Listening for inference involves understanding implied meanings beyond spoken words, while listening for details focuses on accurately capturing specific facts and information. Explore this article to deepen your skills in distinguishing between these crucial listening strategies.
Table of Comparison
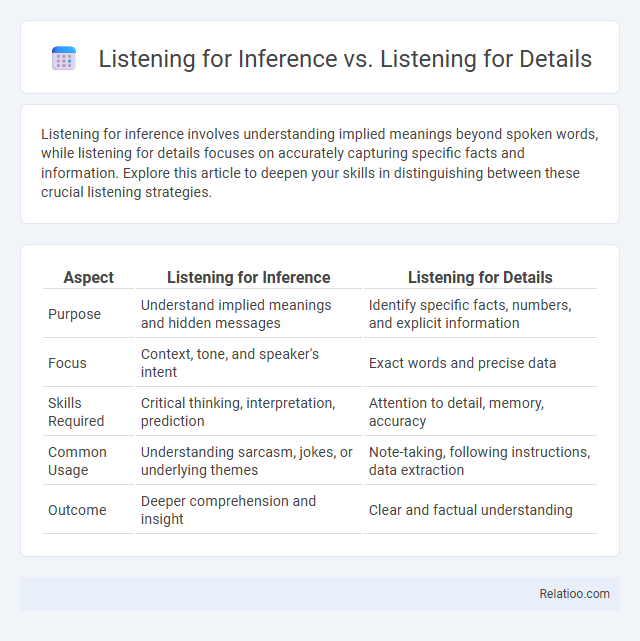
| Aspect | Listening for Inference | Listening for Details |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Understand implied meanings and hidden messages | Identify specific facts, numbers, and explicit information |
| Focus | Context, tone, and speaker's intent | Exact words and precise data |
| Skills Required | Critical thinking, interpretation, prediction | Attention to detail, memory, accuracy |
| Common Usage | Understanding sarcasm, jokes, or underlying themes | Note-taking, following instructions, data extraction |
| Outcome | Deeper comprehension and insight | Clear and factual understanding |
Introduction to Listening Skills
Listening for inference involves interpreting underlying meanings beyond the spoken words, while listening for details requires focusing on specific facts or information presented in the conversation. Developing your listening skills includes mastering both techniques to effectively comprehend and respond during communication. Enhancing these abilities helps you discern implied messages and accurately recall critical details, improving overall understanding.
Defining Listening for Inference
Listening for inference involves interpreting underlying meanings and drawing conclusions based on subtle cues beyond explicit statements. This skill contrasts with listening for details, which emphasizes grasping specific facts or information presented directly. Mastering inference enhances critical thinking by enabling deeper understanding and context recognition in communication.
Understanding Listening for Details
Listening for details involves focusing on specific pieces of information such as dates, names, numbers, and facts, which are essential for accurate comprehension and recall. You enhance your understanding by identifying these key elements, distinguishing them from general context or implied meanings found in listening for inference. Developing strong skills in listening for details supports clearer communication and better decision-making in both academic and professional settings.
Key Differences Between Inference and Details Listening
Listening for inference involves interpreting underlying meanings and drawing conclusions beyond the spoken words, whereas listening for details focuses on accurately capturing specific facts and explicit information. Your ability to distinguish implicit messages relies on inference skills, while detail listening ensures precision in recalling exact data such as dates, names, or numbers. Understanding these key differences improves comprehension by balancing analytical thinking with attentive information gathering.
Importance of Listening for Inference in Communication
Listening for inference enhances communication by allowing the listener to grasp underlying meanings, emotions, and intentions beyond explicit words. This skill bridges gaps between spoken details and unspoken context, fostering deeper understanding and more effective responses. Mastering inference in listening sharpens critical thinking and empathetic engagement, essential for resolving conflicts and building trust in interpersonal interactions.
The Role of Details in Effective Listening
Details serve as the foundation for effective listening by providing concrete information that supports accurate inference. When you listen attentively to details, your brain gathers essential clues that enable deeper understanding beyond surface-level information. Distinguishing between listening for details and making inferences enhances comprehension and allows for more meaningful responses in communication.
Strategies to Improve Inference Listening Skills
Improving inference listening skills involves focusing on understanding implied meanings beyond the explicit details by actively connecting background knowledge with contextual clues. Employ techniques such as predicting outcomes, asking inferential questions, and noting tone or emphasis to grasp underlying messages effectively. Practicing with diverse audio materials and summarizing inferred content enhances the ability to distinguish between surface details and deeper implications.
Techniques to Enhance Listening for Details
Listening for details requires focusing on specific information such as dates, names, and numbers, enabling accurate understanding and recall. Techniques to enhance this skill include active note-taking, repeated listening, and summarizing key points to reinforce memory. Sharpening your ability to distinguish between spoken nuances and explicit facts improves comprehension and critical analysis in various contexts.
Real-Life Examples: Inference vs Details Listening
Listening for inference involves interpreting implied meanings and reading between the lines in conversations, such as discerning a colleague's dissatisfaction from their tone rather than explicit complaints. Listening for details requires focusing on specific facts or information, like remembering a customer's exact order or instructions during a meeting. In real-life scenarios, distinguishing between inference and detail listening helps improve communication accuracy, ensuring both overt information and subtle cues are understood.
Choosing the Right Listening Approach for Different Contexts
Selecting the appropriate listening approach depends on the context and purpose of information gathering. Listening for details emphasizes capturing specific facts and data points, ideal for instructions or factual information. Listening for inference requires interpreting underlying meanings and reading between the lines, essential for understanding intentions, emotions, or implied messages in conversations.
Infographic: Listening for Inference vs Listening for Details
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com