Listening comprehension enhances real-time understanding and emotional connection in relationships, while reading comprehension improves interpretive skills and critical analysis of written emotions. Explore this article to discover how mastering both can strengthen your communication and deepen your relational bonds.
Table of Comparison
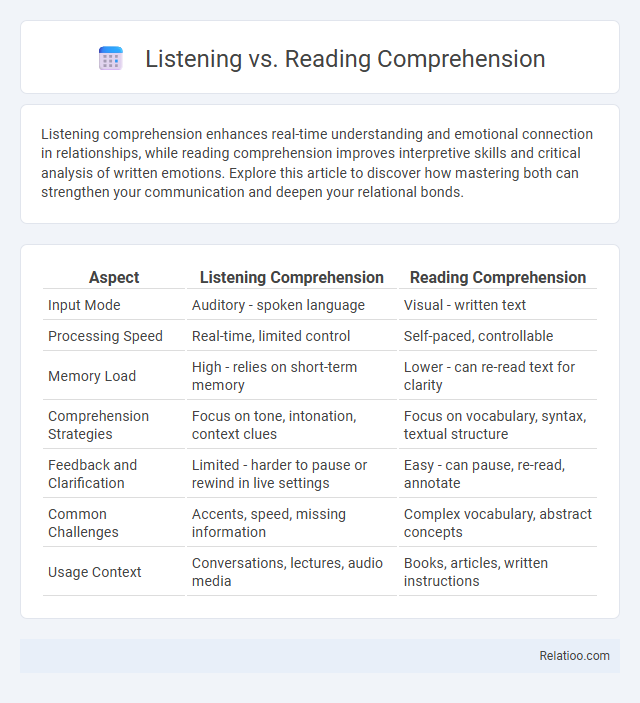
| Aspect | Listening Comprehension | Reading Comprehension |
|---|---|---|
| Input Mode | Auditory - spoken language | Visual - written text |
| Processing Speed | Real-time, limited control | Self-paced, controllable |
| Memory Load | High - relies on short-term memory | Lower - can re-read text for clarity |
| Comprehension Strategies | Focus on tone, intonation, context clues | Focus on vocabulary, syntax, textual structure |
| Feedback and Clarification | Limited - harder to pause or rewind in live settings | Easy - can pause, re-read, annotate |
| Common Challenges | Accents, speed, missing information | Complex vocabulary, abstract concepts |
| Usage Context | Conversations, lectures, audio media | Books, articles, written instructions |
Understanding Listening and Reading Comprehension
Understanding listening comprehension involves the ability to accurately interpret spoken language, focusing on phonetics, intonation, and context clues to grasp meaning. Reading comprehension requires decoding written text, recognizing vocabulary, syntax, and textual structures for effective interpretation. Both skills engage different cognitive processes essential for overall comprehension, yet listening involves real-time processing, whereas reading allows for reanalysis and deeper reflection.
Cognitive Processes Behind Listening and Reading
Listening and reading comprehension engage distinct cognitive processes, with listening relying heavily on auditory processing, working memory, and real-time interpretation of spoken language. Reading comprehension predominantly involves visual decoding, semantic integration, and the activation of prior knowledge through text analysis. Your understanding improves as your brain efficiently coordinates these different cognitive functions tailored to either auditory or visual input.
Key Differences Between Listening and Reading
Listening comprehension involves understanding spoken language through auditory processing, requiring you to decode accents, intonation, and pace in real time. Reading comprehension relies on visual recognition of written text, allowing more time to analyze vocabulary, sentence structures, and contextual clues. Key differences include the immediacy and transient nature of spoken words in listening, contrasted with the permanence and re-readability of written content in reading.
The Role of Context in Comprehension
Context plays a crucial role in both listening and reading comprehension by providing background information that helps decode meaning and infer intent. In listening comprehension, auditory cues such as tone, intonation, and pauses enhance understanding, while reading comprehension relies heavily on textual structure, vocabulary, and contextual clues within the written material. Your ability to effectively use context enables deeper comprehension across modalities by connecting new information to existing knowledge and guiding interpretation.
Challenges Unique to Listening Comprehension
Listening comprehension presents unique challenges compared to reading comprehension, such as the inability to pause or reread spoken content, requiring quick processing of auditory information in real-time. You must rely on tone, intonation, and context to derive meaning, which can be difficult when unfamiliar accents or background noise interfere. These factors demand heightened concentration and adaptive listening strategies to accurately understand and retain spoken language.
Challenges Unique to Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension presents unique challenges such as decoding complex vocabulary, interpreting written context without verbal cues, and managing cognitive load during sustained text analysis. Unlike listening comprehension, which relies on auditory processing and immediate contextual feedback, reading requires You to synthesize explicit and implicit information independently, often demanding stronger inferencing skills. Mastering reading comprehension improves overall comprehension by enabling deeper engagement with nuanced written content, critical for academic success and information retention.
Strategies for Improving Listening Skills
Effective strategies for improving listening skills include active listening, note-taking, and engaging in interactive practice such as discussions or audio exercises. Utilizing multimedia resources like podcasts, audiobooks, and language learning apps enhances auditory comprehension and retention. Consistent exposure to diverse accents and speech speeds further develops the ability to understand spoken language in various contexts.
Strategies for Enhancing Reading Skills
Improving your reading comprehension requires strategies such as active reading, annotating texts, and expanding vocabulary to better decode and understand written material. Unlike listening comprehension, which relies on auditory cues and immediate processing, reading comprehension allows for re-reading and deeper analysis, enhancing retention and critical thinking. Employing techniques like summarizing paragraphs, questioning the content, and visualizing information fosters stronger connections and more effective comprehension of complex texts.
Technologies Supporting Comprehension Development
Technologies supporting comprehension development leverage AI-powered tools to enhance listening, reading, and overall comprehension skills through personalized content and real-time feedback. Tools like speech recognition software, audiobooks with synchronized text, and interactive reading platforms help you engage multisensory learning pathways, improving retention and understanding. Advanced analytics track progress across listening and reading tasks, offering adaptive exercises that target specific comprehension challenges.
Integrating Listening and Reading for Effective Learning
Listening comprehension enhances your ability to process spoken language in real-time, while reading comprehension strengthens understanding of written text and vocabulary. Integrating listening and reading activities builds a more robust language foundation by reinforcing context, improving retention, and exposing learners to diverse linguistic structures. This combined approach accelerates learning efficiency and supports deeper cognitive connections for mastering comprehension skills.
Infographic: Listening vs Reading Comprehension
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com