Active participation in a relationship fosters deeper emotional connections and mutual understanding, while mere attendance often leads to superficial interactions. Discover how embracing engagement over presence can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
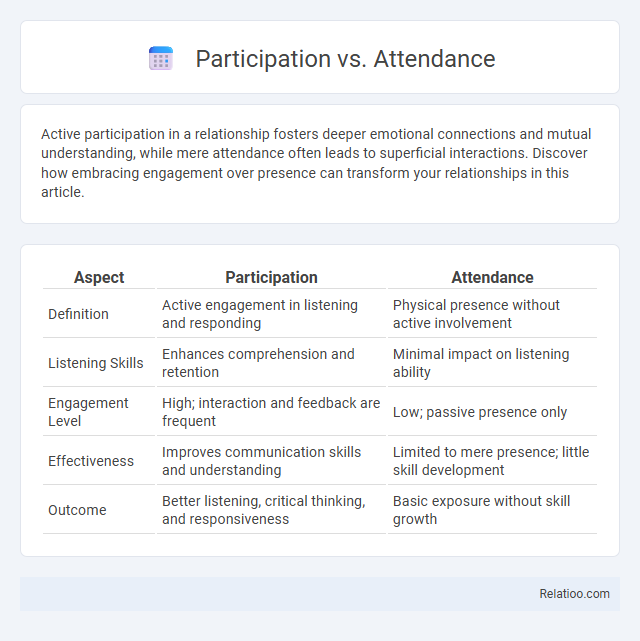
| Aspect | Participation | Attendance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Active engagement in listening and responding | Physical presence without active involvement |
| Listening Skills | Enhances comprehension and retention | Minimal impact on listening ability |
| Engagement Level | High; interaction and feedback are frequent | Low; passive presence only |
| Effectiveness | Improves communication skills and understanding | Limited to mere presence; little skill development |
| Outcome | Better listening, critical thinking, and responsiveness | Basic exposure without skill growth |
Understanding Participation vs Attendance
Understanding participation versus attendance highlights the difference between active engagement and mere presence in an event. Attendance refers to being physically present, while participation involves meaningful interaction, contribution, and involvement in activities or discussions. Effective learning and collaboration depend more on participation, as it drives deeper comprehension and skill development beyond simple attendance.
Defining Attendance in Organizational Contexts
Attendance in organizational contexts refers specifically to the act of being physically present at a designated place or event, such as meetings, training sessions, or work shifts. Unlike participation, which involves active engagement and contribution to discussions or tasks, attendance merely confirms your presence without implying involvement. Accurate tracking of attendance ensures accountability and operational efficiency, serving as a baseline metric for employee management and organizational planning.
What Constitutes True Participation?
True participation involves active engagement, where you contribute ideas, ask questions, and collaborate meaningfully, going beyond mere physical presence or passive attendance. Attendance simply marks your presence, while participation requires involvement that demonstrates understanding and commitment to the task or discussion. Effective participation fosters interaction, critical thinking, and shared responsibility, which are essential for achieving collective goals and personal growth.
The Impact of Mere Attendance
Mere attendance often leads to passive involvement, which diminishes the overall impact on learning outcomes or team dynamics. Active participation requires engaging cognitively and emotionally, enabling you to absorb information deeply and contribute meaningfully. Without this engagement, attendance becomes a superficial metric that fails to reflect true commitment or progress.
Benefits of Active Participation
Active participation enhances your learning experience by engaging multiple senses and fostering critical thinking, leading to better retention and understanding compared to mere attendance. Unlike passive attendance or simple participation, active involvement encourages collaboration, immediate feedback, and personal accountability, which drive deeper skill development and confidence. This dynamic engagement promotes motivation and creates a more meaningful connection to the material, significantly boosting your overall performance and growth.
Key Differences Between Participation and Attendance
Participation involves active engagement and contribution during an event, while attendance simply refers to being present without necessarily contributing. The key difference lies in the quality of involvement: participation requires interaction, feedback, or input, whereas attendance only requires physical presence. Effective participation often leads to better learning outcomes and collaboration, making it more valuable than mere attendance.
Measuring Engagement: Metrics Beyond Attendance
Measuring engagement requires analyzing metrics beyond simple attendance counts, incorporating factors such as interaction frequency, feedback quality, and active involvement in discussions. Participation metrics include contributions to group activities, question-asking rates, and responsiveness in collaborative tasks, which provide deeper insights into engagement levels. Combining attendance with qualitative and quantitative participation data enables a comprehensive evaluation of individual commitment and group dynamics.
Barriers to Participation
Barriers to participation often extend beyond mere attendance, as simply being present does not ensure active engagement or contribution in activities or discussions. Factors such as lack of confidence, insufficient knowledge, social anxiety, and unclear roles can hinder your ability to participate meaningfully. Overcoming these obstacles requires targeted strategies like inclusive facilitation, skill-building opportunities, and creating a supportive environment that encourages active involvement.
Strategies to Encourage Participation
Strategies to encourage participation include creating engaging content that resonates with the audience and employing interactive tools such as polls, Q&A sessions, and group discussions to foster active involvement. Establishing a supportive environment where participants feel valued and heard boosts motivation and commitment, while setting clear expectations and providing incentives can also drive higher engagement levels. Leveraging technology platforms that track and reward participation further enhances attendees' willingness to contribute meaningfully.
Enhancing Outcomes Through Increased Participation
Enhancing outcomes through increased participation involves actively engaging individuals beyond mere attendance, which often reflects passive presence without contribution. Participation emphasizes meaningful involvement and interaction, fostering collaboration, deeper learning, and improved performance outcomes. By prioritizing participation over simple attendance, organizations and educators can drive higher engagement levels, resulting in more effective knowledge retention and innovative problem-solving.
Infographic: Participation vs Attendance
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com