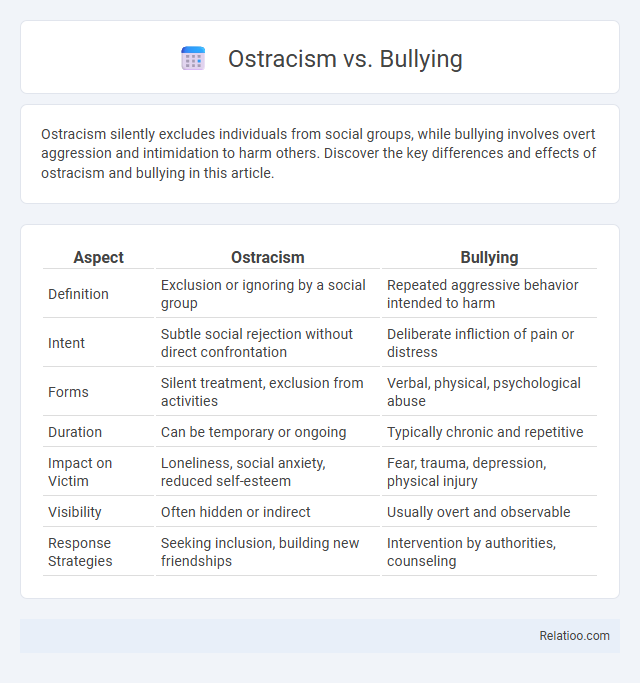
| Aspect | Ostracism | Bullying |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exclusion or ignoring by a social group | Repeated aggressive behavior intended to harm |
| Intent | Subtle social rejection without direct confrontation | Deliberate infliction of pain or distress |
| Forms | Silent treatment, exclusion from activities | Verbal, physical, psychological abuse |
| Duration | Can be temporary or ongoing | Typically chronic and repetitive |
| Impact on Victim | Loneliness, social anxiety, reduced self-esteem | Fear, trauma, depression, physical injury |
| Visibility | Often hidden or indirect | Usually overt and observable |
| Response Strategies | Seeking inclusion, building new friendships | Intervention by authorities, counseling |
Understanding Ostracism: Definition and Key Features
Ostracism involves the deliberate exclusion or ignoring of an individual by a group, characterized by silent treatment and social isolation that damages a person's sense of belonging and self-worth. Unlike bullying, which includes overt aggression and intimidation, ostracism operates through subtle, passive means to exclude without direct confrontation. Understanding ostracism helps you recognize its impact on mental health and the importance of fostering inclusive environments to counteract social rejection.
Bullying Explained: Core Characteristics and Forms
Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior intended to harm or dominate others, characterized by physical, verbal, or psychological abuse that creates a power imbalance. Core forms include direct bullying, such as hitting or name-calling, and indirect bullying, like spreading rumors or social exclusion. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize bullying's impact on individuals and implement effective prevention strategies.
Psychological Impact: Ostracism vs. Bullying
Ostracism leads to feelings of social exclusion, loneliness, and diminished self-worth by silently ignoring or excluding an individual, which can result in long-term emotional distress and anxiety. Bullying involves overt aggressive behaviors such as verbal abuse, threats, or physical violence, causing immediate psychological harm including depression, post-traumatic stress, and lowered self-esteem. While both ostracism and bullying severely impact mental health, bullying's explicit aggression often triggers more acute trauma, whereas ostracism induces chronic psychological pain through rejection and social isolation.
Social Dynamics: Inclusion, Exclusion, and Power
Ostracism involves the deliberate exclusion of an individual from social groups, undermining their sense of belonging and social identity, while bullying includes aggressive behavior that exerts power by causing harm or fear. Both ostracism and bullying operate through social dynamics where inclusion and exclusion serve as mechanisms for establishing dominance and control within group hierarchies. Understanding these processes highlights how power imbalances influence social interactions, with ostracism subtly eroding social ties compared to the overt intimidation tactics characteristic of bullying.
Signs and Symptoms: Detecting Ostracism and Bullying
Signs of ostracism include sudden social exclusion, ignored presence, and decreased group participation, while bullying manifests through aggressive behaviors such as verbal abuse, physical intimidation, and persistent harassment. You may notice victims of ostracism displaying withdrawal, anxiety, and feelings of loneliness, whereas bullied individuals often exhibit fear, low self-esteem, and visible distress. Detecting these behaviors early requires close observation of changes in social dynamics and emotional well-being to address both ostracism and bullying effectively.
Similarities Between Ostracism and Bullying
Ostracism and bullying both involve intentional behaviors that harm individuals by targeting their social standing and emotional well-being. You experience exclusion and rejection in ostracism, similar to the intimidation and humiliation found in bullying, which both undermine self-esteem and foster feelings of isolation. These behaviors share the core dynamic of power imbalance, where aggressors seek control by marginalizing or victimizing others within a group setting.
Key Differences: Ostracism vs. Bullying
Ostracism involves excluding or ignoring individuals as a social rejection tactic, whereas bullying encompasses repeated aggressive behavior intended to harm or intimidate. Key differences include ostracism's passive, indirect nature compared to bullying's active, intentional hostility. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective intervention strategies in social and workplace environments.
Coping Strategies for Victims
Victims of ostracism often cope by seeking social support and building new connections to counteract feelings of exclusion, while bullying victims benefit from assertiveness training and professional counseling to regain confidence and security. Techniques such as mindfulness and emotional regulation help individuals manage stress and reduce the psychological impact associated with both ostracism and bullying. Implementing organizational policies and promoting inclusive environments further empower victims by fostering a safer, more supportive social atmosphere.
Prevention Methods in Schools and Workplaces
Effective prevention methods for ostracism, bullying, and exclusion in schools and workplaces include implementing clear policies that define unacceptable behaviors and promote inclusivity. Training programs focused on empathy development, conflict resolution, and bystander intervention empower individuals to recognize and address harmful social dynamics early. Establishing support systems such as counseling services and peer support groups encourages reporting and provides assistance to victims, fostering a culture of respect and safety.
Long-Term Effects and Recovery Paths
Ostracism leads to long-term social isolation, impacting mental health by increasing feelings of loneliness and depression, while bullying induces anxiety, low self-esteem, and PTSD symptoms that persist if untreated. Recovery from ostracism involves rebuilding social connections and developing emotional resilience, whereas bullying recovery requires trauma-informed therapy and supportive environments to restore self-worth and safety. Both conditions benefit from early intervention and continuous psychological support to mitigate lasting psychological harm and promote reintegration into healthy social contexts.
Infographic: Ostracism vs Bullying
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com