Direct questions explicitly inquire about specific information using clear question words, while indirect questions embed the inquiry within a statement or another question for a more polite tone. Explore the nuanced differences and their impact on communication in this article.
Table of Comparison
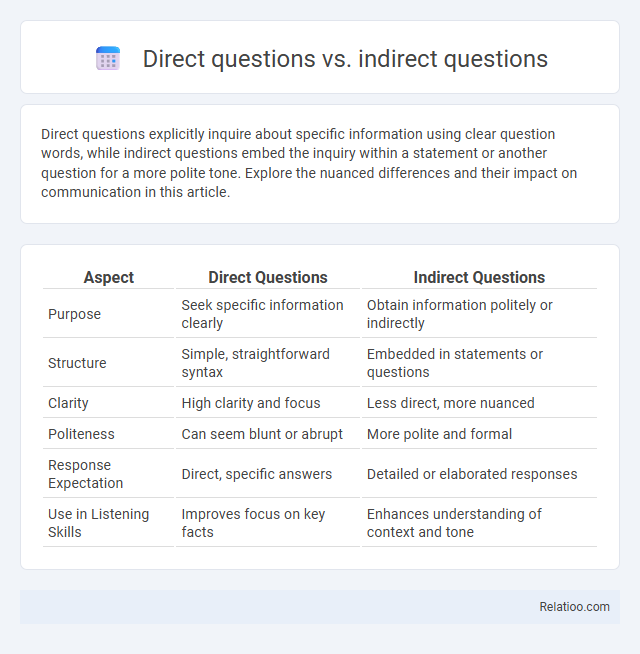
| Aspect | Direct Questions | Indirect Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Seek specific information clearly | Obtain information politely or indirectly |
| Structure | Simple, straightforward syntax | Embedded in statements or questions |
| Clarity | High clarity and focus | Less direct, more nuanced |
| Politeness | Can seem blunt or abrupt | More polite and formal |
| Response Expectation | Direct, specific answers | Detailed or elaborated responses |
| Use in Listening Skills | Improves focus on key facts | Enhances understanding of context and tone |
Introduction to Direct and Indirect Questions
Direct questions ask for specific information using clear, concise phrasing, often beginning with question words like who, what, where, when, why, or how. Indirect questions embed the query within a statement or another question, making them more polite and less direct, such as "Can you tell me where the station is?" Questioning techniques enhance communication skills by helping you discern when to use direct versus indirect questions for clarity or subtlety in conversations.
Defining Direct Questions
Direct questions explicitly request specific information using a clear interrogative structure, often starting with question words like who, what, where, when, why, and how. These questions typically end with a question mark and are straightforward in form and function, ensuring clarity and immediate understanding. Contrastingly, indirect questions embed the query within a statement or another question, making the request less direct and more polite or formal.
Understanding Indirect Questions
Indirect questions are embedded within statements or other questions, requiring a change in word order and often the omission of auxiliary verbs, unlike direct questions which follow a straightforward question format. Understanding indirect questions involves recognizing their polite and less confrontational nature, commonly used in formal or sensitive contexts to seek information without demanding an immediate answer. Mastery of indirect questions improves communication skills by allowing subtler inquiries, enhancing both clarity and social appropriateness.
Key Structural Differences
Direct questions feature a straightforward word order with the auxiliary verb preceding the subject, such as "Are you coming?" Indirect questions embed the query within a statement or another question, maintaining the subject-verb order as in "Can you tell me if you are coming?" Questioning encompasses both forms, but the key structural difference lies in direct questions' inversion of subject and auxiliary verbs, while indirect questions rely on subordinating conjunctions and standard word order to integrate the question into a larger sentence.
Examples of Direct Questions
Direct questions explicitly ask for specific information using clear interrogative phrases like "What is your name?" or "Where do you live?" In contrast, indirect questions embed the query within a statement, such as "Can you tell me where you live?" Your ability to distinguish between these forms enhances clarity and improves response accuracy in communication.
Examples of Indirect Questions
Examples of indirect questions include "Could you tell me where the nearest bank is?" and "Do you know if the meeting starts at 10 AM?" Unlike direct questions that ask straightforwardly, indirect questions embed inquiries within statements or other questions, making them more polite and formal. Your communication becomes more nuanced by mastering indirect questions, enhancing both clarity and social grace.
When to Use Direct Questions
Direct questions are used when you need clear, straightforward answers, making them essential in situations requiring specific information quickly, such as interviews or surveys. You should choose direct questions to eliminate ambiguity and encourage concise, focused responses. Indirect questions and questioning methods are better suited for polite inquiries or when seeking elaborated explanations without pressuring the respondent.
When to Use Indirect Questions
Indirect questions are best used when you want to ask politely or embed a question within a statement or another question, making your speech or writing more formal and less direct. You can use indirect questions when seeking information without sounding confrontational, such as in professional settings or sensitive conversations. Understanding when to use indirect questions enhances your communication skills by allowing you to inquire respectfully while maintaining clarity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Common mistakes in direct questions include omitting the auxiliary verb, leading to grammatical errors such as "You going?" instead of "Are you going?". Indirect questions often suffer from incorrect word order or missing question words, for example, "Can you tell where is the station?" should be "Can you tell where the station is?". When questioning, avoid confusing question forms and ensure clarity by choosing between direct straightforwardness and the politeness of indirect inquiries to make Your communication precise and effective.
Tips for Mastering Question Forms
Mastering question forms involves understanding direct questions, which are clear and straightforward, and indirect questions, which are polite and embedded within statements. Practice transforming direct questions like "Where is the meeting?" into indirect forms such as "Could you tell me where the meeting is?" to enhance your communication skills. Your ability to choose the appropriate question type improves clarity and engagement in conversations.
Infographic: Direct questions vs Indirect questions
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com