Social anxiety involves intense fear of social situations and judgment, while introversion is a personality trait characterized by a preference for solitude and low social stimulation. Discover deeper insights into how social anxiety and introversion differ and overlap in this article.
Table of Comparison
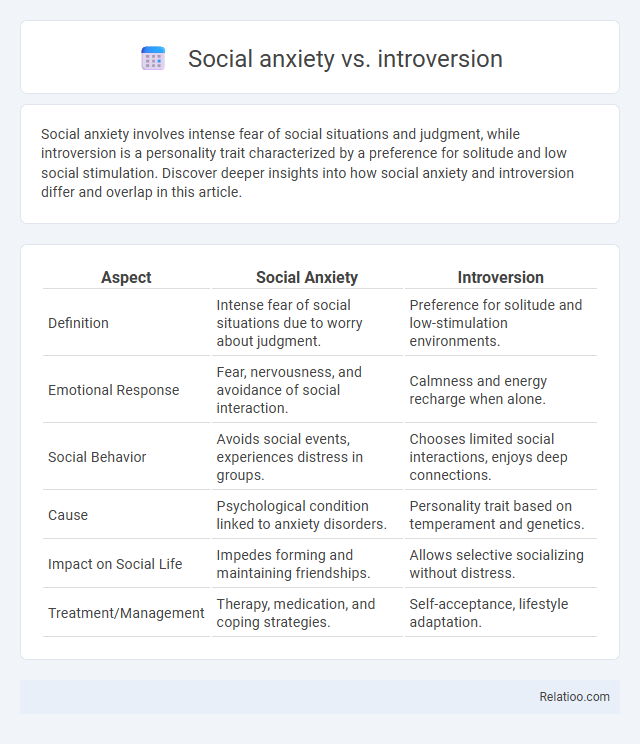
| Aspect | Social Anxiety | Introversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intense fear of social situations due to worry about judgment. | Preference for solitude and low-stimulation environments. |
| Emotional Response | Fear, nervousness, and avoidance of social interaction. | Calmness and energy recharge when alone. |
| Social Behavior | Avoids social events, experiences distress in groups. | Chooses limited social interactions, enjoys deep connections. |
| Cause | Psychological condition linked to anxiety disorders. | Personality trait based on temperament and genetics. |
| Impact on Social Life | Impedes forming and maintaining friendships. | Allows selective socializing without distress. |
| Treatment/Management | Therapy, medication, and coping strategies. | Self-acceptance, lifestyle adaptation. |
Understanding Social Anxiety: Definition and Symptoms
Social anxiety is a chronic mental health condition characterized by intense fear and avoidance of social situations due to the fear of judgment or embarrassment, distinguishing it from introversion, which is a personality trait marked by a preference for solitude or small groups without distress. Symptoms of social anxiety include rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, and difficulty speaking in social settings, often leading to significant impairment in daily life. Understanding these symptoms helps you recognize when social discomfort is more than shyness or introversion, requiring professional support.
What Is Introversion? Traits and Characteristics
Introversion is characterized by a preference for solitary activities and a need to recharge energy through quiet reflection rather than social interaction. Traits include deep thinking, reserved behavior, and a strong focus on internal thoughts and feelings. While social anxiety involves fear and avoidance of social situations, introversion is simply a personality trait that doesn't necessarily involve discomfort in social settings; understanding your introverted nature helps you manage social energy effectively.
Social Anxiety vs Introversion: Key Differences
Social anxiety is a mental health condition characterized by intense fear of social situations and being negatively judged, while introversion is a personality trait marked by a preference for solitude and quiet environments. You may experience discomfort or avoidance in social settings due to social anxiety, whereas introverts might enjoy social interactions but require time alone to recharge. Understanding these key differences helps in recognizing when professional support is needed versus personal lifestyle preferences.
Common Misconceptions About Social Anxiety and Introversion
Social anxiety and introversion are often misunderstood as the same, but social anxiety is a mental health disorder involving intense fear of social situations and judgment, whereas introversion is a personality trait characterized by a preference for solitary or low-stimulation environments. Common misconceptions about social anxiety include the belief that introverts are always socially anxious or that introversion indicates social dysfunction, which is not accurate. Understanding these distinctions helps you recognize that introversion is a natural trait, while social anxiety requires specific attention and management.
Causes of Social Anxiety and Introversion
Social anxiety stems from a combination of genetic predisposition, brain chemistry, and environmental factors such as traumatic social experiences or excessive parental criticism. Introversion is primarily a personality trait influenced by hereditary factors and neurological makeup, characterized by a preference for solitary activities and lower social stimulation. Understanding the distinct causes behind your social anxiety and introversion can help tailor effective coping strategies and support your mental well-being.
How Social Anxiety Affects Daily Life
Social anxiety significantly impacts daily life by causing intense fear of social interactions, leading to avoidance of activities such as work meetings, social gatherings, and even routine errands. Unlike introversion, which is characterized by a preference for solitude or small groups without distress, social anxiety triggers debilitating worry about judgment and embarrassment. This persistent fear can impair relationships, reduce professional opportunities, and contribute to symptoms of depression and low self-esteem.
Navigating Relationships: Introverts vs Socially Anxious Individuals
Introverts naturally prefer solitude or small group interactions, finding energy in quieter environments, while socially anxious individuals experience intense fear or avoidance of social situations due to worry about judgment or embarrassment. Navigating relationships can be challenging for socially anxious individuals, as their anxiety may inhibit communication and trust-building, whereas introverts may simply need downtime without fearing social evaluation. Understanding these distinctions helps tailor support strategies, emphasizing gradual exposure and confidence-building for social anxiety, and respecting personal space for introversion.
Coping Strategies for Social Anxiety and Introversion
Coping strategies for social anxiety often include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure techniques, and mindfulness practices to reduce fear in social situations, while introversion coping focuses on managing energy through planned social interactions and self-reflection. People with social anxiety benefit from gradual social exposure and anxiety-reduction exercises, whereas introverts thrive by balancing solitude with meaningful social engagement. Both groups find benefit in building strong support networks and practicing assertiveness to enhance social confidence.
When to Seek Help: Recognizing Severe Social Anxiety
Severe social anxiety manifests as intense fear of social situations that disrupt daily life and relationships, distinguishing it from introversion, which involves a preference for solitude without significant distress. Recognizing symptoms such as persistent avoidance, physical reactions like sweating or trembling, and impaired functioning in work or school settings signals the need to seek professional help. Early intervention with therapy or medication can significantly improve quality of life and prevent worsening of social anxiety disorder.
Embracing Your Personality: Thriving as an Introvert or with Social Anxiety
Embracing your personality involves recognizing the distinct traits of social anxiety and introversion without conflating the two; social anxiety is characterized by intense fear of social judgment, while introversion reflects a preference for solitary or low-stimulation environments. Thriving as an introvert means leveraging strengths like deep focus and thoughtful reflection, whereas managing social anxiety requires strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and gradual exposure to social situations. Understanding and honoring these differences empowers individuals to cultivate self-acceptance and develop personalized coping mechanisms, ultimately enhancing social confidence and overall well-being.
Infographic: Social anxiety vs introversion
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com