Indifference reflects a lack of emotional interest or concern in a relationship, while neutrality signifies an impartial and balanced stance without bias or preference. Discover how understanding the subtle distinction between indifference and neutrality can improve interpersonal connections in this article.
Table of Comparison
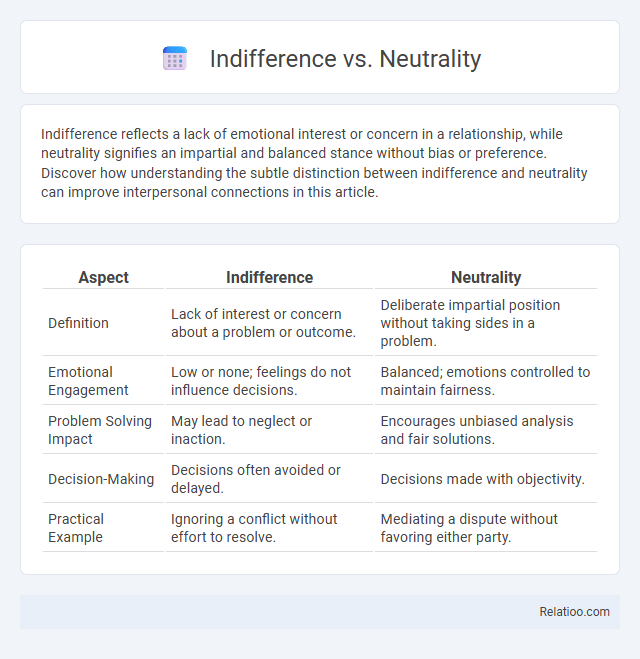
| Aspect | Indifference | Neutrality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lack of interest or concern about a problem or outcome. | Deliberate impartial position without taking sides in a problem. |
| Emotional Engagement | Low or none; feelings do not influence decisions. | Balanced; emotions controlled to maintain fairness. |
| Problem Solving Impact | May lead to neglect or inaction. | Encourages unbiased analysis and fair solutions. |
| Decision-Making | Decisions often avoided or delayed. | Decisions made with objectivity. |
| Practical Example | Ignoring a conflict without effort to resolve. | Mediating a dispute without favoring either party. |
Understanding Indifference and Neutrality
Indifference refers to a lack of interest or concern toward a particular issue, characterized by emotional detachment and apathy. Neutrality involves maintaining an unbiased position, refraining from taking sides or expressing opinions in a conflict or debate. Understanding indifference requires recognizing the absence of emotional investment, whereas neutrality emphasizes objective balance without endorsing any viewpoint.
Defining Indifference: What Does It Mean?
Indifference refers to a lack of interest, concern, or emotional investment in a particular subject, event, or outcome, characterized by an absence of preference or bias. Unlike neutrality, which implies a deliberate choice to remain impartial or unbiased in a conflict or debate, indifference embodies apathy and disengagement without active judgment. Understanding indifference involves recognizing its psychological and behavioral dimensions, where individuals neither support nor oppose a matter, often resulting in passive response or inaction.
Exploring the Concept of Neutrality
Neutrality denotes a deliberate stance of impartiality, refraining from favoring any side in a conflict or debate, unlike indifference, which implies a lack of interest or concern. It requires conscious effort to maintain balance and avoid bias, often observed in diplomatic relations, legal proceedings, and journalistic integrity. Understanding neutrality is crucial for fostering trust and credibility in environments demanding fairness and objective judgment.
Emotional Implications of Indifference
Indifference reflects a lack of emotional engagement or concern toward a particular situation, often resulting in feelings of detachment or apathy. Neutrality implies an unbiased position without emotional involvement, maintaining an objective stance without favor or opposition. Understanding these distinctions clarifies how Your emotional response--or lack thereof--shapes interactions and decision-making in various contexts.
The Role of Neutrality in Conflict
Neutrality plays a critical role in conflict resolution by ensuring impartiality and fostering trust among opposing parties, contrasting with indifference, which implies a lack of concern or engagement. Unlike indifference, neutrality actively involves maintaining a balanced stance without favoring any side, enabling mediators to facilitate dialogue and negotiations effectively. Recognizing the distinction helps clarify that neutrality supports constructive conflict management while indifference can exacerbate tensions by ignoring underlying issues.
Indifference vs Neutrality: Key Differences
Indifference refers to a lack of interest, concern, or preference towards a particular issue, leading to emotional detachment or apathy. Neutrality implies an intentional, balanced stance without taking sides, often adopted to maintain impartiality in conflicts or debates. Unlike indifference, neutrality is a deliberate position that respects all viewpoints without bias, while indifference often reflects disengagement or disregard.
Social and Ethical Impact of Indifference
Indifference in social and ethical contexts often results in the neglect of moral responsibilities, leading to the perpetuation of injustice and suffering by failing to address or challenge harmful behaviors. Unlike neutrality, which implies an impartial stance in conflicts or debates, indifference signifies a lack of concern or emotional engagement, which can erode social cohesion and empathy within communities. This apathetic attitude undermines ethical accountability and can contribute to systemic inequalities by allowing harmful conditions to persist unchallenged.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Being Neutral
Being neutral allows individuals or organizations to avoid conflicts and maintain unbiased positions, which can foster trust and facilitate dialogue among opposing parties. However, neutrality may also lead to perceptions of passivity or lack of commitment, potentially resulting in missed opportunities to influence outcomes or advocate for ethical principles. While indifference implies a lack of concern and engagement, true neutrality requires active balance and awareness, which can be both strategically beneficial and challenging to sustain.
Real-World Examples: Indifference vs Neutrality
Indifference means lacking interest or concern, such as a bystander ignoring a car accident, while neutrality reflects a deliberate choice not to take sides, like Switzerland's stance during most conflicts. Your understanding of these concepts deepens when recognizing that indifference often leads to passivity, whereas neutrality involves active non-alignment despite awareness. Real-world examples highlight that indifference can perpetuate problems, whereas neutrality aims to maintain impartiality without bias.
Choosing Between Indifference and Neutrality
Choosing between indifference and neutrality involves understanding their impact on decision-making and ethical stance. Indifference implies a lack of concern or interest, often leading to apathy or inaction, while neutrality signifies an unbiased position that avoids taking sides but remains engaged. Opting for neutrality can preserve impartiality and credibility in disputes, whereas indifference risks alienation and missed opportunities for influence or resolution.
Infographic: Indifference vs Neutrality
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com