Defensive listening occurs when a person perceives criticism and responds protectively, while selective listening involves focusing only on parts of a message that interest or confirm existing beliefs. Discover effective strategies to improve communication by understanding these listening behaviors in this article.
Table of Comparison
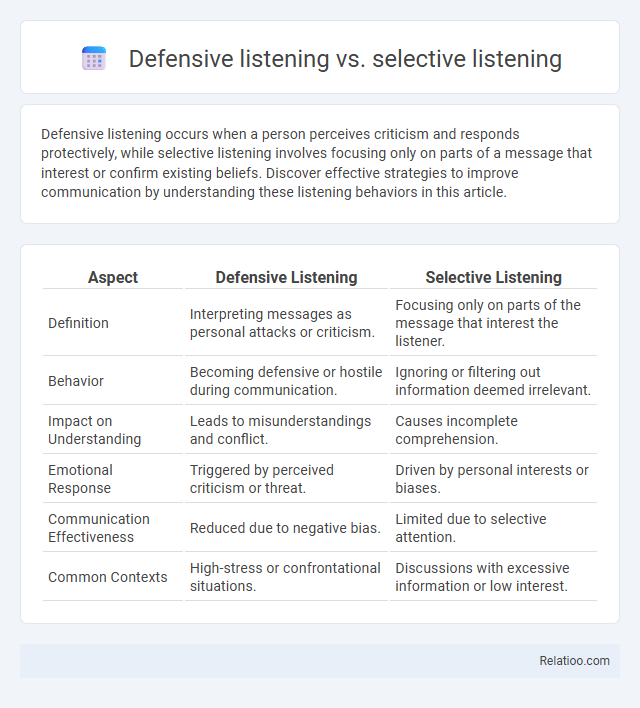
| Aspect | Defensive Listening | Selective Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interpreting messages as personal attacks or criticism. | Focusing only on parts of the message that interest the listener. |
| Behavior | Becoming defensive or hostile during communication. | Ignoring or filtering out information deemed irrelevant. |
| Impact on Understanding | Leads to misunderstandings and conflict. | Causes incomplete comprehension. |
| Emotional Response | Triggered by perceived criticism or threat. | Driven by personal interests or biases. |
| Communication Effectiveness | Reduced due to negative bias. | Limited due to selective attention. |
| Common Contexts | High-stress or confrontational situations. | Discussions with excessive information or low interest. |
Understanding Defensive Listening
Defensive listening occurs when you perceive comments as personal attacks, causing emotional reactions rather than objective understanding, which hinders effective communication. Selective listening involves hearing only parts of the conversation that match your beliefs, leading to misinterpretation, while defensive listening specifically triggers a protective response that distorts the intended message. Recognizing and managing defensive listening helps improve your communication skills by fostering empathy and reducing misunderstandings.
What Is Selective Listening?
Selective listening is the process of focusing on specific sounds or information while ignoring other stimuli, allowing individuals to concentrate on relevant messages in a noisy environment. Defensive listening occurs when a person perceives comments as personal attacks, leading to misunderstandings and emotional reactions. Unlike defensive listening, which is driven by emotional bias, selective listening is a deliberate cognitive strategy aimed at filtering and prioritizing information efficiently.
Key Differences Between Defensive and Selective Listening
Defensive listening involves perceiving and reacting to messages as personal attacks, leading to misunderstandings and emotional responses, whereas selective listening means focusing only on specific parts of the conversation that interest you or align with your beliefs, often ignoring other important information. Your ability to recognize these differences enhances communication effectiveness by reducing unnecessary conflicts caused by defensive interpretations and improving attention to relevant details through selective focus. Key differences include the emotional response in defensive listening versus the intentional focus in selective listening, influencing how you process and respond to information.
Psychological Roots of Defensive Listening
Defensive listening often stems from underlying psychological factors such as low self-esteem, past experiences of criticism, or fear of negative evaluation, causing individuals to perceive messages as personal attacks. Unlike selective listening, which involves focusing only on certain parts of a conversation to reinforce pre-existing beliefs, defensive listening is characterized by heightened sensitivity and emotional reactivity. Understanding the psychological roots of defensive listening is essential for improving communication and fostering empathy in interpersonal interactions.
Common Triggers for Selective Listening
Common triggers for selective listening include emotional bias, preconceived notions, and stress, which cause You to filter information based on personal preferences rather than the speaker's intent. Defensive listening occurs when You perceive a message as a personal attack, leading to heightened sensitivity and misunderstanding. Unlike selective and defensive listening, active listening requires full attention and openness to understand the complete message without judgment.
Impact on Communication and Relationships
Defensive listening creates barriers in communication by triggering misunderstandings and fostering distrust, often resulting in strained relationships. Selective listening limits effective communication as individuals only hear parts of the message that align with their interests, causing misinterpretations and weakening interpersonal connections. Genuine listening, by contrast, enhances mutual understanding, builds trust, and strengthens relational bonds through open and empathetic communication.
Signs You’re Engaging in Defensive Listening
Signs you're engaging in defensive listening include interpreting neutral comments as personal attacks, frequently interrupting to justify yourself, and focusing on rebutting rather than understanding. Defensive listening contrasts with selective listening, where you tune in only to parts of the message that interest or align with your views, often missing important details. Recognizing these behaviors can improve communication by fostering openness and reducing misunderstandings.
How to Recognize Selective Listening Patterns
Selective listening patterns can be recognized by noticing when a listener only hears parts of a message that align with their interests or beliefs, often ignoring contradictory information. This behavior contrasts with defensive listening, where the listener perceives a hidden attack, and typical attentive listening, which involves processing the entire message objectively. Identifying selective listening requires observing inconsistent responses or repeated focus on specific words or topics while other relevant information is overlooked.
Strategies to Overcome Defensive Listening
Strategies to overcome defensive listening involve cultivating active listening skills, such as maintaining open body language and focusing on the speaker's message without immediate judgment. Practicing empathy helps reduce defensive reactions by recognizing the speaker's intent and separating personal feelings from the content. Engaging in reflective listening, which includes paraphrasing and asking clarifying questions, further promotes understanding and minimizes misunderstandings caused by selective or defensive listening behaviors.
Tips for Becoming a More Effective Listener
Defensive listening occurs when you interpret messages as personal attacks, while selective listening involves focusing only on parts that interest you, often missing the full message. To become a more effective listener, practice active listening by maintaining eye contact, withholding judgment, and asking clarifying questions to fully understand the speaker's intent. Your ability to recognize these listening styles and consciously shift toward open, empathetic hearing enhances communication and reduces misunderstandings.
Infographic: Defensive listening vs Selective listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com