Conformity often pressures individuals to align with group norms, while individuality empowers unique self-expression and personal values. Explore the balance between these dynamics in relationships by reading this article.
Table of Comparison
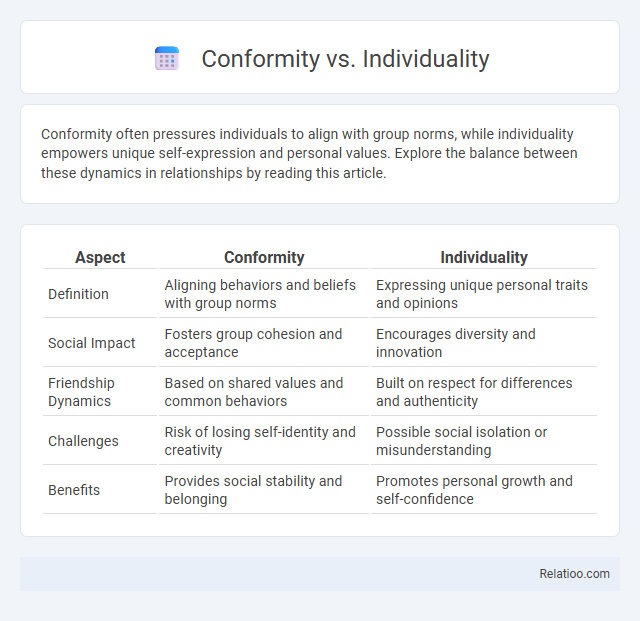
| Aspect | Conformity | Individuality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Aligning behaviors and beliefs with group norms | Expressing unique personal traits and opinions |
| Social Impact | Fosters group cohesion and acceptance | Encourages diversity and innovation |
| Friendship Dynamics | Based on shared values and common behaviors | Built on respect for differences and authenticity |
| Challenges | Risk of losing self-identity and creativity | Possible social isolation or misunderstanding |
| Benefits | Provides social stability and belonging | Promotes personal growth and self-confidence |
Understanding Conformity: Definition and Origins
Understanding conformity involves recognizing its definition as the act of aligning attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors with group norms, often driven by social pressure or the desire for acceptance. Originating from foundational studies in social psychology, conformity is influenced by cultural, situational, and psychological factors that shape how individuals respond to group dynamics. Your awareness of these underlying mechanisms helps navigate the balance between maintaining individuality and adapting within group settings.
Individuality Explained: What Sets Us Apart
Individuality is defined by unique personality traits, values, and beliefs that distinguish you from others in social groups. Unlike conformity, which involves aligning behaviors to group norms, individuality emphasizes authentic self-expression and personal autonomy. Understanding individuality within group dynamics highlights the balance between maintaining your distinct identity while navigating social influences.
Historical Perspectives on Conformity and Individuality
Historical perspectives on conformity and individuality highlight shifts from collectivist societies, where conformity maintained social order, to Enlightenment ideals emphasizing personal freedom and self-expression. Early social structures prioritized group cohesion, often suppressing individual dissent to ensure survival and stability. The evolution of these concepts shaped modern attitudes, balancing societal norms with the value of individual identity within group dynamics.
Psychological Drivers Behind Conformity
Psychological drivers behind conformity include the need for social acceptance, fear of rejection, and desire to avoid conflict, which compel individuals to align their attitudes and behaviors with group norms. Social identity theory highlights how individuals derive self-esteem from group membership, reinforcing conformity to maintain group cohesion. Informational influence leads people to conform when they perceive the group's knowledge as superior, especially in ambiguous situations.
The Benefits and Drawbacks of Following the Crowd
Following the crowd can enhance social cohesion and provide a sense of belonging, promoting stability within group dynamics. However, conformity may suppress individuality, leading to diminished creativity and critical thinking. This balance between social harmony and personal expression significantly influences decision-making processes and group performance.
The Role of Individuality in Personal Growth
Individuality serves as a cornerstone in personal growth by fostering self-awareness, creativity, and authentic decision-making that resist blind conformity. Embracing your unique traits enables the development of critical thinking skills essential to navigating and positively influencing group dynamics. Prioritizing individuality within social contexts encourages personal empowerment and the cultivation of meaningful relationships grounded in mutual respect.
Social Pressures: Balancing Group Norms and Self-Expression
Social pressures often challenge your ability to balance conformity with individuality, influencing how you navigate group dynamics. Adhering to group norms can strengthen social bonds but may suppress personal expression, while asserting individuality risks social exclusion. Understanding these tensions helps in managing your identity within social contexts effectively.
Cultural Influences: How Societies Shape Conformity and Individuality
Cultural influences significantly shape the balance between conformity and individuality within group dynamics by establishing societal norms and values that dictate acceptable behavior. Collectivist cultures tend to emphasize conformity and interdependence to maintain social harmony, while individualistic societies prioritize personal expression and autonomy, encouraging distinct identities. These cultural frameworks affect how individuals negotiate their roles in groups, influencing social cohesion, decision-making processes, and conflict resolution patterns.
Real-Life Examples: Conformity vs Individuality in Action
Real-life examples of conformity vs individuality in action often emerge in workplace settings, where employees may follow group norms to maintain harmony while risking the suppression of unique ideas that drive innovation. Social experiments like Solomon Asch's conformity tests reveal how peer pressure can compel individuals to align with majority opinions despite personal beliefs. Understanding these dynamics helps you navigate group interactions by balancing the benefits of collaboration with the importance of authentic self-expression.
Finding Harmony: Embracing Uniqueness Within Community
Finding harmony within community involves balancing conformity with individuality by recognizing how your unique traits contribute to group dynamics. Embracing your authenticity while respecting shared values fosters collaboration and innovation, allowing both personal growth and collective success. This balance enhances social cohesion and empowers diverse perspectives to thrive in a supportive environment.
Infographic: Conformity vs Individuality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com