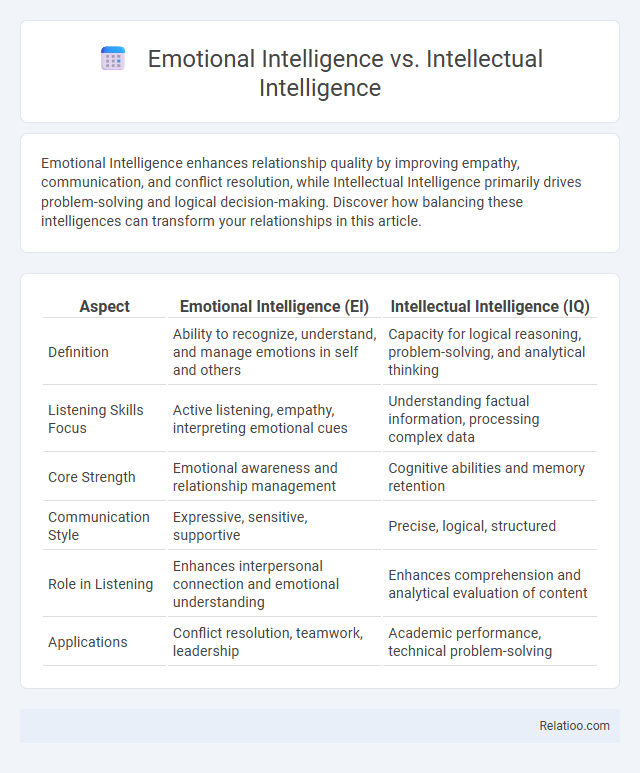
Emotional Intelligence enhances relationship quality by improving empathy, communication, and conflict resolution, while Intellectual Intelligence primarily drives problem-solving and logical decision-making. Discover how balancing these intelligences can transform your relationships in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Emotional Intelligence (EI) | Intellectual Intelligence (IQ) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions in self and others | Capacity for logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical thinking |
| Listening Skills Focus | Active listening, empathy, interpreting emotional cues | Understanding factual information, processing complex data |
| Core Strength | Emotional awareness and relationship management | Cognitive abilities and memory retention |
| Communication Style | Expressive, sensitive, supportive | Precise, logical, structured |
| Role in Listening | Enhances interpersonal connection and emotional understanding | Enhances comprehension and analytical evaluation of content |
| Applications | Conflict resolution, teamwork, leadership | Academic performance, technical problem-solving |
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Understanding Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves recognizing and managing one's own emotions while effectively responding to others' emotional cues, enhancing interpersonal relationships and decision-making. Unlike Intellectual Intelligence (IQ), which measures cognitive abilities such as reasoning and problem-solving, EI emphasizes empathy, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. Emotional resonance plays a crucial role in EI by facilitating a deep connection and alignment between individuals' emotional experiences, promoting trust and collaboration in social interactions.
Defining Intellectual Intelligence
Intellectual intelligence refers to your ability to analyze, reason, and solve problems using logic and knowledge, often measured through IQ tests. It contrasts with emotional intelligence, which involves recognizing and managing emotions, and emotional resonance, the capacity to deeply connect and empathize with others' feelings. Understanding these distinctions helps you leverage your cognitive strengths while balancing emotional awareness for effective interpersonal interactions.
Core Components of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence encompasses self-awareness, self-regulation, social awareness, empathy, and relationship management, serving as core components that allow You to navigate interpersonal dynamics effectively. Intellectual Intelligence focuses primarily on cognitive abilities like logic, reasoning, and problem-solving, distinct from the emotional and social skills that drive Emotional Intelligence. Emotional resonance, a subset of empathy, reflects the ability to deeply connect and mirror others' emotions, reinforcing interpersonal bonds and enhancing effective communication.
Key Aspects of Intellectual Intelligence
Intellectual intelligence primarily involves logical reasoning, analytical skills, and problem-solving capabilities critical for academic success and professional expertise. Unlike emotional intelligence, which centers on understanding and managing emotions, intellectual intelligence emphasizes cognitive processes such as memory, attention, and verbal comprehension. Enhancing your intellectual intelligence strengthens decision-making and complex information processing vital for innovation and critical thinking.
Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace
Emotional Intelligence in the workplace enhances interpersonal communication, problem-solving, and leadership effectiveness by enabling individuals to recognize, understand, and manage their own emotions and those of others. Unlike Intellectual Intelligence, which focuses on cognitive abilities such as reasoning and analytical skills, Emotional Intelligence drives collaboration, empathy, and conflict resolution in professional environments. Emotional resonance, the ability to deeply connect with others' feelings, complements Emotional Intelligence by fostering trust and stronger workplace relationships.
Intellectual Intelligence in Academic Settings
Intellectual Intelligence (IQ) in academic settings measures your ability to analyze information, solve problems, and acquire knowledge efficiently. This cognitive capacity significantly influences academic performance through skills like logical reasoning, critical thinking, and memory retention. While Emotional Intelligence and Emotional Resonance enhance social interactions and empathy, Intellectual Intelligence remains the cornerstone for mastering complex subjects and excelling in standardized assessments.
Emotional vs Intellectual Intelligence: Key Differences
Emotional Intelligence (EI) involves recognizing, understanding, and managing emotions in oneself and others, crucial for empathy, social skills, and emotional regulation. Intellectual Intelligence (IQ) measures cognitive abilities such as logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical thinking, primarily focused on academic and technical skills. Unlike IQ, EI emphasizes emotional awareness and interpersonal effectiveness, which are essential for leadership, collaboration, and personal well-being.
The Role of EI and IQ in Personal Relationships
Emotional Intelligence (EI) plays a crucial role in personal relationships by enabling individuals to recognize, understand, and manage their own emotions as well as empathize with others, fostering deeper emotional connections. Intellectual Intelligence (IQ) contributes to problem-solving and communication skills but lacks the emotional sensitivity necessary for nurturing intimacy and resolving conflicts effectively. Emotional resonance, a key aspect of EI, enhances relationship quality by creating shared emotional experiences that strengthen trust and mutual understanding.
Developing Emotional and Intellectual Intelligence
Developing emotional intelligence involves enhancing self-awareness, empathy, and emotional regulation to improve interpersonal relationships and decision-making. Intellectual intelligence focuses on analytical thinking, problem-solving, and knowledge acquisition essential for academic and professional success. Emotional resonance bridges both by fostering deeper connections through shared feelings, amplifying communication effectiveness and social bonding.
Balancing Emotional and Intellectual Intelligence for Success
Balancing emotional intelligence (EI) and intellectual intelligence (IQ) is crucial for achieving success, as EI enhances self-awareness, empathy, and social skills while IQ drives analytical thinking and problem-solving. Emotional resonance, the ability to deeply connect and synchronize with others' emotions, amplifies the effectiveness of emotional intelligence in leadership and teamwork. Integrating strong IQ with well-developed EI and emotional resonance fosters better decision-making, collaboration, and adaptive performance in complex environments.
Infographic: Emotional Intelligence vs Intellectual Intelligence
 relatioo.com
relatioo.com