Ostracism involves passive social exclusion, while shunning actively rejects and isolates an individual, often with punitive intent. Discover the key differences and psychological impacts of both in this article.
Table of Comparison
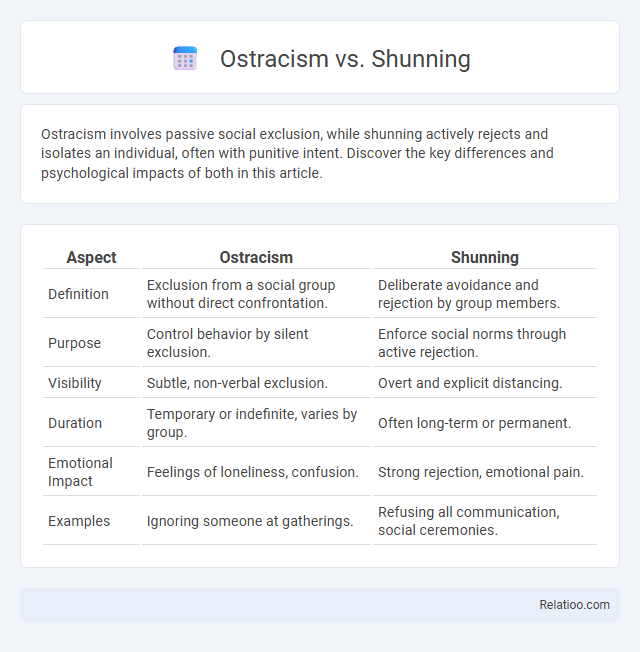
| Aspect | Ostracism | Shunning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exclusion from a social group without direct confrontation. | Deliberate avoidance and rejection by group members. |
| Purpose | Control behavior by silent exclusion. | Enforce social norms through active rejection. |
| Visibility | Subtle, non-verbal exclusion. | Overt and explicit distancing. |
| Duration | Temporary or indefinite, varies by group. | Often long-term or permanent. |
| Emotional Impact | Feelings of loneliness, confusion. | Strong rejection, emotional pain. |
| Examples | Ignoring someone at gatherings. | Refusing all communication, social ceremonies. |
Defining Ostracism and Shunning
Ostracism refers to the social exclusion of an individual by a group, often characterized by ignoring or excluding them from social interactions without direct confrontation. Shunning involves a more deliberate and active rejection, where the group members avoid all forms of contact and communication with the targeted person to enforce social or moral norms. Both practices function as mechanisms of social control, but ostracism tends to be subtle and passive, whereas shunning is overt and intentional.
Historical Origins of Ostracism
Ostracism originated in ancient Athens as a democratic practice allowing citizens to vote annually to exile a person for ten years to protect the city-state from potential tyrants or threats. Historically, this legal procedure involved inscribing names on pottery shards called ostraka, reflecting its deep roots in Athenian civic governance and political culture. Unlike shunning, which is a social or religious exclusion, ostracism served as a formal mechanism codified within the political system of classical Greece.
The Roots and Evolution of Shunning
Shunning originated from religious and social mechanisms designed to enforce conformity and maintain group cohesion by excluding noncompliant members. Its evolution reflects shifts from formal, communal punishments to more individualized and culturally embedded practices that impact social identity and personal relationships. Understanding the roots of shunning helps you recognize its enduring role in regulating behavior within diverse societies.
Key Differences Between Ostracism and Shunning
Ostracism involves excluding an individual from a group or society by ignoring or ignoring their presence, often without direct confrontation, while shunning actively involves avoiding and rejecting the person through explicit actions and social isolation. Ostracism is typically a passive and indirect social control mechanism, whereas shunning is an active, deliberate process aiming to punish or reform the individual. Your understanding of these distinctions helps navigate social dynamics and responses within various cultural or community contexts.
Psychological Impact on Individuals
Ostracism, shunning, and exile each inflict profound psychological impacts, often leading to feelings of rejection, isolation, and diminished self-worth. You may experience heightened anxiety, depression, or a fractured sense of identity as social bonds are severed through these forms of social exclusion. The emotional distress from being excluded in these ways can undermine mental health and disrupt interpersonal relationships, emphasizing the critical need for social connection to psychological well-being.
Social Consequences in Communities
Ostracism, shunning, and exclusion each result in significant social consequences within communities, impacting individuals' sense of belonging and mental health. Ostracism typically leads to invisibility and emotional distress, while shunning often involves active avoidance and can cause social isolation and stigma. Both practices disrupt social cohesion and trust, potentially weakening community bonds and amplifying feelings of marginalization.
Ostracism in Modern Society
Ostracism in modern society refers to the deliberate exclusion of individuals from social groups or communities, often leading to emotional distress and social isolation. Unlike shunning, which is typically rooted in religious or cultural practices, ostracism is more broadly applied across various social and professional environments, impacting Your mental health and social well-being. Understanding the psychological effects of ostracism helps address the issues of loneliness and alienation prevalent in contemporary digital and physical interactions.
Shunning in Religious and Cultural Contexts
Shunning in religious and cultural contexts functions as a social and spiritual disciplinary tool, primarily aimed at enforcing conformity and maintaining group purity by excluding individuals who deviate from established norms or beliefs. Unlike ostracism, which broadly involves social exclusion, and basic ostracism, often a temporary or informal act, shunning is a formalized practice embedded in communities like the Amish, Jehovah's Witnesses, and certain Hindu castes, where it extends beyond social rejection to include prohibitions on communication, commerce, and communal participation. This systematic exclusion reinforces internal cohesion, deters dissent, and sustains the authority of religious or cultural leadership through the threat of intense and prolonged isolation.
Coping Strategies for Victims
Victims of ostracism and shunning often employ coping strategies such as seeking social support from trusted friends or online communities to counteract isolation. Developing resilience through mindfulness and cognitive behavioral techniques helps mitigate the emotional impact by reframing negative experiences and reducing stress. Engaging in new social activities or support groups fosters a sense of belonging, which is crucial for emotional recovery and restoring self-esteem.
Prevention and Resolution Techniques
Ostracism and shunning are social exclusion tactics that can significantly impact mental health, making prevention through open communication and empathy crucial. To resolve ostracism, encouraging inclusive environments and promoting conflict resolution skills helps reintegrate individuals into social groups. Your proactive approach to fostering understanding and addressing underlying issues can prevent the harmful effects of both ostracism and shunning.
Infographic: Ostracism vs Shunning
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com