Selective listening targets specific information while ignoring other details, often leading to misunderstandings in relationships. Comprehensive listening captures the full message and emotional context, fostering deeper connection and empathy. Discover how mastering these listening styles can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
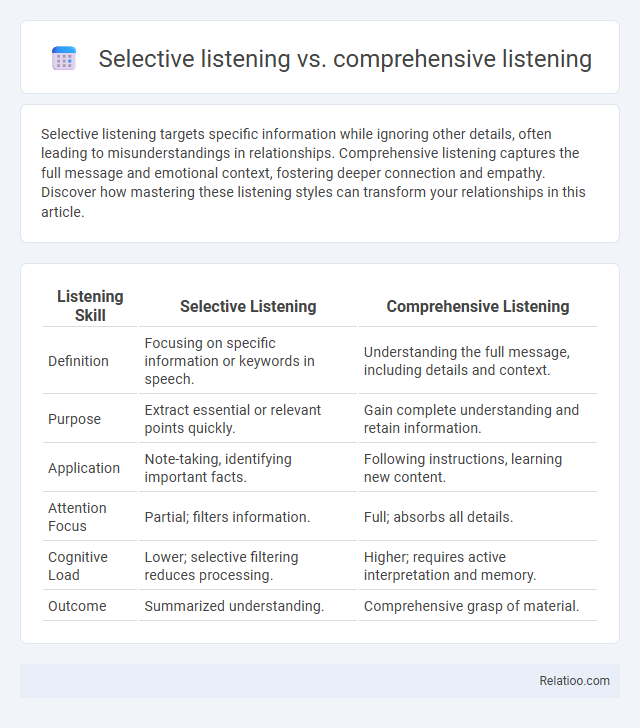
| Listening Skill | Selective Listening | Comprehensive Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focusing on specific information or keywords in speech. | Understanding the full message, including details and context. |
| Purpose | Extract essential or relevant points quickly. | Gain complete understanding and retain information. |
| Application | Note-taking, identifying important facts. | Following instructions, learning new content. |
| Attention Focus | Partial; filters information. | Full; absorbs all details. |
| Cognitive Load | Lower; selective filtering reduces processing. | Higher; requires active interpretation and memory. |
| Outcome | Summarized understanding. | Comprehensive grasp of material. |
Introduction to Selective and Comprehensive Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific sounds or information while filtering out irrelevant noise, which enhances your ability to identify critical details quickly in conversations or presentations. Comprehensive listening requires understanding and processing all spoken content to grasp the full meaning, crucial for effective communication and learning environments. Mastering both listening types improves overall participation by allowing you to adapt your attention based on context and communication goals.
Defining Selective Listening
Selective listening involves focusing on specific information while filtering out unrelated details, allowing you to concentrate on key messages in a conversation. Unlike comprehensive listening, which requires understanding all aspects of the dialogue, selective listening targets particular points based on relevance or interest. This skill helps in efficiently processing communication, especially in environments with overwhelming or excessive information.
Understanding Comprehensive Listening
Comprehensive listening involves grasping the full message, including facts, ideas, and underlying meaning to ensure accurate interpretation and retention. Unlike selective listening, which filters specific information, comprehensive listening requires active engagement and mental effort to capture all details for a complete understanding. Your ability to practice comprehensive listening enhances effective communication and informed decision-making in personal and professional contexts.
Core Differences Between Selective and Comprehensive Listening
Selective listening targets specific information or key points within a conversation, filtering out unrelated details to enhance efficiency in communication. Comprehensive listening involves fully understanding and processing all aspects of the message, including context, tone, and nuanced meanings, to gain a complete grasp of the content. Participation in listening extends beyond reception to active engagement, contributing feedback, asking questions, and fostering interaction based on selective or comprehensive understanding.
Psychological Factors Influencing Listening Styles
Psychological factors such as attention span, motivation, and cognitive load significantly influence selective listening, where You focus on specific information while filtering out other stimuli. Comprehensive listening relies on higher cognitive engagement and memory retention to grasp the full message, often affected by stress and emotional state. Participation in listening involves active processing and interpersonal dynamics, with self-confidence and social anxiety playing key roles in how effectively You engage and respond.
Benefits of Selective Listening
Selective listening enhances information retention by allowing individuals to focus on key points and filter out distractions, thus improving decision-making and problem-solving skills. This targeted approach reduces cognitive overload, making communication more efficient and purposeful. By prioritizing relevant information, selective listening boosts productivity and encourages active engagement in both personal and professional settings.
Advantages of Comprehensive Listening
Comprehensive listening enhances understanding by enabling individuals to grasp complex ideas, retain detailed information, and follow intricate instructions effectively. It supports critical thinking and problem-solving by allowing listeners to process entire messages rather than isolated parts. This type of listening promotes better communication outcomes in educational, professional, and interpersonal contexts.
Common Challenges in Both Listening Approaches
Selective listening often leads to missing critical information due to focusing only on specific keywords, while comprehensive listening can overwhelm individuals with excessive details, causing reduced retention and misunderstandings. Common challenges in both approaches include maintaining sustained attention, filtering out distractions, and accurately interpreting the speaker's intent in dynamic communication environments. Effective participation requires balancing selective focus with comprehensive understanding to enhance engagement and ensure meaningful interaction.
Practical Scenarios for Each Listening Style
Selective listening is effective in meetings where prioritizing key information, such as project deadlines or budget updates, is crucial to decision-making. Comprehensive listening proves essential during training sessions or lectures, enabling full understanding of detailed concepts and instructions. Participation-oriented listening thrives in team brainstorming or collaborative discussions where active engagement and feedback drive innovation and problem-solving.
Tips to Enhance Both Selective and Comprehensive Listening Skills
Enhance selective listening by practicing focused attention on key words and filtering out distractions, using note-taking to highlight important points during conversations or lectures. Improve comprehensive listening through active engagement, such as summarizing information mentally and asking clarifying questions to ensure full understanding. Combining both skills requires balancing attention between critical details and overall context, enabling effective participation in discussions and decision-making processes.
Infographic: Selective Listening vs Comprehensive Listening
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com