Attending involves actively focusing on the speaker's verbal and nonverbal cues, while listening requires processing and understanding the message conveyed. Explore this article to enhance your relationship skills through effective attending and listening techniques.
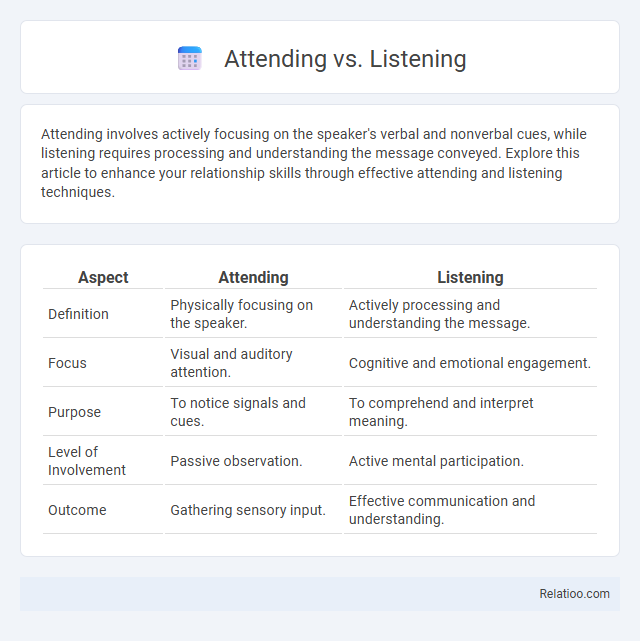
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Attending | Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physically focusing on the speaker. | Actively processing and understanding the message. |
| Focus | Visual and auditory attention. | Cognitive and emotional engagement. |
| Purpose | To notice signals and cues. | To comprehend and interpret meaning. |
| Level of Involvement | Passive observation. | Active mental participation. |
| Outcome | Gathering sensory input. | Effective communication and understanding. |
Understanding the Difference Between Attending and Listening
Attending involves fully focusing your attention on the speaker without distractions, while listening goes beyond by actively processing and interpreting the message being communicated. You improve communication skills by recognizing that attending is the initial stage of receiving information, whereas listening requires engagement, reflection, and understanding. Mastering both ensures clearer comprehension and more effective interactions in personal and professional contexts.
The Importance of Attending in Effective Communication
Attending in effective communication involves fully focusing on the speaker through non-verbal cues such as eye contact, nodding, and body language, which signals genuine interest and respect. Unlike passive listening or merely hearing, attending fosters deeper understanding and encourages the speaker to express themselves openly. This active engagement enhances message clarity, reduces misunderstandings, and strengthens interpersonal relationships.
Active Listening: Going Beyond Hearing Words
Active listening requires more than merely hearing words; it involves fully attending to the speaker's message, interpreting nonverbal cues, and providing thoughtful feedback. Your ability to concentrate on the speaker fosters deeper understanding, empathy, and effective communication. Developing active listening skills enhances relationships and ensures accurate comprehension beyond passive auditory perception.
Nonverbal Cues: How Attending Shapes Understanding
Attending involves actively focusing on nonverbal cues such as eye contact, body language, and facial expressions, which are essential for accurate understanding in communication. Listening without attending often results in missing subtle signals that convey emotions and intentions beyond words. Effective attending enhances comprehension by integrating these nonverbal elements, shaping a deeper and more empathetic connection between communicators.
Barriers to Attending and Listening
Barriers to attending and listening include distractions, psychological noise, and lack of interest, all of which impede effective information processing and retention. Environmental factors such as background noise and multitasking further diminish the ability to focus attention and fully engage in active listening. Overcoming these barriers requires intentional effort to minimize external disruptions and develop concentration skills for improved communication and comprehension.
Techniques to Improve Attending Skills
Effective attending skills involve focused body language, such as maintaining eye contact and nodding, which signals your full engagement in the conversation. Using verbal techniques like summarizing or paraphrasing ensures you truly understand the speaker's message and reduces miscommunication. Practicing mindfulness and eliminating distractions can significantly enhance your ability to attend, thereby improving your overall communication effectiveness.
The Role of Empathy in Attending and Listening
Empathy plays a crucial role in attending and listening by enabling you to fully engage with the speaker's emotions and perspectives, fostering a deeper connection. Attending involves giving your focused physical and psychological presence, while listening requires interpreting and understanding the underlying feelings behind words. Your empathetic response helps build trust and encourages open, meaningful communication.
Attending vs Listening in Relationships
Attending in relationships involves fully focusing on your partner's verbal and non-verbal cues, showing genuine presence and engagement, whereas listening primarily refers to hearing and understanding the spoken words. Your ability to attend demonstrates empathy and emotional connection, fostering trust and intimacy beyond just processing information. Effective attending strengthens communication by validating your partner's feelings and encouraging deeper relational bonds.
Real-Life Scenarios: When Attending is Not Enough
In real-life scenarios, attending requires more than simply being present; it involves actively engaging with the speaker's message to fully comprehend the content. Listening goes beyond attending by processing and interpreting information, enabling you to respond thoughtfully and build effective communication. Your ability to distinguish between merely attending and truly listening enhances understanding and strengthens relationships in both personal and professional contexts.
Enhancing Communication: Integrating Attending and Listening
Integrating attending and listening enhances communication by fostering deeper understanding and active engagement during interactions. Attending involves focusing your full attention through nonverbal cues like eye contact and body language, while listening requires processing and interpreting verbal messages accurately. Combining these skills enables you to respond thoughtfully and build stronger connections.
Infographic: Attending vs Listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com