Listening for understanding enhances empathy and strengthens relationships by truly grasping others' perspectives. Discover effective techniques to improve your communication skills in this article.
Table of Comparison
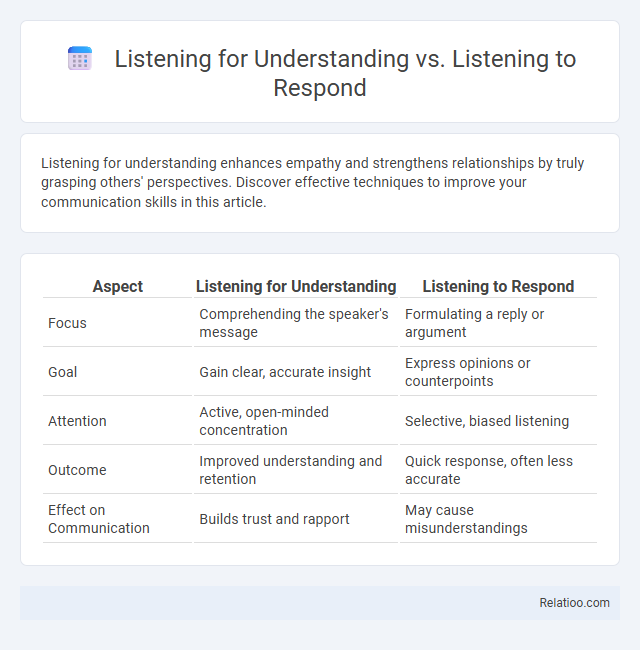
| Aspect | Listening for Understanding | Listening to Respond |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Comprehending the speaker's message | Formulating a reply or argument |
| Goal | Gain clear, accurate insight | Express opinions or counterpoints |
| Attention | Active, open-minded concentration | Selective, biased listening |
| Outcome | Improved understanding and retention | Quick response, often less accurate |
| Effect on Communication | Builds trust and rapport | May cause misunderstandings |
Introduction to Listening: Understanding the Two Approaches
Listening for understanding involves fully processing and interpreting the speaker's message, emphasizing empathy and accurate comprehension. Listening to respond prioritizes formulating a reply, often leading to missed nuances and weakened communication. Your ability to distinguish between these approaches enhances rapport and fosters deeper, more meaningful interactions.
Defining Listening for Understanding
Listening for Understanding involves fully concentrating on the speaker's message to grasp their emotions, intentions, and underlying meanings, fostering deeper comprehension. Unlike Listening to Respond, which prioritizes crafting a reply, this empathetic approach prioritizes absorbing information without judgment or interruption. Building rapport relies on Listening for Understanding to create trust and meaningful connections through genuine engagement and validation.
Defining Listening to Respond
Listening to Respond involves processing spoken information with the primary goal of formulating a reply rather than fully understanding the speaker's message. This type of listening often leads to interruptions and missed details because the focus shifts from comprehension to preparing a counter or contribution. Developing effective communication requires shifting from listening to respond toward active listening, which prioritizes understanding before reacting.
Key Differences Between the Two Listening Styles
Listening for understanding involves fully concentrating on the speaker's message to accurately interpret and internalize the information, whereas listening to respond focuses primarily on preparing a reply, often leading to missed details or misunderstandings. Rapport listening emphasizes creating a connection and building trust through empathy and active engagement, contrasting with the transactional nature of the other two styles. Key differences lie in the intent: comprehension in listening for understanding, reaction in listening to respond, and relationship-building in rapport listening.
Psychological Impact on Communication
Listening for understanding fosters deep psychological safety by validating emotions and promoting empathy, which strengthens trust and openness in communication. Listening to respond often triggers defensiveness and psychological barriers, as it signals a focus on one's own agenda rather than truly hearing the other person. Building rapport through active, empathetic listening creates a positive feedback loop that enhances mutual respect and emotional connection, improving overall communication outcomes for you.
Benefits of Listening for Understanding
Listening for understanding enhances communication by fostering accurate comprehension of the speaker's message, reducing misunderstandings and conflicts. It builds trust and rapport by showing empathy and genuine interest, encouraging openness and stronger relationships. This approach improves problem-solving and collaboration by ensuring all perspectives are fully considered before responding.
Common Pitfalls of Listening to Respond
Listening to respond often leads to missing key information because your focus shifts from understanding to preparing your reply. This common pitfall causes misunderstandings and weakens communication, as You may overlook emotional cues and context critical for building rapport. Prioritizing active listening skills can enhance your ability to truly comprehend messages and foster stronger connections.
Practical Tips to Improve Your Listening Skills
Active listening enhances understanding by focusing fully on the speaker's message without planning your response, which improves communication accuracy and trust. Practice reflective listening by summarizing or paraphrasing key points to ensure clarity and show empathy, strengthening rapport. Avoid interrupting and maintain open body language to create a comfortable environment that encourages honest dialogue and deeper connection.
Real-life Scenarios: When Each Approach Matters
Listening for understanding is crucial in conflict resolution scenarios where grasping the speaker's emotions and perspective prevents misunderstandings and builds trust. Listening to respond is often necessary in dynamic discussions or debates, allowing for timely feedback and clarifications that keep the conversation productive. Building rapport depends on empathetic listening, especially in customer service or team settings, where establishing connection and mutual respect fosters collaboration and loyalty.
Conclusion: Cultivating Effective Listening Habits
Cultivating effective listening habits enhances your ability to truly understand others rather than merely preparing to respond, fostering deeper rapport and trust in communication. Prioritizing active, empathetic listening over reactive listening transforms conversations into meaningful exchanges where all parties feel heard and valued. Building this skill not only improves personal and professional relationships but also creates a foundation for mutual respect and collaboration.
Infographic: Listening for Understanding vs Listening to Respond
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com