Attending to someone in a relationship means fully engaging and understanding their feelings, while hearing refers to merely perceiving their words without true connection. Discover how shifting from hearing to attending can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
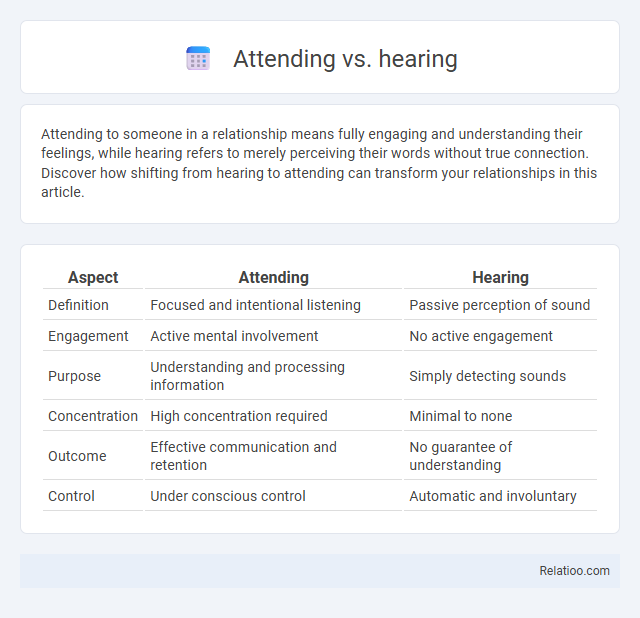
| Aspect | Attending | Hearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focused and intentional listening | Passive perception of sound |
| Engagement | Active mental involvement | No active engagement |
| Purpose | Understanding and processing information | Simply detecting sounds |
| Concentration | High concentration required | Minimal to none |
| Outcome | Effective communication and retention | No guarantee of understanding |
| Control | Under conscious control | Automatic and involuntary |
Overview: Understanding Attending vs Hearing
Attending involves actively focusing on and interpreting sensory input, while hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound without engagement. In the context of communication, attending requires cognitive effort to process and respond to messages, whereas hearing merely captures auditory signals. Understanding the distinction between attending and hearing is crucial for effective listening, ensuring meaningful interaction and comprehension.
Defining Hearing: The Passive Process
Hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound waves through the ear, involving no conscious effort or focus from you. Unlike attending, which requires actively selecting and concentrating on specific auditory information, hearing happens automatically and continuously. This distinction highlights that hearing is merely reception of sounds, whereas attending involves processing and responding to those sounds.
Defining Attending: The Active Engagement
Defining attending involves active engagement characterized by focused attention, intentional observation, and responsive interaction. Attending requires cognitive and emotional involvement, enabling deeper understanding and meaningful communication. This contrasts with merely hearing, which is passive reception of sound without processing or interaction.
Key Differences Between Attending and Hearing
Attending involves actively focusing on and processing auditory stimuli, whereas hearing refers to the passive reception of sound without conscious effort. Key differences between attending and hearing include the level of cognitive engagement, with attending requiring selective attention and comprehension, while hearing is merely the sensory perception of sound. Attending also involves filtering out background noise to concentrate on specific sounds, unlike hearing, which registers all sounds indiscriminately.
The Role of Attention in Effective Listening
Effective listening hinges on the role of attention, which involves actively attending to the speaker's message rather than merely hearing the words. Attending requires you to focus cognitive resources on decoding and understanding verbal and nonverbal cues, enabling deeper comprehension and meaningful responses. Without proper attention, information retention and interpretation suffer, reducing overall communication efficacy.
Psychological and Cognitive Aspects
Attending involves actively focusing cognitive resources on specific stimuli, enhancing information processing and memory retention compared to passive hearing, which is merely perceiving sounds without conscious focus. Hearing operates at a sensory level, registering auditory signals without necessarily engaging deeper cognitive functions essential for comprehension and learning. Attending engages selective attention mechanisms, facilitating better discrimination of relevant information, reducing cognitive overload, and promoting effective mental encoding and retrieval.
Real-World Examples of Attending vs Hearing
Attending involves actively focusing your mental and sensory resources on a speaker or event, such as listening to a colleague during a meeting and responding thoughtfully. Hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound, like catching background conversations without processing their meaning. Your ability to distinguish between attending and hearing impacts communication effectiveness in real-world scenarios, influencing collaboration and information retention.
Benefits of Active Attending Over Passive Hearing
Active attending engages your full attention and cognitive resources, leading to better comprehension and retention compared to passive hearing. By focusing intentionally on the speaker's words, you enhance understanding, reduce misunderstandings, and improve your ability to respond thoughtfully. This mindful participation fosters deeper connections and more effective communication in both personal and professional settings.
Improving Your Attending Skills
Improving your attending skills involves active listening, maintaining eye contact, and providing nonverbal feedback that shows engagement and understanding. Hearing is the passive process of perceiving sound, while attending requires focused attention and cognitive processing to truly comprehend the speaker's message. Developing strong attending abilities enhances communication, fosters trust, and ensures more effective interactions in both personal and professional settings.
Conclusion: Why Attending Matters More Than Hearing
Attending involves actively processing and engaging with information, whereas hearing is the passive perception of sound without understanding. Attending leads to better comprehension, retention, and meaningful responses, which are crucial in effective communication and learning processes. Your ability to attend rather than just hear determines the quality of interaction and outcome in any conversation or task.
Infographic: Attending vs Hearing
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com